Yucheng Ruan
Language Modeling on Tabular Data: A Survey of Foundations, Techniques and Evolution
Aug 20, 2024



Abstract:Tabular data, a prevalent data type across various domains, presents unique challenges due to its heterogeneous nature and complex structural relationships. Achieving high predictive performance and robustness in tabular data analysis holds significant promise for numerous applications. Influenced by recent advancements in natural language processing, particularly transformer architectures, new methods for tabular data modeling have emerged. Early techniques concentrated on pre-training transformers from scratch, often encountering scalability issues. Subsequently, methods leveraging pre-trained language models like BERT have been developed, which require less data and yield enhanced performance. The recent advent of large language models, such as GPT and LLaMA, has further revolutionized the field, facilitating more advanced and diverse applications with minimal fine-tuning. Despite the growing interest, a comprehensive survey of language modeling techniques for tabular data remains absent. This paper fills this gap by providing a systematic review of the development of language modeling for tabular data, encompassing: (1) a categorization of different tabular data structures and data types; (2) a review of key datasets used in model training and tasks used for evaluation; (3) a summary of modeling techniques including widely-adopted data processing methods, popular architectures, and training objectives; (4) the evolution from adapting traditional Pre-training/Pre-trained language models to the utilization of large language models; (5) an identification of persistent challenges and potential future research directions in language modeling for tabular data analysis. GitHub page associated with this survey is available at: https://github.com/lanxiang1017/Language-Modeling-on-Tabular-Data-Survey.git.
A Survey of Large Language Models for Healthcare: from Data, Technology, and Applications to Accountability and Ethics
Oct 09, 2023



Abstract:The utilization of large language models (LLMs) in the Healthcare domain has generated both excitement and concern due to their ability to effectively respond to freetext queries with certain professional knowledge. This survey outlines the capabilities of the currently developed LLMs for Healthcare and explicates their development process, with the aim of providing an overview of the development roadmap from traditional Pretrained Language Models (PLMs) to LLMs. Specifically, we first explore the potential of LLMs to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of various Healthcare applications highlighting both the strengths and limitations. Secondly, we conduct a comparison between the previous PLMs and the latest LLMs, as well as comparing various LLMs with each other. Then we summarize related Healthcare training data, training methods, optimization strategies, and usage. Finally, the unique concerns associated with deploying LLMs in Healthcare settings are investigated, particularly regarding fairness, accountability, transparency and ethics. Our survey provide a comprehensive investigation from perspectives of both computer science and Healthcare specialty. Besides the discussion about Healthcare concerns, we supports the computer science community by compiling a collection of open source resources, such as accessible datasets, the latest methodologies, code implementations, and evaluation benchmarks in the Github. Summarily, we contend that a significant paradigm shift is underway, transitioning from PLMs to LLMs. This shift encompasses a move from discriminative AI approaches to generative AI approaches, as well as a shift from model-centered methodologies to datacentered methodologies.
Medical Intervention Duration Estimation Using Language-enhanced Transformer Encoder with Medical Prompts
Mar 30, 2023Abstract:In recent years, estimating the duration of medical intervention based on electronic health records (EHRs) has gained significant attention in the filed of clinical decision support. However, current models largely focus on structured data, leaving out information from the unstructured clinical free-text data. To address this, we present a novel language-enhanced transformer-based framework, which projects all relevant clinical data modalities (continuous, categorical, binary, and free-text features) into a harmonized language latent space using a pre-trained sentence encoder with the help of medical prompts. The proposed method enables the integration of information from different modalities within the cell transformer encoder and leads to more accurate duration estimation for medical intervention. Our experimental results on both US-based (length of stay in ICU estimation) and Asian (surgical duration prediction) medical datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework, which outperforms tailored baseline approaches and exhibits robustness to data corruption in EHRs.
UFRC: A Unified Framework for Reliable COVID-19 Detection on Crowdsourced Cough Audio
Apr 16, 2022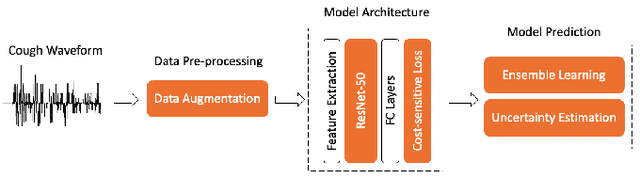
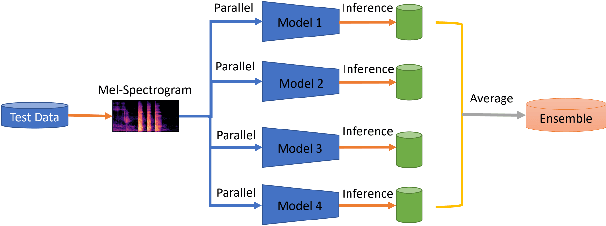
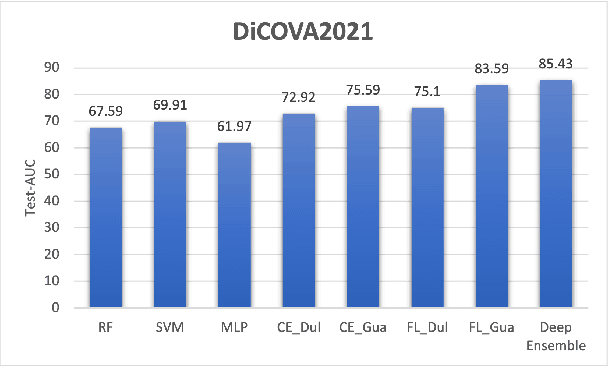
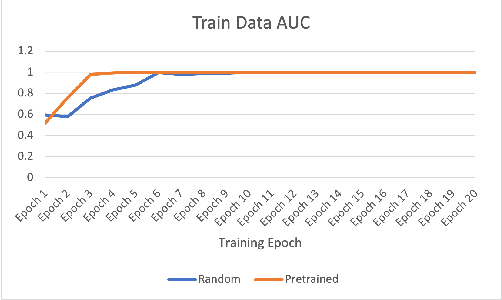
Abstract:We suggested a unified system with core components of data augmentation, ImageNet-pretrained ResNet-50, cost-sensitive loss, deep ensemble learning, and uncertainty estimation to quickly and consistently detect COVID-19 using acoustic evidence. To increase the model's capacity to identify a minority class, data augmentation and cost-sensitive loss are incorporated (infected samples). In the COVID-19 detection challenge, ImageNet-pretrained ResNet-50 has been found to be effective. The unified framework also integrates deep ensemble learning and uncertainty estimation to integrate predictions from various base classifiers for generalisation and reliability. We ran a series of tests using the DiCOVA2021 challenge dataset to assess the efficacy of our proposed method, and the results show that our method has an AUC-ROC of 85.43 percent, making it a promising method for COVID-19 detection. The unified framework also demonstrates that audio may be used to quickly diagnose different respiratory disorders.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge