Yu-Wei Shih
Identifying and Clustering Counter Relationships of Team Compositions in PvP Games for Efficient Balance Analysis
Aug 30, 2024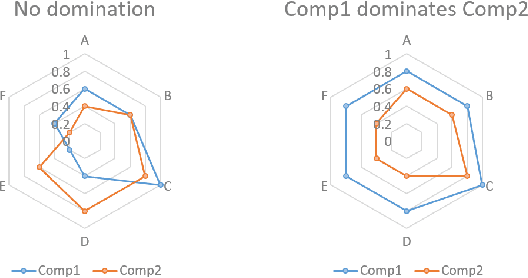
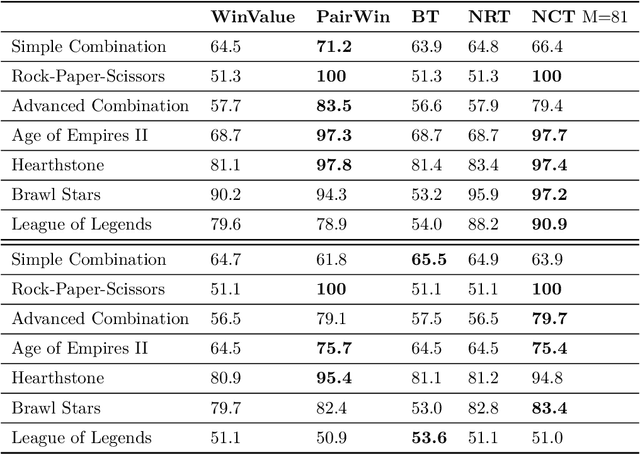
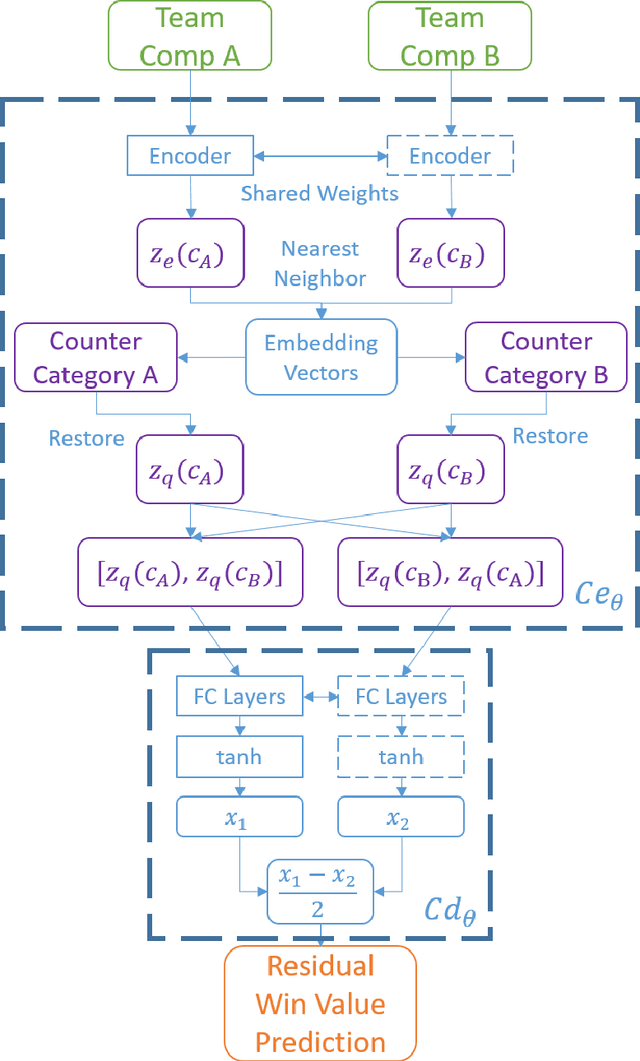
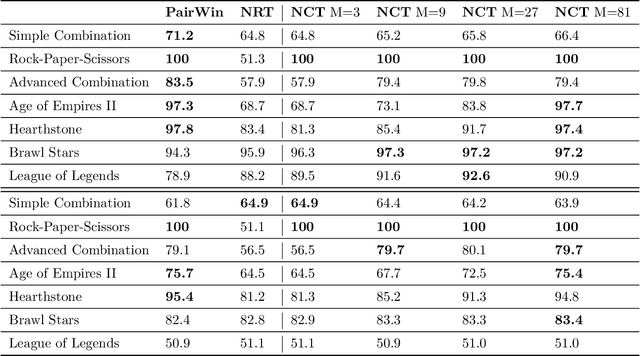
Abstract:How can balance be quantified in game settings? This question is crucial for game designers, especially in player-versus-player (PvP) games, where analyzing the strength relations among predefined team compositions-such as hero combinations in multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA) games or decks in card games-is essential for enhancing gameplay and achieving balance. We have developed two advanced measures that extend beyond the simplistic win rate to quantify balance in zero-sum competitive scenarios. These measures are derived from win value estimations, which employ strength rating approximations via the Bradley-Terry model and counter relationship approximations via vector quantization, significantly reducing the computational complexity associated with traditional win value estimations. Throughout the learning process of these models, we identify useful categories of compositions and pinpoint their counter relationships, aligning with the experiences of human players without requiring specific game knowledge. Our methodology hinges on a simple technique to enhance codebook utilization in discrete representation with a deterministic vector quantization process for an extremely small state space. Our framework has been validated in popular online games, including Age of Empires II, Hearthstone, Brawl Stars, and League of Legends. The accuracy of the observed strength relations in these games is comparable to traditional pairwise win value predictions, while also offering a more manageable complexity for analysis. Ultimately, our findings contribute to a deeper understanding of PvP game dynamics and present a methodology that significantly improves game balance evaluation and design.
Image-based Regularization for Action Smoothness in Autonomous Miniature Racing Car with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jul 17, 2023



Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning has achieved significant results in low-level controlling tasks. However, for some applications like autonomous driving and drone flying, it is difficult to control behavior stably since the agent may suddenly change its actions which often lowers the controlling system's efficiency, induces excessive mechanical wear, and causes uncontrollable, dangerous behavior to the vehicle. Recently, a method called conditioning for action policy smoothness (CAPS) was proposed to solve the problem of jerkiness in low-dimensional features for applications such as quadrotor drones. To cope with high-dimensional features, this paper proposes image-based regularization for action smoothness (I-RAS) for solving jerky control in autonomous miniature car racing. We also introduce a control based on impact ratio, an adaptive regularization weight to control the smoothness constraint, called IR control. In the experiment, an agent with I-RAS and IR control significantly improves the success rate from 59% to 95%. In the real-world-track experiment, the agent also outperforms other methods, namely reducing the average finish lap time, while also improving the completion rate even without real world training. This is also justified by an agent based on I-RAS winning the 2022 AWS DeepRacer Final Championship Cup.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge