Youssef Shoeb
Following the Clues: Experiments on Person Re-ID using Cross-Modal Intelligence
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:The collection and release of street-level recordings as Open Data play a vital role in advancing autonomous driving systems and AI research. However, these datasets pose significant privacy risks, particularly for pedestrians, due to the presence of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) that extends beyond biometric traits such as faces. In this paper, we present cRID, a novel cross-modal framework combining Large Vision-Language Models, Graph Attention Networks, and representation learning to detect textual describable clues of PII and enhance person re-identification (Re-ID). Our approach focuses on identifying and leveraging interpretable features, enabling the detection of semantically meaningful PII beyond low-level appearance cues. We conduct a systematic evaluation of PII presence in person image datasets. Our experiments show improved performance in practical cross-dataset Re-ID scenarios, notably from Market-1501 to CUHK03-np (detected), highlighting the framework's practical utility. Code is available at https://github.com/RAufschlaeger/cRID.
Segment-Level Road Obstacle Detection Using Visual Foundation Model Priors and Likelihood Ratios
Dec 07, 2024



Abstract:Detecting road obstacles is essential for autonomous vehicles to navigate dynamic and complex traffic environments safely. Current road obstacle detection methods typically assign a score to each pixel and apply a threshold to generate final predictions. However, selecting an appropriate threshold is challenging, and the per-pixel classification approach often leads to fragmented predictions with numerous false positives. In this work, we propose a novel method that leverages segment-level features from visual foundation models and likelihood ratios to predict road obstacles directly. By focusing on segments rather than individual pixels, our approach enhances detection accuracy, reduces false positives, and offers increased robustness to scene variability. We benchmark our approach against existing methods on the RoadObstacle and LostAndFound datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance without needing a predefined threshold.
A Likelihood Ratio-Based Approach to Segmenting Unknown Objects
Sep 10, 2024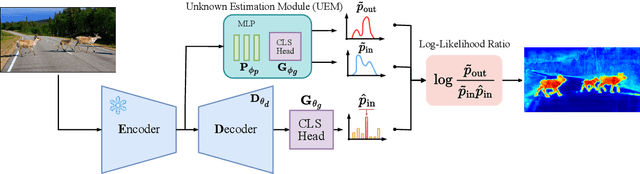

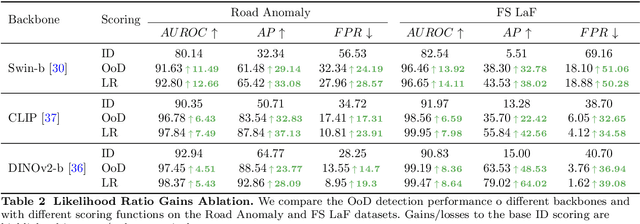
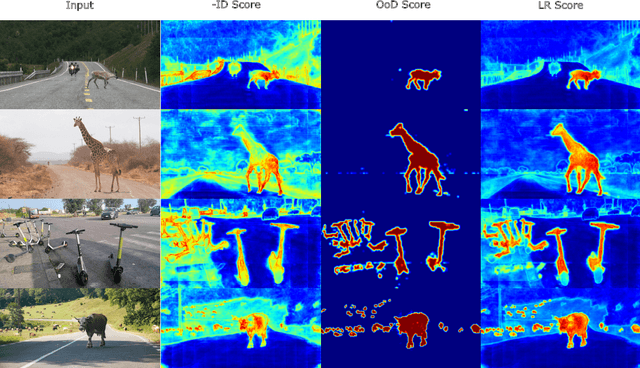
Abstract:Addressing the Out-of-Distribution (OoD) segmentation task is a prerequisite for perception systems operating in an open-world environment. Large foundational models are frequently used in downstream tasks, however, their potential for OoD remains mostly unexplored. We seek to leverage a large foundational model to achieve robust representation. Outlier supervision is a widely used strategy for improving OoD detection of the existing segmentation networks. However, current approaches for outlier supervision involve retraining parts of the original network, which is typically disruptive to the model's learned feature representation. Furthermore, retraining becomes infeasible in the case of large foundational models. Our goal is to retrain for outlier segmentation without compromising the strong representation space of the foundational model. To this end, we propose an adaptive, lightweight unknown estimation module (UEM) for outlier supervision that significantly enhances the OoD segmentation performance without affecting the learned feature representation of the original network. UEM learns a distribution for outliers and a generic distribution for known classes. Using the learned distributions, we propose a likelihood-ratio-based outlier scoring function that fuses the confidence of UEM with that of the pixel-wise segmentation inlier network to detect unknown objects. We also propose an objective to optimize this score directly. Our approach achieves a new state-of-the-art across multiple datasets, outperforming the previous best method by 5.74% average precision points while having a lower false-positive rate. Importantly, strong inlier performance remains unaffected.
How Could Generative AI Support Compliance with the EU AI Act? A Review for Safe Automated Driving Perception
Aug 30, 2024



Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have become central for the perception functions of autonomous vehicles, substantially enhancing their ability to understand and interpret the environment. However, these systems exhibit inherent limitations such as brittleness, opacity, and unpredictable behavior in out-of-distribution scenarios. The European Union (EU) Artificial Intelligence (AI) Act, as a pioneering legislative framework, aims to address these challenges by establishing stringent norms and standards for AI systems, including those used in autonomous driving (AD), which are categorized as high-risk AI. In this work, we explore how the newly available generative AI models can potentially support addressing upcoming regulatory requirements in AD perception, particularly with respect to safety. This short review paper summarizes the requirements arising from the EU AI Act regarding DNN-based perception systems and systematically categorizes existing generative AI applications in AD. While generative AI models show promise in addressing some of the EU AI Acts requirements, such as transparency and robustness, this review examines their potential benefits and discusses how developers could leverage these methods to enhance compliance with the Act. The paper also highlights areas where further research is needed to ensure reliable and safe integration of these technologies.
Have We Ever Encountered This Before? Retrieving Out-of-Distribution Road Obstacles from Driving Scenes
Sep 08, 2023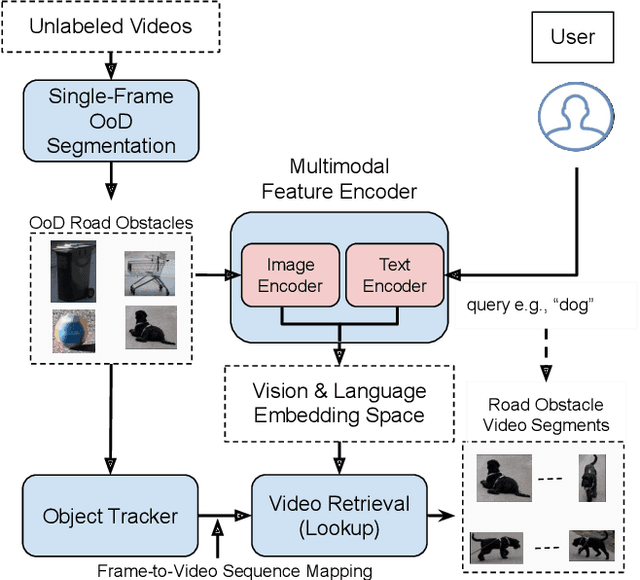
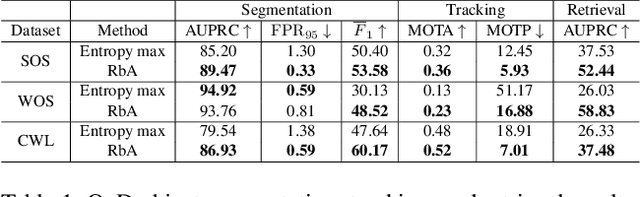
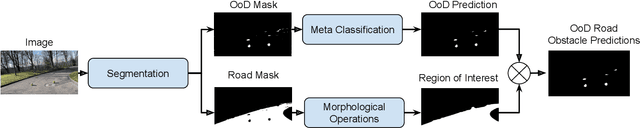
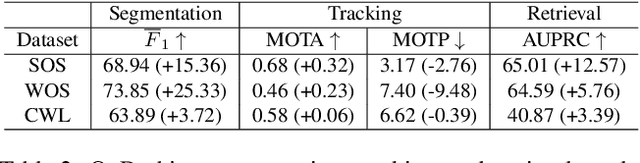
Abstract:In the life cycle of highly automated systems operating in an open and dynamic environment, the ability to adjust to emerging challenges is crucial. For systems integrating data-driven AI-based components, rapid responses to deployment issues require fast access to related data for testing and reconfiguration. In the context of automated driving, this especially applies to road obstacles that were not included in the training data, commonly referred to as out-of-distribution (OoD) road obstacles. Given the availability of large uncurated recordings of driving scenes, a pragmatic approach is to query a database to retrieve similar scenarios featuring the same safety concerns due to OoD road obstacles. In this work, we extend beyond identifying OoD road obstacles in video streams and offer a comprehensive approach to extract sequences of OoD road obstacles using text queries, thereby proposing a way of curating a collection of OoD data for subsequent analysis. Our proposed method leverages the recent advances in OoD segmentation and multi-modal foundation models to identify and efficiently extract safety-relevant scenes from unlabeled videos. We present a first approach for the novel task of text-based OoD object retrieval, which addresses the question ''Have we ever encountered this before?''.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge