Youngseok Jang
HERE: Hierarchical Active Exploration of Radiance Field with Epistemic Uncertainty Minimization
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:We present HERE, an active 3D scene reconstruction framework based on neural radiance fields, enabling high-fidelity implicit mapping. Our approach centers around an active learning strategy for camera trajectory generation, driven by accurate identification of unseen regions, which supports efficient data acquisition and precise scene reconstruction. The key to our approach is epistemic uncertainty quantification based on evidential deep learning, which directly captures data insufficiency and exhibits a strong correlation with reconstruction errors. This allows our framework to more reliably identify unexplored or poorly reconstructed regions compared to existing methods, leading to more informed and targeted exploration. Additionally, we design a hierarchical exploration strategy that leverages learned epistemic uncertainty, where local planning extracts target viewpoints from high-uncertainty voxels based on visibility for trajectory generation, and global planning uses uncertainty to guide large-scale coverage for efficient and comprehensive reconstruction. The effectiveness of the proposed method in active 3D reconstruction is demonstrated by achieving higher reconstruction completeness compared to previous approaches on photorealistic simulated scenes across varying scales, while a hardware demonstration further validates its real-world applicability.
Category-level Neural Field for Reconstruction of Partially Observed Objects in Indoor Environment
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Neural implicit representation has attracted attention in 3D reconstruction through various success cases. For further applications such as scene understanding or editing, several works have shown progress towards object compositional reconstruction. Despite their superior performance in observed regions, their performance is still limited in reconstructing objects that are partially observed. To better treat this problem, we introduce category-level neural fields that learn meaningful common 3D information among objects belonging to the same category present in the scene. Our key idea is to subcategorize objects based on their observed shape for better training of the category-level model. Then we take advantage of the neural field to conduct the challenging task of registering partially observed objects by selecting and aligning against representative objects selected by ray-based uncertainty. Experiments on both simulation and real-world datasets demonstrate that our method improves the reconstruction of unobserved parts for several categories.
Design and Operation of Autonomous Wheelchair Towing Robot
May 23, 2023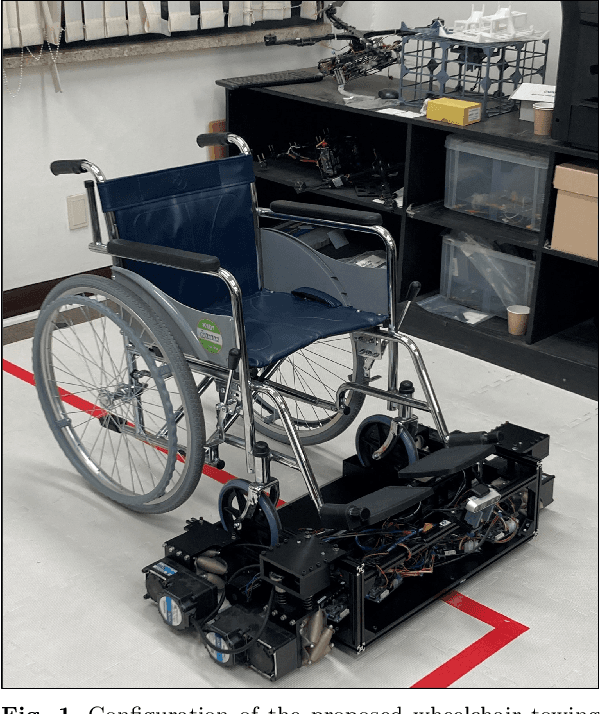


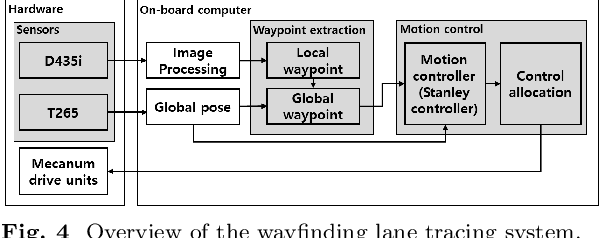
Abstract:In this study, a new concept of a wheelchair-towing robot for the facile electrification of manual wheelchairs is introduced. The development of this concept includes the design of towing robot hardware and an autonomous driving algorithm to ensure the safe transportation of patients to their intended destinations inside the hospital. We developed a novel docking mechanism to facilitate easy docking and separation between the towing robot and the manual wheelchair, which is connected to the front caster wheel of the manual wheelchair. The towing robot has a mecanum wheel drive, enabling the robot to move with a high degree of freedom in the standalone driving mode while adhering to kinematic constraints in the docking mode. Our novel towing robot features a camera sensor that can observe the ground ahead which allows the robot to autonomously follow color-coded wayfinding lanes installed in hospital corridors. This study introduces dedicated image processing techniques for capturing the lanes and control algorithms for effectively tracing a path to achieve autonomous path following. The autonomous towing performance of our proposed platform was validated by a real-world experiment in which a hospital environment with colored lanes was created.
Object-based SLAM utilizing unambiguous pose parameters considering general symmetry types
Mar 13, 2023



Abstract:Existence of symmetric objects, whose observation at different viewpoints can be identical, can deteriorate the performance of simultaneous localization and mapping(SLAM). This work proposes a system for robustly optimizing the pose of cameras and objects even in the presence of symmetric objects. We classify objects into three categories depending on their symmetry characteristics, which is efficient and effective in that it allows to deal with general objects and the objects in the same category can be associated with the same type of ambiguity. Then we extract only the unambiguous parameters corresponding to each category and use them in data association and joint optimization of the camera and object pose. The proposed approach provides significant robustness to the SLAM performance by removing the ambiguous parameters and utilizing as much useful geometric information as possible. Comparison with baseline algorithms confirms the superior performance of the proposed system in terms of object tracking and pose estimation, even in challenging scenarios where the baseline fails.
Topology-Guided Path Planning for Reliable Visual Navigation of MAVs
Jul 19, 2021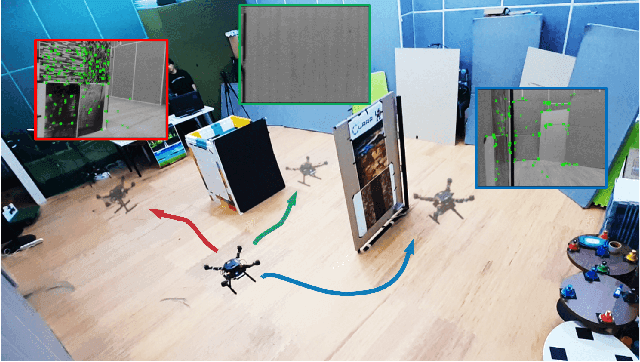
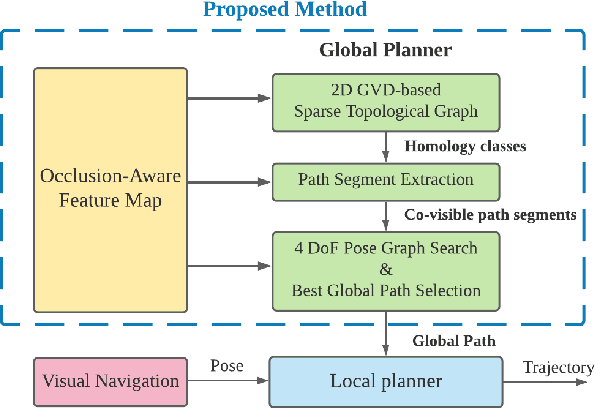
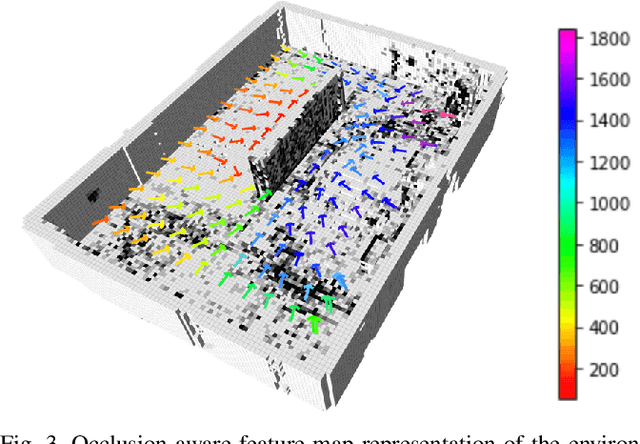

Abstract:Visual navigation has been widely used for state estimation of micro aerial vehicles (MAVs). For stable visual navigation, MAVs should generate perception-aware paths which guarantee enough visible landmarks. Many previous works on perception-aware path planning focused on sampling-based planners. However, they may suffer from sample inefficiency, which leads to computational burden for finding a global optimal path. To address this issue, we suggest a perception-aware path planner which utilizes topological information of environments. Since the topological class of a path and visible landmarks during traveling the path are closely related, the proposed algorithm checks distinctive topological classes to choose the class with abundant visual information. Topological graph is extracted from the generalized Voronoi diagram of the environment and initial paths with different topological classes are found. To evaluate the perception quality of the classes, we divide the initial path into discrete segments where the points in each segment share similar visual information. The optimal class with high perception quality is selected, and a graph-based planner is utilized to generate path within the class. With simulations and real-world experiments, we confirmed that the proposed method could guarantee accurate visual navigation compared with the perception-agnostic method while showing improved computational efficiency than the sampling-based perception-aware planner.
Pose Correction Algorithm for Relative Frames between Keyframes in SLAM
Sep 18, 2020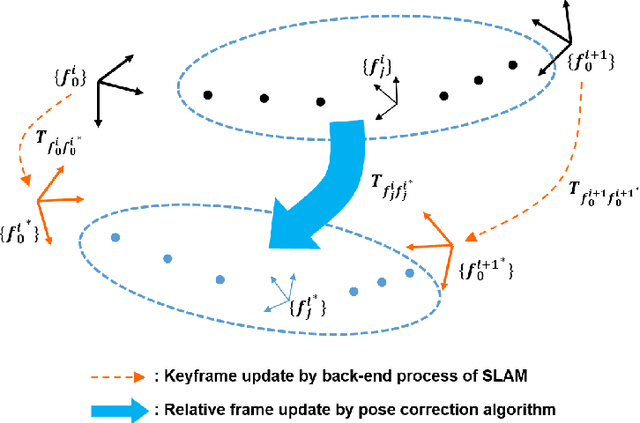
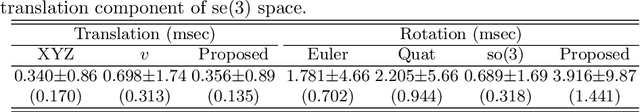

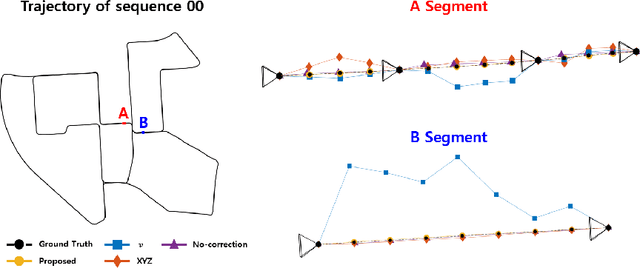
Abstract:With the dominance of keyframe-based SLAM in the field of robotics, the relative frame poses between keyframes have typically been sacrificed for a faster algorithm to achieve online applications. However, those approaches can become insufficient for applications that may require refined poses of all frames, not just keyframes which are relatively sparse compared to all input frames. This paper proposes a novel algorithm to correct the relative frames between keyframes after the keyframes have been updated by a back-end optimization process. The correction model is derived using conservation of the measurement constraint between landmarks and the robot pose. The proposed algorithm is designed to be easily integrable to existing keyframe-based SLAM systems while exhibiting robust and accurate performance superior to existing interpolation methods. The algorithm also requires low computational resources and hence has a minimal burden on the whole SLAM pipeline. We provide the evaluation of the proposed pose correction algorithm in comparison to existing interpolation methods in various vector spaces, and our method has demonstrated excellent accuracy in both KITTI and EuRoC datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge