Youkow Homma
AutoHint: Automatic Prompt Optimization with Hint Generation
Jul 13, 2023
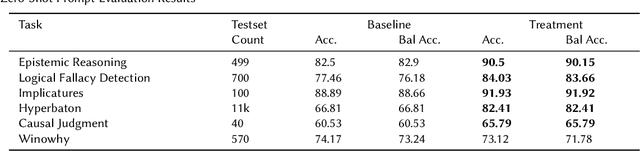
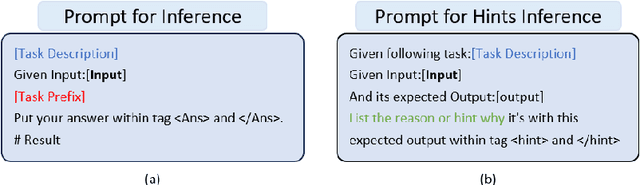
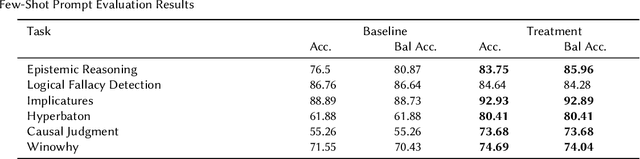
Abstract:This paper presents AutoHint, a novel framework for automatic prompt engineering and optimization for Large Language Models (LLM). While LLMs have demonstrated remarkable ability in achieving high-quality annotation in various tasks, the key to applying this ability to specific tasks lies in developing high-quality prompts. Thus we propose a framework to inherit the merits of both in-context learning and zero-shot learning by incorporating enriched instructions derived from input-output demonstrations to optimize original prompt. We refer to the enrichment as the hint and propose a framework to automatically generate the hint from labeled data. More concretely, starting from an initial prompt, our method first instructs a LLM to deduce new hints for selected samples from incorrect predictions, and then summarizes from per-sample hints and adds the results back to the initial prompt to form a new, enriched instruction. The proposed method is evaluated on the BIG-Bench Instruction Induction dataset for both zero-shot and few-short prompts, where experiments demonstrate our method is able to significantly boost accuracy for multiple tasks.
Extract Dynamic Information To Improve Time Series Modeling: a Case Study with Scientific Workflow
May 19, 2022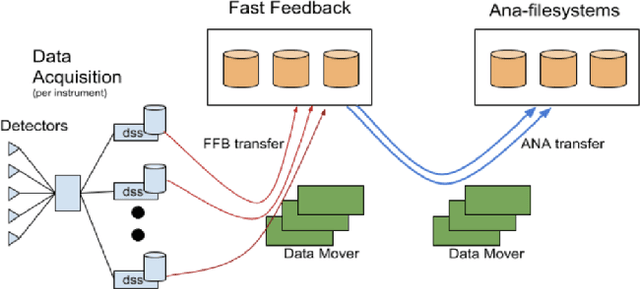
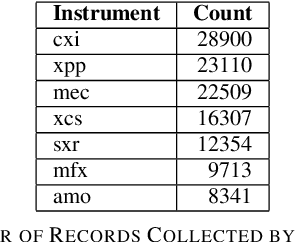
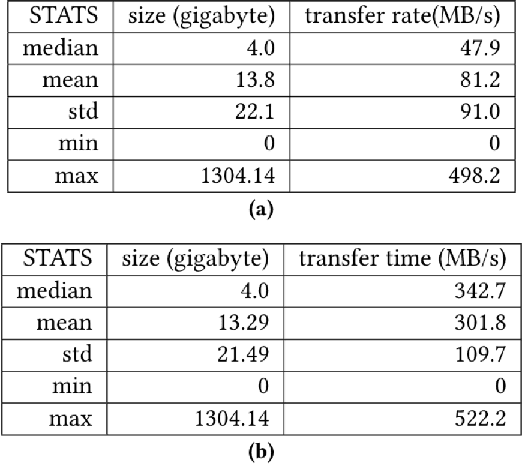
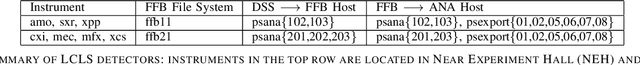
Abstract:In modeling time series data, we often need to augment the existing data records to increase the modeling accuracy. In this work, we describe a number of techniques to extract dynamic information about the current state of a large scientific workflow, which could be generalized to other types of applications. The specific task to be modeled is the time needed for transferring a file from an experimental facility to a data center. The key idea of our approach is to find recent past data transfer events that match the current event in some ways. Tests showed that we could identify recent events matching some recorded properties and reduce the prediction error by about 12% compared to the similar models with only static features. We additionally explored an application specific technique to extract information about the data production process, and was able to reduce the average prediction error by 44%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge