Youhuan Li
SchemaAgent: A Multi-Agents Framework for Generating Relational Database Schema
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:The relational database design would output a schema based on user's requirements, which defines table structures and their interrelated relations. Translating requirements into accurate schema involves several non-trivial subtasks demanding both database expertise and domain-specific knowledge. This poses unique challenges for automated design of relational databases. Existing efforts are mostly based on customized rules or conventional deep learning models, often producing suboptimal schema. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have significantly advanced intelligent application development across various domains. In this paper, we propose SchemaAgent, a unified LLM-based multi-agent framework for the automated generation of high-quality database schema. SchemaAgent is the first to apply LLMs for schema generation, which emulates the workflow of manual schema design by assigning specialized roles to agents and enabling effective collaboration to refine their respective subtasks. Schema generation is a streamlined workflow, where directly applying the multi-agent framework may cause compounding impact of errors. To address this, we incorporate dedicated roles for reflection and inspection, alongside an innovative error detection and correction mechanism to identify and rectify issues across various phases. For evaluation, we present a benchmark named \textit{RSchema}, which contains more than 500 pairs of requirement description and schema. Experimental results on this benchmark demonstrate the superiority of our approach over mainstream LLMs for relational database schema generation.
Graph Neural Networks for Databases: A Survey
Feb 19, 2025



Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) are powerful deep learning models for graph-structured data, demonstrating remarkable success across diverse domains. Recently, the database (DB) community has increasingly recognized the potentiality of GNNs, prompting a surge of researches focusing on improving database systems through GNN-based approaches. However, despite notable advances, There is a lack of a comprehensive review and understanding of how GNNs could improve DB systems. Therefore, this survey aims to bridge this gap by providing a structured and in-depth overview of GNNs for DB systems. Specifically, we propose a new taxonomy that classifies existing methods into two key categories: (1) Relational Databases, which includes tasks like performance prediction, query optimization, and text-to-SQL, and (2) Graph Databases, addressing challenges like efficient graph query processing and graph similarity computation. We systematically review key methods in each category, highlighting their contributions and practical implications. Finally, we suggest promising avenues for integrating GNNs into Database systems.
Diving into Unified Data-Model Sparsity for Class-Imbalanced Graph Representation Learning
Oct 01, 2022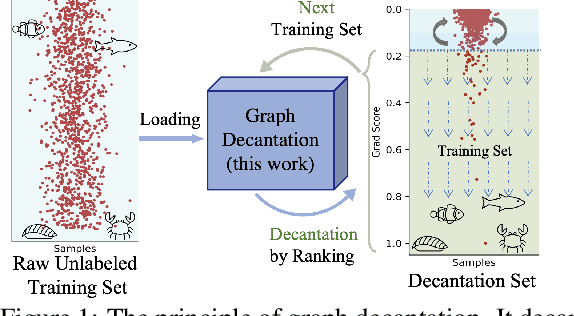
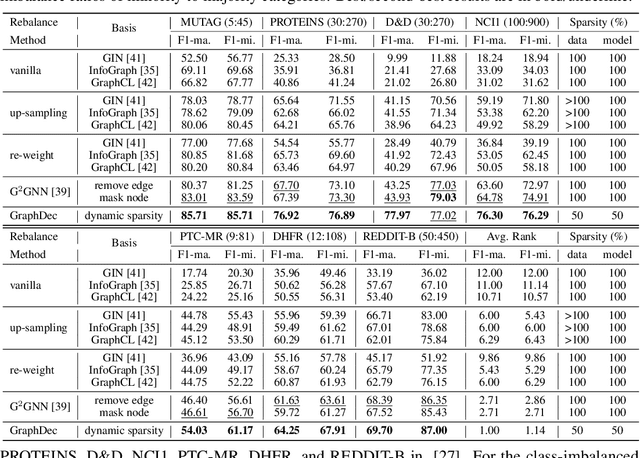
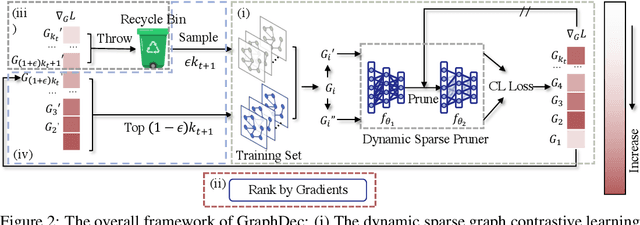
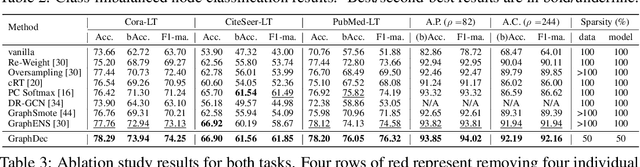
Abstract:Even pruned by the state-of-the-art network compression methods, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) training upon non-Euclidean graph data often encounters relatively higher time costs, due to its irregular and nasty density properties, compared with data in the regular Euclidean space. Another natural property concomitantly with graph is class-imbalance which cannot be alleviated by the massive graph data while hindering GNNs' generalization. To fully tackle these unpleasant properties, (i) theoretically, we introduce a hypothesis about what extent a subset of the training data can approximate the full dataset's learning effectiveness. The effectiveness is further guaranteed and proved by the gradients' distance between the subset and the full set; (ii) empirically, we discover that during the learning process of a GNN, some samples in the training dataset are informative for providing gradients to update model parameters. Moreover, the informative subset is not fixed during training process. Samples that are informative in the current training epoch may not be so in the next one. We also notice that sparse subnets pruned from a well-trained GNN sometimes forget the information provided by the informative subset, reflected in their poor performances upon the subset. Based on these findings, we develop a unified data-model dynamic sparsity framework named Graph Decantation (GraphDec) to address challenges brought by training upon a massive class-imbalanced graph data. The key idea of GraphDec is to identify the informative subset dynamically during the training process by adopting sparse graph contrastive learning. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that GraphDec outperforms baselines for graph and node tasks, with respect to classification accuracy and data usage efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge