Yong Keong Yap
Ladder-of-Thought: Using Knowledge as Steps to Elevate Stance Detection
Sep 07, 2023Abstract:Stance detection aims to identify the attitude expressed in a document towards a given target. Techniques such as Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting have advanced this task, enhancing a model's reasoning capabilities through the derivation of intermediate rationales. However, CoT relies primarily on a model's pre-trained internal knowledge during reasoning, thereby neglecting the valuable external information that is previously unknown to the model. This omission, especially within the unsupervised reasoning process, can affect the model's overall performance. Moreover, while CoT enhances Large Language Models (LLMs), smaller LMs, though efficient operationally, face challenges in delivering nuanced reasoning. In response to these identified gaps, we introduce the Ladder-of-Thought (LoT) for the stance detection task. Constructed through a dual-phase Progressive Optimization Framework, LoT directs the small LMs to assimilate high-quality external knowledge, refining the intermediate rationales produced. These bolstered rationales subsequently serve as the foundation for more precise predictions - akin to how a ladder facilitates reaching elevated goals. LoT achieves a balance between efficiency and performance. Our empirical evaluations underscore LoT's efficacy, marking a 16% improvement over GPT-3.5 and a 10% enhancement compared to GPT-3.5 with CoT on stance detection task.
Guiding Computational Stance Detection with Expanded Stance Triangle Framework
May 31, 2023
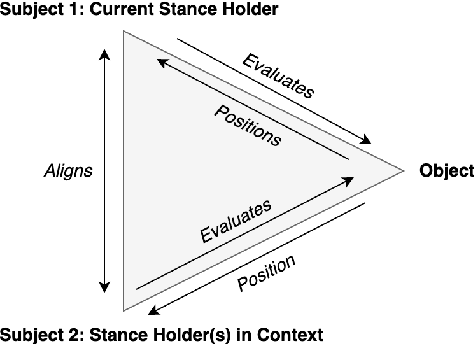
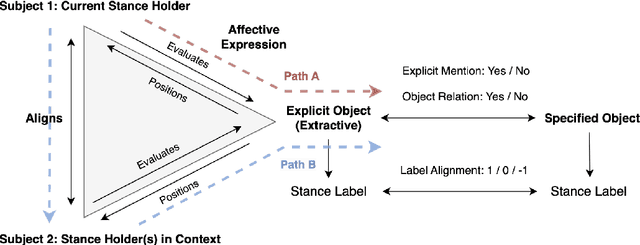
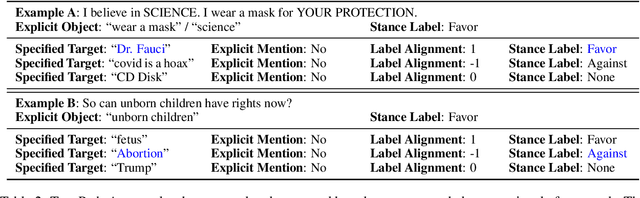
Abstract:Stance detection determines whether the author of a piece of text is in favor of, against, or neutral towards a specified target, and can be used to gain valuable insights into social media. The ubiquitous indirect referral of targets makes this task challenging, as it requires computational solutions to model semantic features and infer the corresponding implications from a literal statement. Moreover, the limited amount of available training data leads to subpar performance in out-of-domain and cross-target scenarios, as data-driven approaches are prone to rely on superficial and domain-specific features. In this work, we decompose the stance detection task from a linguistic perspective, and investigate key components and inference paths in this task. The stance triangle is a generic linguistic framework previously proposed to describe the fundamental ways people express their stance. We further expand it by characterizing the relationship between explicit and implicit objects. We then use the framework to extend one single training corpus with additional annotation. Experimental results show that strategically-enriched data can significantly improve the performance on out-of-domain and cross-target evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge