Yixiao Duan
Net2: A Graph Attention Network Method Customized for Pre-Placement Net Length Estimation
Nov 27, 2020
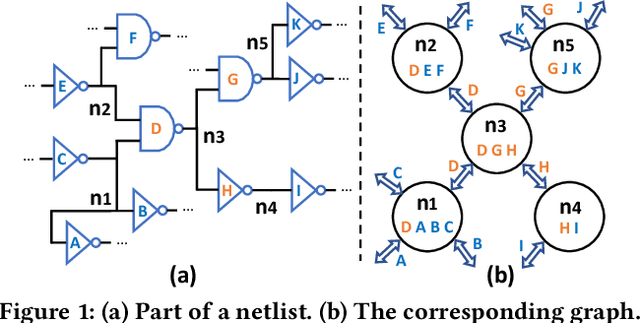
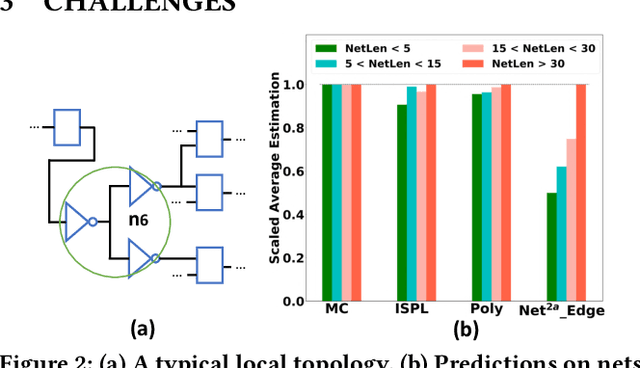
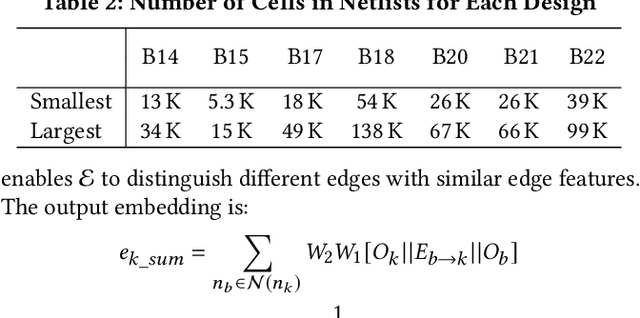
Abstract:Net length is a key proxy metric for optimizing timing and power across various stages of a standard digital design flow. However, the bulk of net length information is not available until cell placement, and hence it is a significant challenge to explicitly consider net length optimization in design stages prior to placement, such as logic synthesis. This work addresses this challenge by proposing a graph attention network method with customization, called Net2, to estimate individual net length before cell placement. Its accuracy-oriented version Net2a achieves about 15% better accuracy than several previous works in identifying both long nets and long critical paths. Its fast version Net2f is more than 1000 times faster than placement while still outperforms previous works and other neural network techniques in terms of various accuracy metrics.
TIPRDC: Task-Independent Privacy-Respecting Data Crowdsourcing Framework with Anonymized Intermediate Representations
Jun 12, 2020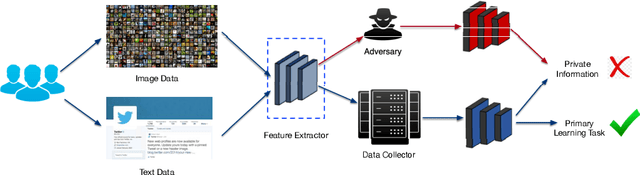
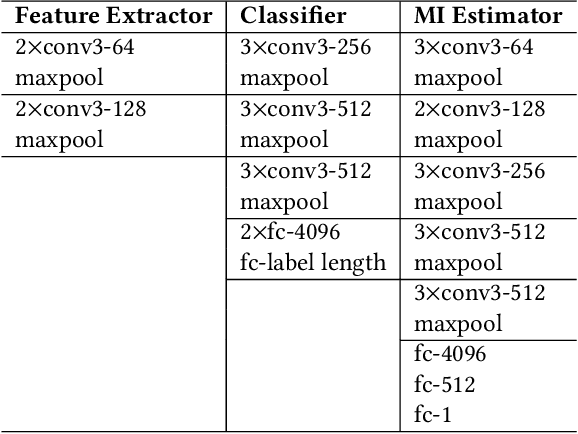
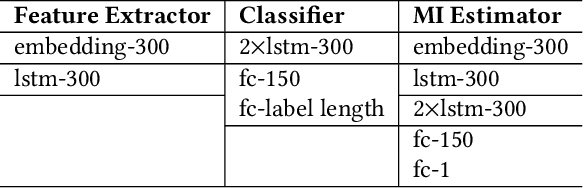
Abstract:The success of deep learning partially benefits from the availability of various large-scale datasets. These datasets are often crowdsourced from individual users and contain private information like gender, age, etc. The emerging privacy concerns from users on data sharing hinder the generation or use of crowdsourcing datasets and lead to hunger of training data for new deep learning applications. One na\"{\i}ve solution is to pre-process the raw data to extract features at the user-side, and then only the extracted features will be sent to the data collector. Unfortunately, attackers can still exploit these extracted features to train an adversary classifier to infer private attributes. Some prior arts leveraged game theory to protect private attributes. However, these defenses are designed for known primary learning tasks, the extracted features work poorly for unknown learning tasks. To tackle the case where the learning task may be unknown or changing, we present TIPRDC, a task-independent privacy-respecting data crowdsourcing framework with anonymized intermediate representation. The goal of this framework is to learn a feature extractor that can hide the privacy information from the intermediate representations; while maximally retaining the original information embedded in the raw data for the data collector to accomplish unknown learning tasks. We design a hybrid training method to learn the anonymized intermediate representation: (1) an adversarial training process for hiding private information from features; (2) maximally retain original information using a neural-network-based mutual information estimator.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge