Yipin Zhang
Boosting Deductive Reasoning with Step Signals In RLHF
Oct 12, 2024Abstract:Logical reasoning is a crucial task for Large Language Models (LLMs), enabling them to tackle complex problems. Among reasoning tasks, multi-step reasoning poses a particular challenge. Grounded in the theory of formal logic, we have developed an automated method, Multi-step Deduction (MuseD), for deductive reasoning data. MuseD has allowed us to create training and testing datasets for multi-step reasoning. Our generation method enables control over the complexity of the generated instructions, facilitating training and evaluation of models across different difficulty levels. Through RLHF training, our training data has demonstrated significant improvements in logical capabilities for both in-domain of out-of-domain reasoning tasks. Additionally, we have conducted tests to assess the multi-step reasoning abilities of various models.
3D-Properties: Identifying Challenges in DPO and Charting a Path Forward
Jun 11, 2024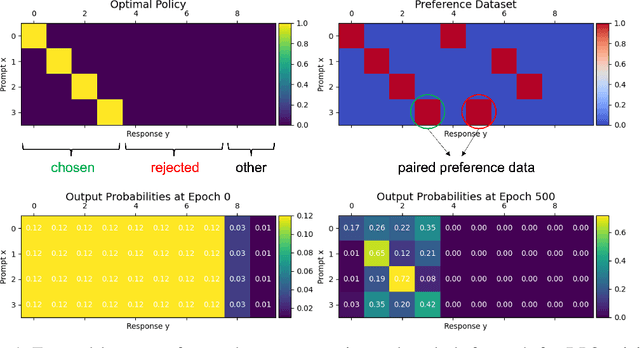
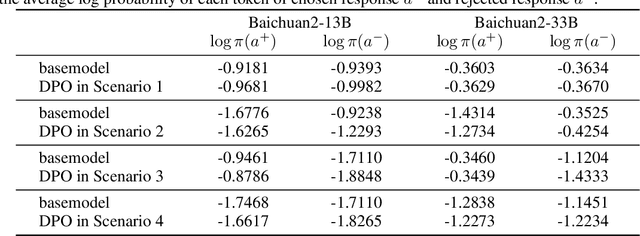
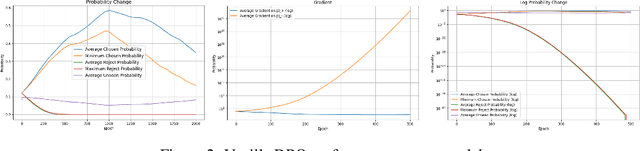
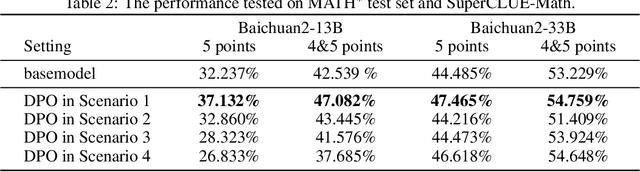
Abstract:Aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preference has recently gained tremendous attention, with the canonical yet costly RLHF-PPO and the simple and straightforward Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) as two examples. Despite the efficiency, DPO has rarely be used in the state-of-the-art production-level LLMs, implying its potential pathologies. In this work, we revisit DPO with a comprehensive examination of its empirical efficacy and a systematic comparison with RLHF-PPO. We identify the \textbf{3D}-properties of DPO's learning outcomes: the \textbf{D}rastic drop in the likelihood of rejected responses, the \textbf{D}egradation into LLM unlearning, and the \textbf{D}ispersion effect on unseen responses through experiments with both a carefully designed toy model and practical LLMs on tasks including mathematical problem-solving and instruction following. These findings inherently connect to some observations made by related works and we additionally contribute a plausible theoretical explanation for them. Accordingly, we propose easy regularization methods to mitigate the issues caused by \textbf{3D}-properties, improving the training stability and final performance of DPO. Our contributions also include an investigation into how the distribution of the paired preference data impacts the effectiveness of DPO. We hope this work could offer research directions to narrow the gap between reward-free preference learning methods and reward-based ones.
Exploring the LLM Journey from Cognition to Expression with Linear Representations
May 27, 2024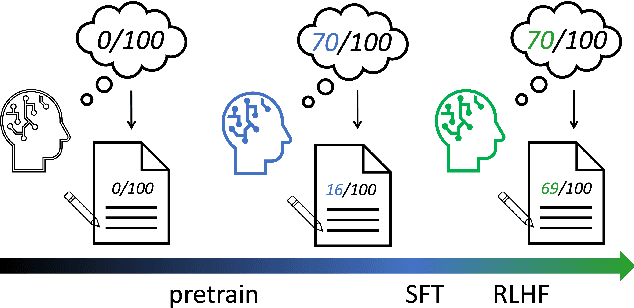
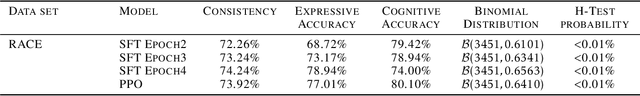
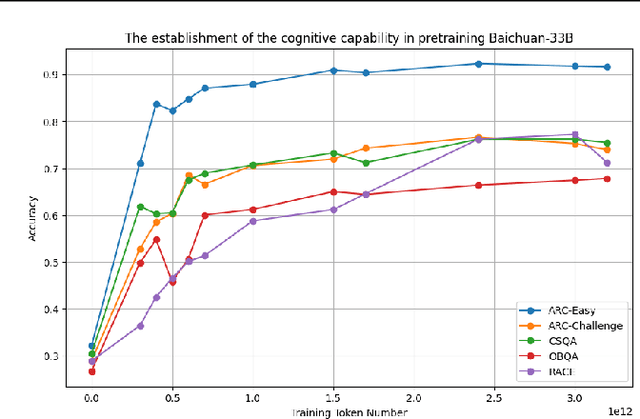
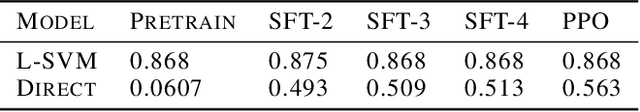
Abstract:This paper presents an in-depth examination of the evolution and interplay of cognitive and expressive capabilities in large language models (LLMs), with a specific focus on Baichuan-7B and Baichuan-33B, an advanced bilingual (Chinese and English) LLM series. We define and explore the model's cognitive and expressive capabilities through linear representations across three critical phases: Pretraining, Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). Cognitive capability is defined as the quantity and quality of information conveyed by the neuron output vectors within the network, similar to the neural signal processing in human cognition. Expressive capability is defined as the model's capability to produce word-level output. Our findings unveil a sequential development pattern, where cognitive abilities are largely established during Pretraining, whereas expressive abilities predominantly advance during SFT and RLHF. Statistical analyses confirm a significant correlation between the two capabilities, suggesting that cognitive capacity may limit expressive potential. The paper also explores the theoretical underpinnings of these divergent developmental trajectories and their connection to the LLMs' architectural design. Moreover, we evaluate various optimization-independent strategies, such as few-shot learning and repeated sampling, which bridge the gap between cognitive and expressive capabilities. This research reveals the potential connection between the hidden space and the output space, contributing valuable insights into the interpretability and controllability of their training processes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge