Yingtao Jiang
Spectral Complex Autoencoder Pruning: A Fidelity-Guided Criterion for Extreme Structured Channel Compression
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:We propose Spectral Complex Autoencoder Pruning (SCAP), a reconstruction-based criterion that measures functional redundancy at the level of individual output channels. For each convolutional layer, we construct a complex interaction field by pairing the full multi-channel input activation as the real part with a single output-channel activation (spatially aligned and broadcast across input channels) as the imaginary part. We transform this complex field to the frequency domain and train a low-capacity autoencoder to reconstruct normalized spectra. Channels whose spectra are reconstructed with high fidelity are interpreted as lying close to a low-dimensional manifold captured by the autoencoder and are therefore more compressible; conversely, channels with low fidelity are retained as they encode information that cannot be compactly represented by the learned manifold. This yields an importance score (optionally fused with the filter L1 norm) that supports simple threshold-based pruning and produces a structurally consistent pruned network. On VGG16 trained on CIFAR-10, at a fixed threshold of 0.6, we obtain 90.11% FLOP reduction and 96.30% parameter reduction with an absolute Top-1 accuracy drop of 1.67% from a 93.44% baseline after fine-tuning, demonstrating that spectral reconstruction fidelity of complex interaction fields is an effective proxy for channel-level redundancy under aggressive compression.
One-Shot Structured Pruning of Quantum Neural Networks via $q$-Group Engineering and Quantum Geometric Metrics
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Quantum neural networks (QNNs) suffer from severe gate-level redundancy, which hinders their deployment on noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) devices. In this work, we propose q-iPrune, a one-shot structured pruning framework grounded in the algebraic structure of $q$-deformed groups and task-conditioned quantum geometry. Unlike prior heuristic or gradient-based pruning methods, q-iPrune formulates redundancy directly at the gate level. Each gate is compared within an algebraically consistent subgroup using a task-conditioned $q$-overlap distance, which measures functional similarity through state overlaps on a task-relevant ensemble. A gate is removed only when its replacement by a subgroup representative provably induces a bounded deviation on all task observables. We establish three rigorous theoretical guarantees. First, we prove completeness of redundancy pruning: no gate that violates the prescribed similarity threshold is removed. Second, we show that the pruned circuit is functionally equivalent up to an explicit, task-conditioned error bound, with a closed-form dependence on the redundancy tolerance and the number of replaced gates. Third, we prove that the pruning procedure is computationally feasible, requiring only polynomial-time comparisons and avoiding exponential enumeration over the Hilbert space. To adapt pruning decisions to hardware imperfections, we introduce a noise-calibrated deformation parameter $λ$ that modulates the $q$-geometry and redundancy tolerance. Experiments on standard quantum machine learning benchmarks demonstrate that q-iPrune achieves substantial gate reduction while maintaining bounded task performance degradation, consistent with our theoretical guarantees.
LiePrune: Lie Group and Quantum Geometric Dual Representation for One-Shot Structured Pruning of Quantum Neural Networks
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Quantum neural networks (QNNs) and parameterized quantum circuits (PQCs) are key building blocks for near-term quantum machine learning. However, their scalability is constrained by excessive parameters, barren plateaus, and hardware limitations. We propose LiePrune, the first mathematically grounded one-shot structured pruning framework for QNNs that leverages Lie group structure and quantum geometric information. Each gate is jointly represented in a Lie group--Lie algebra dual space and a quantum geometric feature space, enabling principled redundancy detection and aggressive compression. Experiments on quantum classification (MNIST, FashionMNIST), quantum generative modeling (Bars-and-Stripes), and quantum chemistry (LiH VQE) show that LiePrune achieves over $10\times$ compression with negligible or even improved task performance, while providing provable guarantees on redundancy detection, functional approximation, and computational complexity.
Development of a Platform to Enable Real Time, Non-disruptive Testing and Early Fault Detection of Critical High Voltage Transformers and Switchgears in High Speed-rail
Oct 01, 2024Abstract:Partial discharge (PD) incidents can occur in critical components of high-speed rail electric systems, such as transformers and switchgears, due to localized insulation defects that cannot withstand electric stress, leading to potential flashovers. These incidents can escalate over time, resulting in breakdowns, downtime, and safety risks. Fortunately, PD activities emit radio frequency (RF) signals, allowing for the development of a hardware platform for real-time, non-invasive PD detection and monitoring. The system uses an RF antenna and high-speed data acquisition to scan signals across a configurable frequency range (100MHz to 3GHz), utilizing intermediate frequency modulation and sliding frequency windows for detailed analysis. When signals exceed a threshold, the system records the events, capturing both raw signal data and spectrum snapshots. Real-time data is streamed to a cloud server, offering remote access through a dedicated smartphone application, enabling maintenance teams to monitor and respond promptly. Laboratory testing has confirmed the system's ability to accurately capture RF signals and provide real-time PD monitoring, enhancing the reliability and safety of high-speed rail infrastructure.
Toward Precise Robotic Weed Flaming Using a Mobile Manipulator with a Flamethrower
Jul 06, 2024Abstract:Robotic weed flaming is a new and environmentally friendly approach to weed removal in the agricultural field. Using a mobile manipulator equipped with a flamethrower, we design a new system and algorithm to enable effective weed flaming, which requires robotic manipulation with a soft and deformable end effector, as the thermal coverage of the flame is affected by dynamic or unknown environmental factors such as gravity, wind, atmospheric pressure, fuel tank pressure, and pose of the nozzle. System development includes overall design, hardware integration, and software pipeline. To enable precise weed removal, the greatest challenge is to detect and predict dynamic flame coverage in real time before motion planning, which is quite different from a conventional rigid gripper in grasping or a spray gun in painting. Based on the images from two onboard infrared cameras and the pose information of the flamethrower nozzle on a mobile manipulator, we propose a new dynamic flame coverage model. The flame model uses a center-arc curve with a Gaussian cross-section model to describe the flame coverage in real time. The experiments have demonstrated the working system and shown that our model and algorithm can achieve a mean average precision (mAP) of more than 76\% in the reprojected images during online prediction.
Data Streaming and Traffic Gathering in Mesh-based NoC for Deep Neural Network Acceleration
Aug 01, 2021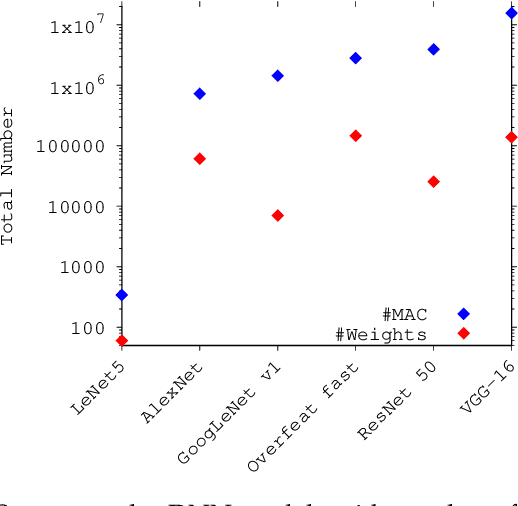
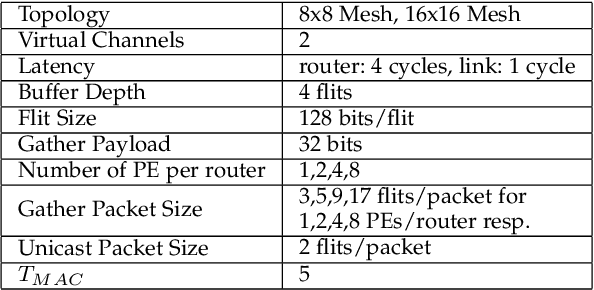
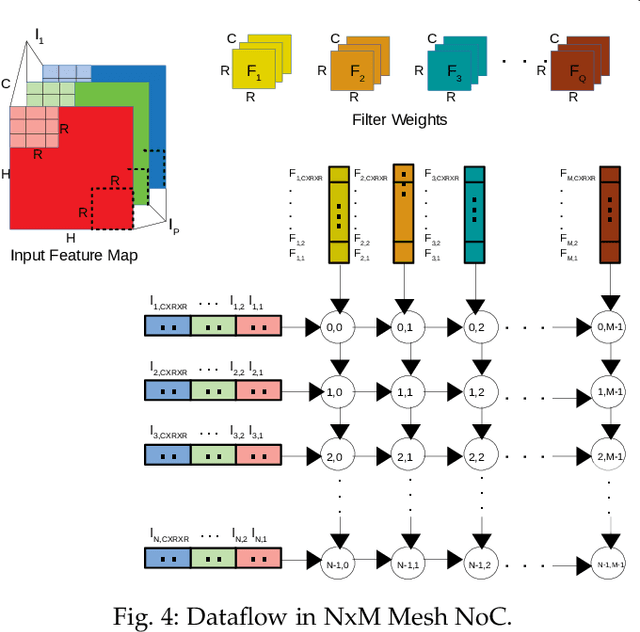
Abstract:The increasing popularity of deep neural network (DNN) applications demands high computing power and efficient hardware accelerator architecture. DNN accelerators use a large number of processing elements (PEs) and on-chip memory for storing weights and other parameters. As the communication backbone of a DNN accelerator, networks-on-chip (NoC) play an important role in supporting various dataflow patterns and enabling processing with communication parallelism in a DNN accelerator. However, the widely used mesh-based NoC architectures inherently cannot support the efficient one-to-many and many-to-one traffic largely existing in DNN workloads. In this paper, we propose a modified mesh architecture with a one-way/two-way streaming bus to speedup one-to-many (multicast) traffic, and the use of gather packets to support many-to-one (gather) traffic. The analysis of the runtime latency of a convolutional layer shows that the two-way streaming architecture achieves better improvement than the one-way streaming architecture for an Output Stationary (OS) dataflow architecture. The simulation results demonstrate that the gather packets can help to reduce the runtime latency up to 1.8 times and network power consumption up to 1.7 times, compared with the repetitive unicast method on modified mesh architectures supporting two-way streaming.
Improving the Performance of a NoC-based CNN Accelerator with Gather Support
Aug 01, 2021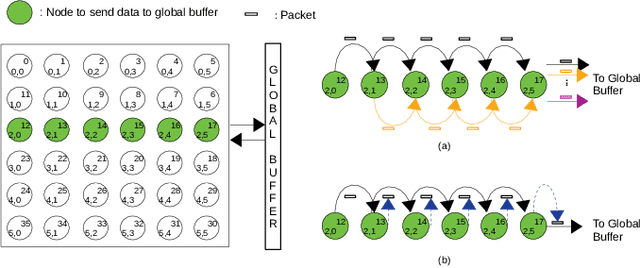
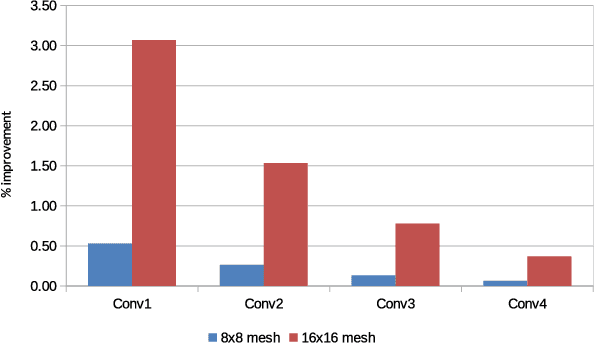
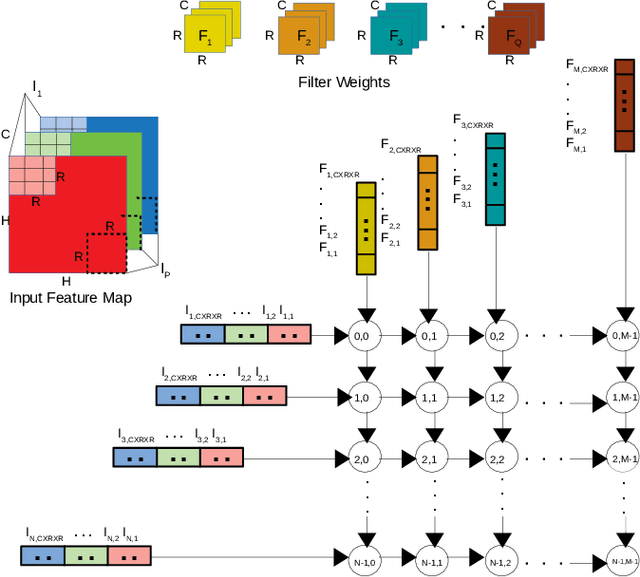
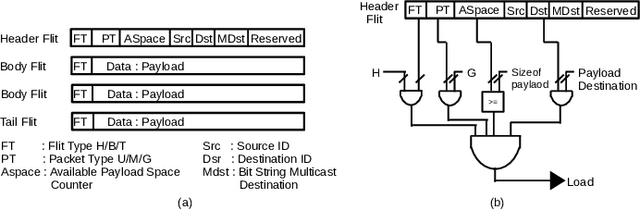
Abstract:The increasing application of deep learning technology drives the need for an efficient parallel computing architecture for Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). A significant challenge faced when designing a many-core CNN accelerator is to handle the data movement between the processing elements. The CNN workload introduces many-to-one traffic in addition to one-to-one and one-to-many traffic. As the de-facto standard for on-chip communication, Network-on-Chip (NoC) can support various unicast and multicast traffic. For many-to-one traffic, repetitive unicast is employed which is not an efficient way. In this paper, we propose to use the gather packet on mesh-based NoCs employing output stationary systolic array in support of many-to-one traffic. The gather packet will collect the data from the intermediate nodes eventually leading to the destination efficiently. This method is evaluated using the traffic traces generated from the convolution layer of AlexNet and VGG-16 with improvement in the latency and power than the repetitive unicast method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge