Binayak Tiwari
Data Streaming and Traffic Gathering in Mesh-based NoC for Deep Neural Network Acceleration
Aug 01, 2021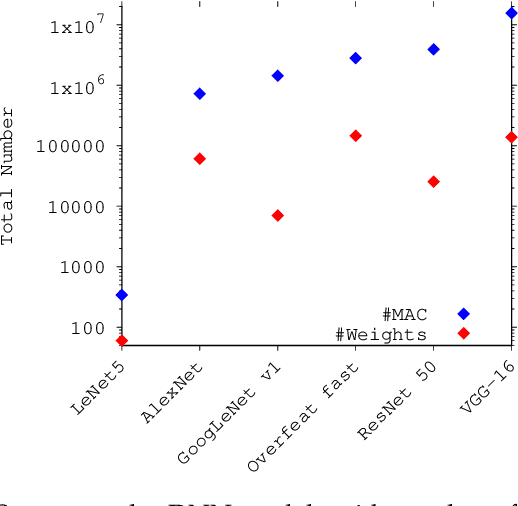
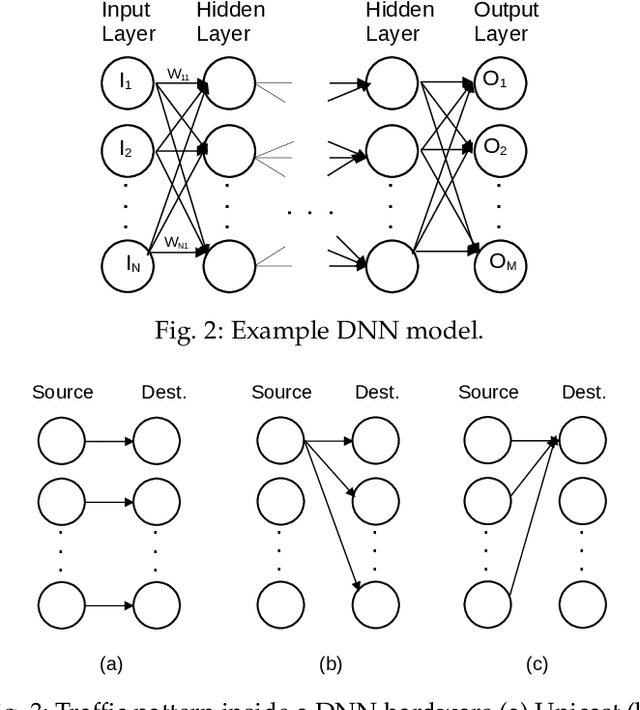
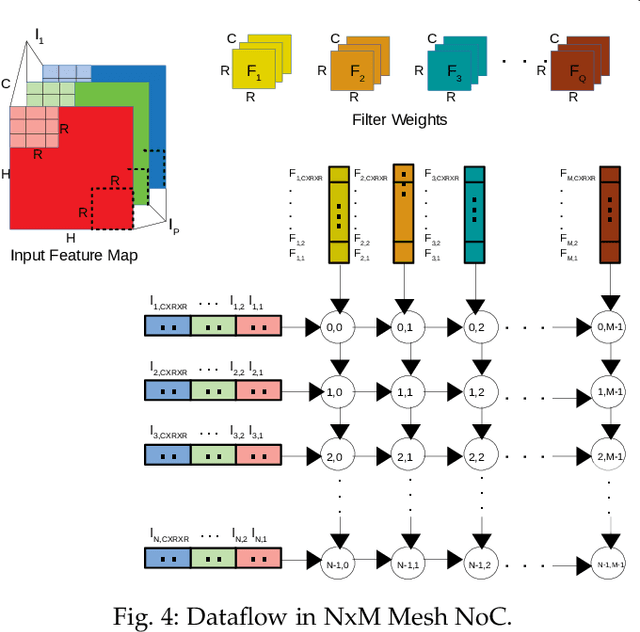
Abstract:The increasing popularity of deep neural network (DNN) applications demands high computing power and efficient hardware accelerator architecture. DNN accelerators use a large number of processing elements (PEs) and on-chip memory for storing weights and other parameters. As the communication backbone of a DNN accelerator, networks-on-chip (NoC) play an important role in supporting various dataflow patterns and enabling processing with communication parallelism in a DNN accelerator. However, the widely used mesh-based NoC architectures inherently cannot support the efficient one-to-many and many-to-one traffic largely existing in DNN workloads. In this paper, we propose a modified mesh architecture with a one-way/two-way streaming bus to speedup one-to-many (multicast) traffic, and the use of gather packets to support many-to-one (gather) traffic. The analysis of the runtime latency of a convolutional layer shows that the two-way streaming architecture achieves better improvement than the one-way streaming architecture for an Output Stationary (OS) dataflow architecture. The simulation results demonstrate that the gather packets can help to reduce the runtime latency up to 1.8 times and network power consumption up to 1.7 times, compared with the repetitive unicast method on modified mesh architectures supporting two-way streaming.
Improving the Performance of a NoC-based CNN Accelerator with Gather Support
Aug 01, 2021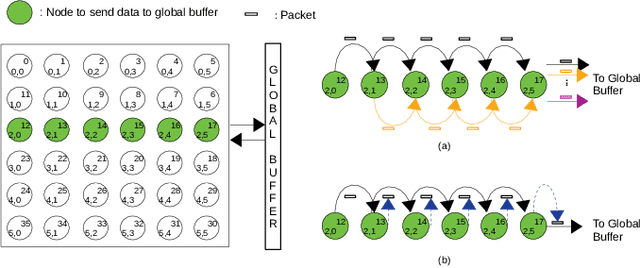
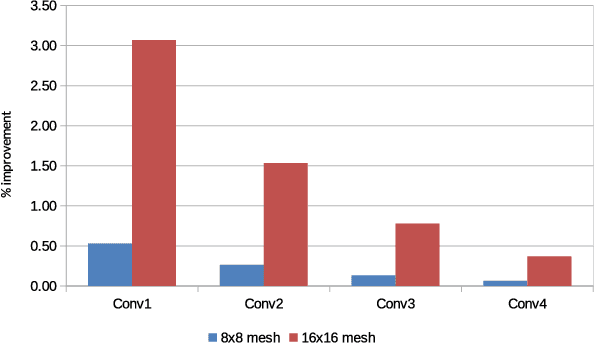
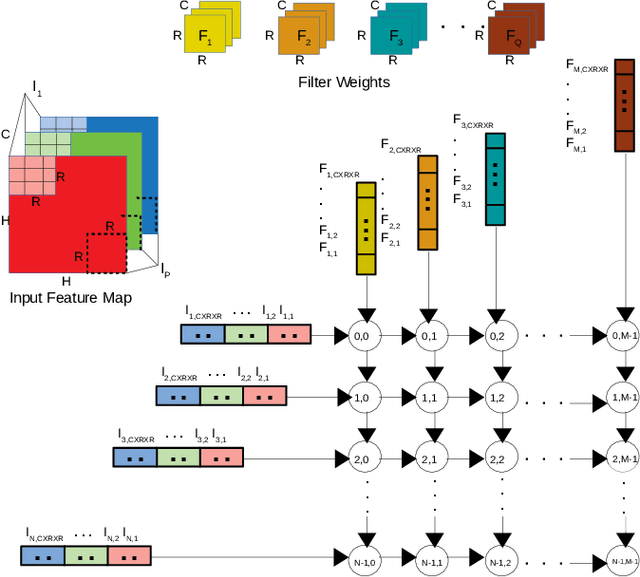
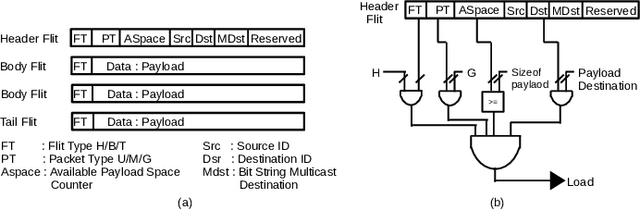
Abstract:The increasing application of deep learning technology drives the need for an efficient parallel computing architecture for Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). A significant challenge faced when designing a many-core CNN accelerator is to handle the data movement between the processing elements. The CNN workload introduces many-to-one traffic in addition to one-to-one and one-to-many traffic. As the de-facto standard for on-chip communication, Network-on-Chip (NoC) can support various unicast and multicast traffic. For many-to-one traffic, repetitive unicast is employed which is not an efficient way. In this paper, we propose to use the gather packet on mesh-based NoCs employing output stationary systolic array in support of many-to-one traffic. The gather packet will collect the data from the intermediate nodes eventually leading to the destination efficiently. This method is evaluated using the traffic traces generated from the convolution layer of AlexNet and VGG-16 with improvement in the latency and power than the repetitive unicast method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge