Yingkai Fu
Distractor-aware Event-based Tracking
Oct 29, 2023



Abstract:Event cameras, or dynamic vision sensors, have recently achieved success from fundamental vision tasks to high-level vision researches. Due to its ability to asynchronously capture light intensity changes, event camera has an inherent advantage to capture moving objects in challenging scenarios including objects under low light, high dynamic range, or fast moving objects. Thus event camera are natural for visual object tracking. However, the current event-based trackers derived from RGB trackers simply modify the input images to event frames and still follow conventional tracking pipeline that mainly focus on object texture for target distinction. As a result, the trackers may not be robust dealing with challenging scenarios such as moving cameras and cluttered foreground. In this paper, we propose a distractor-aware event-based tracker that introduces transformer modules into Siamese network architecture (named DANet). Specifically, our model is mainly composed of a motion-aware network and a target-aware network, which simultaneously exploits both motion cues and object contours from event data, so as to discover motion objects and identify the target object by removing dynamic distractors. Our DANet can be trained in an end-to-end manner without any post-processing and can run at over 80 FPS on a single V100. We conduct comprehensive experiments on two large event tracking datasets to validate the proposed model. We demonstrate that our tracker has superior performance against the state-of-the-art trackers in terms of both accuracy and efficiency.
Object Tracking by Jointly Exploiting Frame and Event Domain
Sep 19, 2021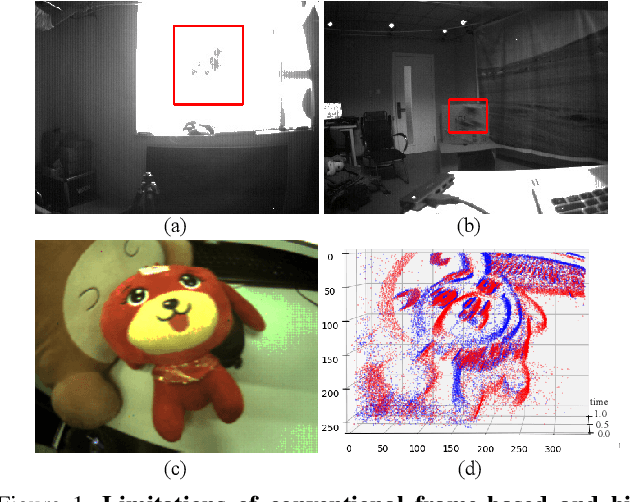
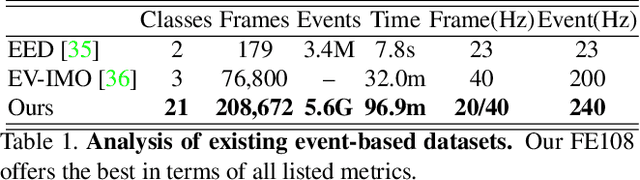
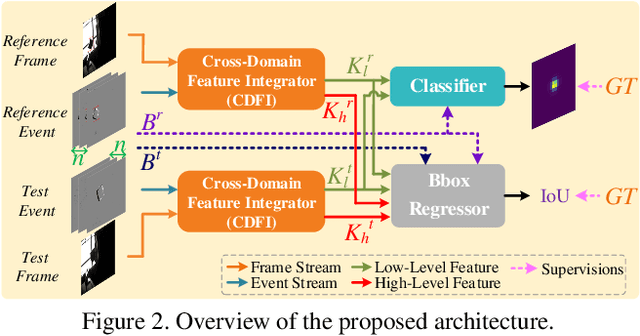
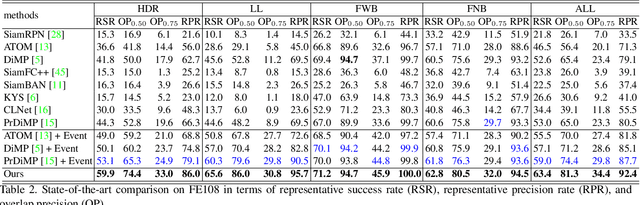
Abstract:Inspired by the complementarity between conventional frame-based and bio-inspired event-based cameras, we propose a multi-modal based approach to fuse visual cues from the frame- and event-domain to enhance the single object tracking performance, especially in degraded conditions (e.g., scenes with high dynamic range, low light, and fast-motion objects). The proposed approach can effectively and adaptively combine meaningful information from both domains. Our approach's effectiveness is enforced by a novel designed cross-domain attention schemes, which can effectively enhance features based on self- and cross-domain attention schemes; The adaptiveness is guarded by a specially designed weighting scheme, which can adaptively balance the contribution of the two domains. To exploit event-based visual cues in single-object tracking, we construct a large-scale frame-event-based dataset, which we subsequently employ to train a novel frame-event fusion based model. Extensive experiments show that the proposed approach outperforms state-of-the-art frame-based tracking methods by at least 10.4% and 11.9% in terms of representative success rate and precision rate, respectively. Besides, the effectiveness of each key component of our approach is evidenced by our thorough ablation study.
Multi-domain Collaborative Feature Representation for Robust Visual Object Tracking
Aug 10, 2021
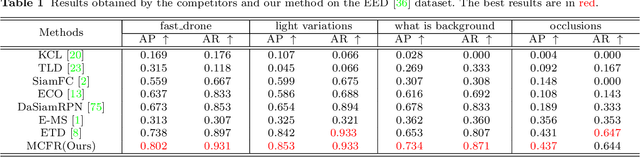
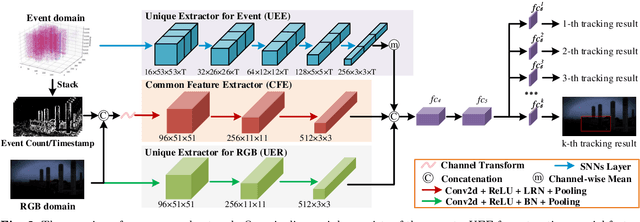
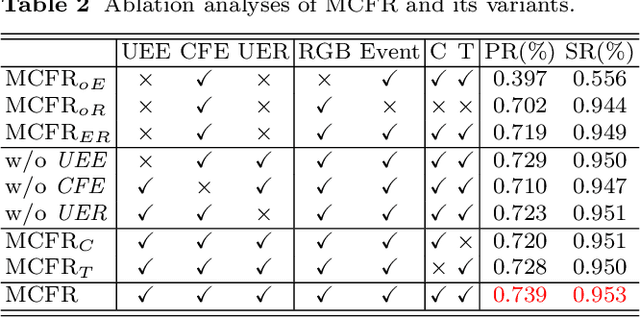
Abstract:Jointly exploiting multiple different yet complementary domain information has been proven to be an effective way to perform robust object tracking. This paper focuses on effectively representing and utilizing complementary features from the frame domain and event domain for boosting object tracking performance in challenge scenarios. Specifically, we propose Common Features Extractor (CFE) to learn potential common representations from the RGB domain and event domain. For learning the unique features of the two domains, we utilize a Unique Extractor for Event (UEE) based on Spiking Neural Networks to extract edge cues in the event domain which may be missed in RGB in some challenging conditions, and a Unique Extractor for RGB (UER) based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks to extract texture and semantic information in RGB domain. Extensive experiments on standard RGB benchmark and real event tracking dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. We show our approach outperforms all compared state-of-the-art tracking algorithms and verify event-based data is a powerful cue for tracking in challenging scenes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge