Yichuan Ding
Hummer: Towards Limited Competitive Preference Dataset
May 21, 2024Abstract:Preference datasets are essential for incorporating human preferences into pre-trained language models, playing a key role in the success of Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback. However, these datasets often demonstrate conflicting alignment objectives, leading to increased vulnerability to jailbreak attacks and challenges in adapting downstream tasks to prioritize specific alignment objectives without negatively impacting others. In this work, we introduce a novel statistical metric, Alignment Dimension Conflict, to quantify the degree of conflict within preference datasets. We then present \texttt{Hummer} and its fine-grained variant, \texttt{Hummer-F}, as innovative pairwise preference datasets with reduced-conflict alignment objectives. \texttt{Hummer} is built based on UltraFeedback and is enhanced by AI feedback from GPT-4, marking as the first preference dataset aimed at reducing the competition between alignment objectives. Furthermore, we develop reward models, HummerRM and HummerRM-F, which employ a hybrid sampling approach to balance diverse alignment objectives effectively. This sampling method positions HummerRM as an ideal model for domain-specific further fine-tuning and reducing vulnerabilities to attacks.
A High-fidelity, Machine-learning Enhanced Queueing Network Simulation Model for Hospital Ultrasound Operations
Apr 12, 2021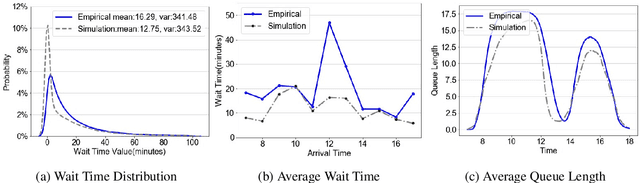

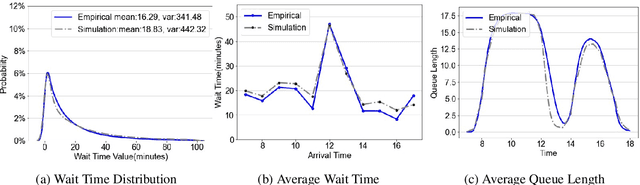
Abstract:We collaborate with a large teaching hospital in Shenzhen, China and build a high-fidelity simulation model for its ultrasound center to predict key performance metrics, including the distributions of queue length, waiting time and sojourn time, with high accuracy. The key challenge to build an accurate simulation model is to understanding the complicated patient routing at the ultrasound center. To address the issue, we propose a novel two-level routing component to the queueing network model. We apply machine learning tools to calibrate the key components of the queueing model from data with enhanced accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge