Yi-Chi Liao
Group Inertial Poser: Multi-Person Pose and Global Translation from Sparse Inertial Sensors and Ultra-Wideband Ranging
Oct 24, 2025Abstract:Tracking human full-body motion using sparse wearable inertial measurement units (IMUs) overcomes the limitations of occlusion and instrumentation of the environment inherent in vision-based approaches. However, purely IMU-based tracking compromises translation estimates and accurate relative positioning between individuals, as inertial cues are inherently self-referential and provide no direct spatial reference for others. In this paper, we present a novel approach for robustly estimating body poses and global translation for multiple individuals by leveraging the distances between sparse wearable sensors - both on each individual and across multiple individuals. Our method Group Inertial Poser estimates these absolute distances between pairs of sensors from ultra-wideband ranging (UWB) and fuses them with inertial observations as input into structured state-space models to integrate temporal motion patterns for precise 3D pose estimation. Our novel two-step optimization further leverages the estimated distances for accurately tracking people's global trajectories through the world. We also introduce GIP-DB, the first IMU+UWB dataset for two-person tracking, which comprises 200 minutes of motion recordings from 14 participants. In our evaluation, Group Inertial Poser outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods in accuracy and robustness across synthetic and real-world data, showing the promise of IMU+UWB-based multi-human motion capture in the wild. Code, models, dataset: https://github.com/eth-siplab/GroupInertialPoser
3HANDS Dataset: Learning from Humans for Generating Naturalistic Handovers with Supernumerary Robotic Limbs
Mar 06, 2025



Abstract:Supernumerary robotic limbs (SRLs) are robotic structures integrated closely with the user's body, which augment human physical capabilities and necessitate seamless, naturalistic human-machine interaction. For effective assistance in physical tasks, enabling SRLs to hand over objects to humans is crucial. Yet, designing heuristic-based policies for robots is time-consuming, difficult to generalize across tasks, and results in less human-like motion. When trained with proper datasets, generative models are powerful alternatives for creating naturalistic handover motions. We introduce 3HANDS, a novel dataset of object handover interactions between a participant performing a daily activity and another participant enacting a hip-mounted SRL in a naturalistic manner. 3HANDS captures the unique characteristics of SRL interactions: operating in intimate personal space with asymmetric object origins, implicit motion synchronization, and the user's engagement in a primary task during the handover. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our dataset, we present three models: one that generates naturalistic handover trajectories, another that determines the appropriate handover endpoints, and a third that predicts the moment to initiate a handover. In a user study (N=10), we compare the handover interaction performed with our method compared to a baseline. The findings show that our method was perceived as significantly more natural, less physically demanding, and more comfortable.
Investigating Positive and Negative Qualities of Human-in-the-Loop Optimization for Designing Interaction Techniques
Apr 15, 2022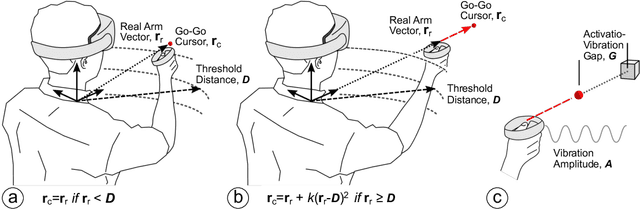

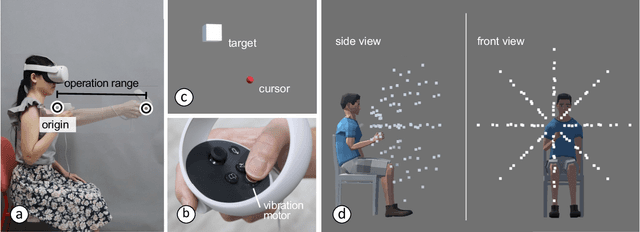
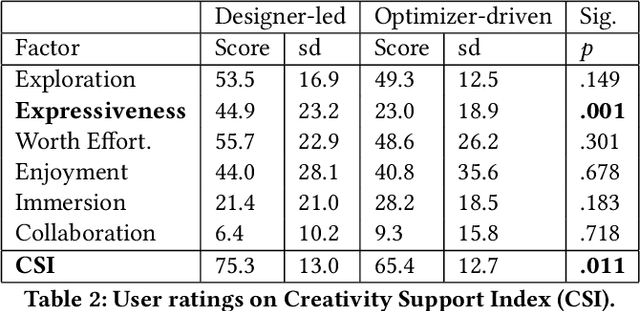
Abstract:Designers reportedly struggle with design optimization tasks where they are asked to find a combination of design parameters that maximizes a given set of objectives. In HCI, design optimization problems are often exceedingly complex, involving multiple objectives and expensive empirical evaluations. Model-based computational design algorithms assist designers by generating design examples during design, however they assume a model of the interaction domain. Black box methods for assistance, on the other hand, can work with any design problem. However, virtually all empirical studies of this human-in-the-loop approach have been carried out by either researchers or end-users. The question stands out if such methods can help designers in realistic tasks. In this paper, we study Bayesian optimization as an algorithmic method to guide the design optimization process. It operates by proposing to a designer which design candidate to try next, given previous observations. We report observations from a comparative study with 40 novice designers who were tasked to optimize a complex 3D touch interaction technique. The optimizer helped designers explore larger proportions of the design space and arrive at a better solution, however they reported lower agency and expressiveness. Designers guided by an optimizer reported lower mental effort but also felt less creative and less in charge of the progress. We conclude that human-in-the-loop optimization can support novice designers in cases where agency is not critical.
Rediscovering Affordance: A Reinforcement Learning Perspective
Jan 07, 2022
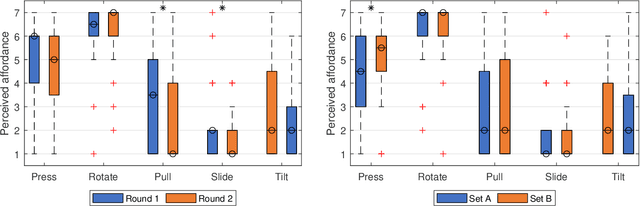
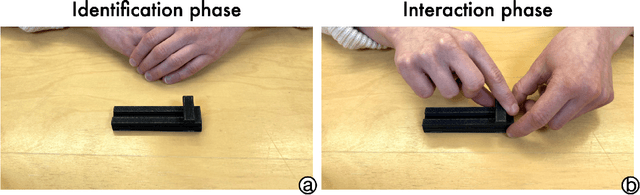
Abstract:Affordance refers to the perception of possible actions allowed by an object. Despite its relevance to human-computer interaction, no existing theory explains the mechanisms that underpin affordance-formation; that is, how affordances are discovered and adapted via interaction. We propose an integrative theory of affordance-formation based on the theory of reinforcement learning in cognitive sciences. The key assumption is that users learn to associate promising motor actions to percepts via experience when reinforcement signals (success/failure) are present. They also learn to categorize actions (e.g., "rotating" a dial), giving them the ability to name and reason about affordance. Upon encountering novel widgets, their ability to generalize these actions determines their ability to perceive affordances. We implement this theory in a virtual robot model, which demonstrates human-like adaptation of affordance in interactive widgets tasks. While its predictions align with trends in human data, humans are able to adapt affordances faster, suggesting the existence of additional mechanisms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge