Aditya Acharya
Classifiers in High Dimensional Hilbert Metrics
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Classifying points in high dimensional spaces is a fundamental geometric problem in machine learning. In this paper, we address classifying points in the $d$-dimensional Hilbert polygonal metric. The Hilbert metric is a generalization of the Cayley-Klein hyperbolic distance to arbitrary convex bodies and has a diverse range of applications in machine learning and convex geometry. We first present an efficient LP-based algorithm in the metric for the large-margin SVM problem. Our algorithm runs in time polynomial to the number of points, bounding facets, and dimension. This is a significant improvement on previous works, which either provide no theoretical guarantees on running time, or suffer from exponential runtime. We also consider the closely related Funk metric. We also present efficient algorithms for the soft-margin SVM problem and for nearest neighbor-based classification in the Hilbert metric.
Rediscovering Affordance: A Reinforcement Learning Perspective
Jan 07, 2022
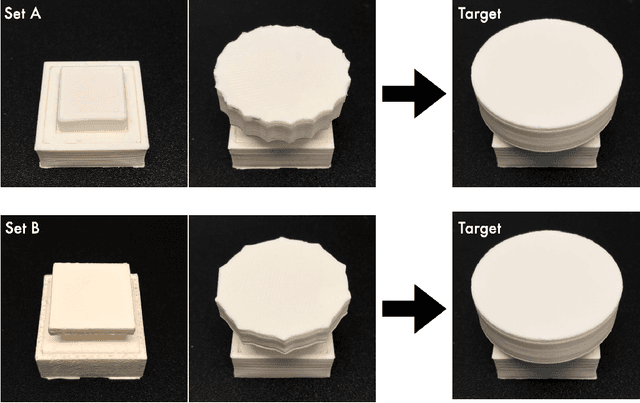
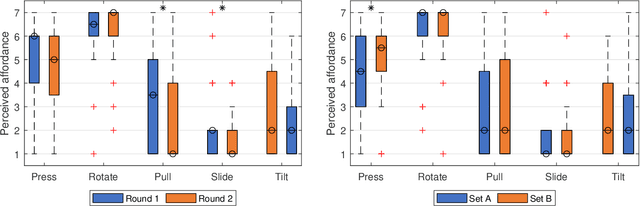
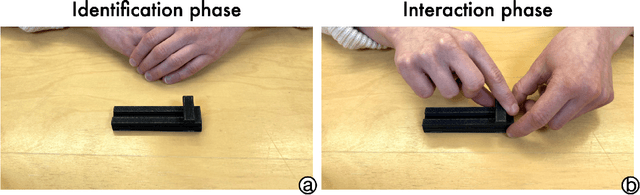
Abstract:Affordance refers to the perception of possible actions allowed by an object. Despite its relevance to human-computer interaction, no existing theory explains the mechanisms that underpin affordance-formation; that is, how affordances are discovered and adapted via interaction. We propose an integrative theory of affordance-formation based on the theory of reinforcement learning in cognitive sciences. The key assumption is that users learn to associate promising motor actions to percepts via experience when reinforcement signals (success/failure) are present. They also learn to categorize actions (e.g., "rotating" a dial), giving them the ability to name and reason about affordance. Upon encountering novel widgets, their ability to generalize these actions determines their ability to perceive affordances. We implement this theory in a virtual robot model, which demonstrates human-like adaptation of affordance in interactive widgets tasks. While its predictions align with trends in human data, humans are able to adapt affordances faster, suggesting the existence of additional mechanisms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge