Martin Schmitz
3HANDS Dataset: Learning from Humans for Generating Naturalistic Handovers with Supernumerary Robotic Limbs
Mar 06, 2025



Abstract:Supernumerary robotic limbs (SRLs) are robotic structures integrated closely with the user's body, which augment human physical capabilities and necessitate seamless, naturalistic human-machine interaction. For effective assistance in physical tasks, enabling SRLs to hand over objects to humans is crucial. Yet, designing heuristic-based policies for robots is time-consuming, difficult to generalize across tasks, and results in less human-like motion. When trained with proper datasets, generative models are powerful alternatives for creating naturalistic handover motions. We introduce 3HANDS, a novel dataset of object handover interactions between a participant performing a daily activity and another participant enacting a hip-mounted SRL in a naturalistic manner. 3HANDS captures the unique characteristics of SRL interactions: operating in intimate personal space with asymmetric object origins, implicit motion synchronization, and the user's engagement in a primary task during the handover. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our dataset, we present three models: one that generates naturalistic handover trajectories, another that determines the appropriate handover endpoints, and a third that predicts the moment to initiate a handover. In a user study (N=10), we compare the handover interaction performed with our method compared to a baseline. The findings show that our method was perceived as significantly more natural, less physically demanding, and more comfortable.
Learning to Untangle Genome Assembly with Graph Convolutional Networks
Jun 01, 2022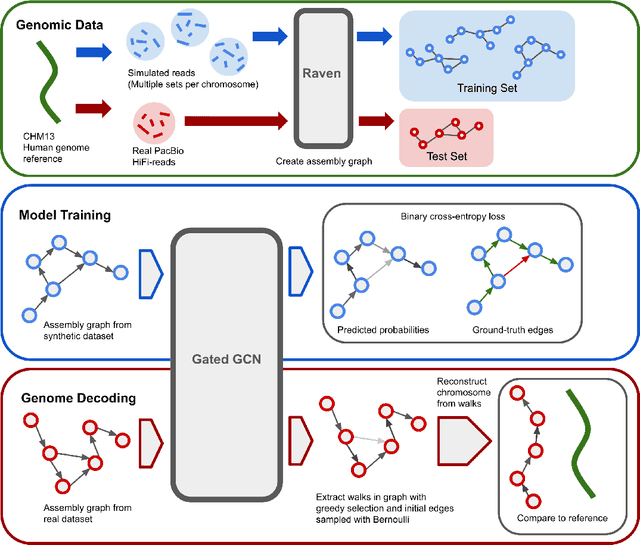
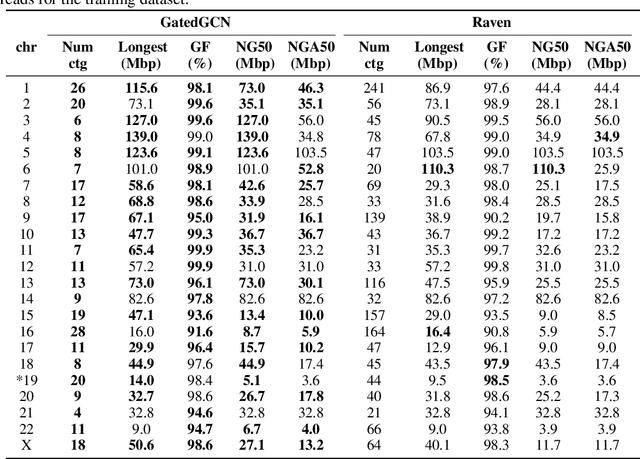
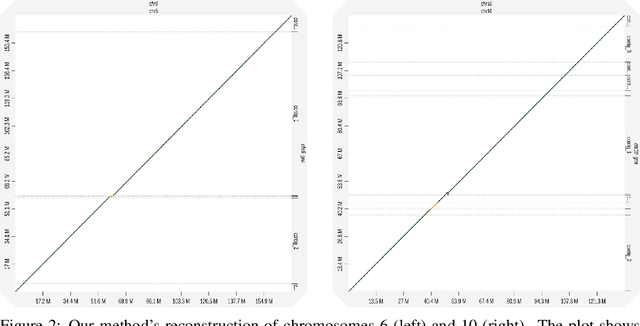
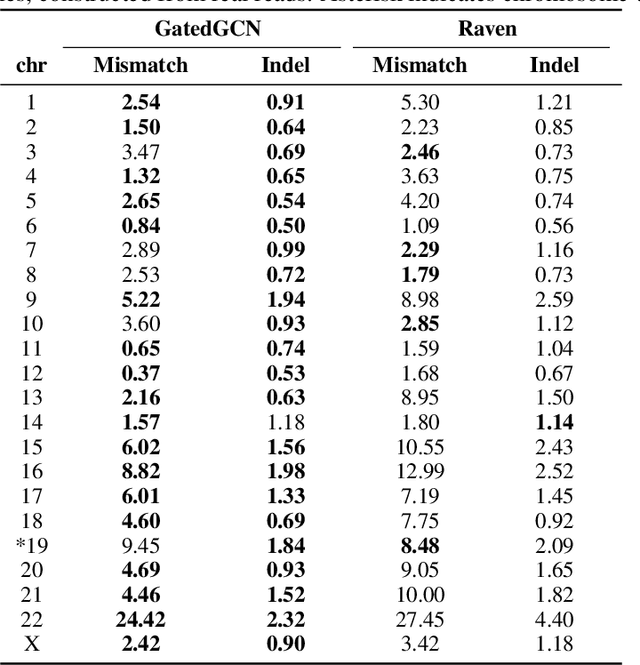
Abstract:A quest to determine the complete sequence of a human DNA from telomere to telomere started three decades ago and was finally completed in 2021. This accomplishment was a result of a tremendous effort of numerous experts who engineered various tools and performed laborious manual inspection to achieve the first gapless genome sequence. However, such method can hardly be used as a general approach to assemble different genomes, especially when the assembly speed is critical given the large amount of data. In this work, we explore a different approach to the central part of the genome assembly task that consists of untangling a large assembly graph from which a genomic sequence needs to be reconstructed. Our main motivation is to reduce human-engineered heuristics and use deep learning to develop more generalizable reconstruction techniques. Precisely, we introduce a new learning framework to train a graph convolutional network to resolve assembly graphs by finding a correct path through them. The training is supervised with a dataset generated from the resolved CHM13 human sequence and tested on assembly graphs built using real human PacBio HiFi reads. Experimental results show that a model, trained on simulated graphs generated solely from a single chromosome, is able to remarkably resolve all other chromosomes. Moreover, the model outperforms hand-crafted heuristics from a state-of-the-art \textit{de novo} assembler on the same graphs. Reconstructed chromosomes with graph networks are more accurate on nucleotide level, report lower number of contigs, higher genome reconstructed fraction and NG50/NGA50 assessment metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge