Yera Choi
BTS: Bridging Text and Sound Modalities for Metadata-Aided Respiratory Sound Classification
Jun 10, 2024Abstract:Respiratory sound classification (RSC) is challenging due to varied acoustic signatures, primarily influenced by patient demographics and recording environments. To address this issue, we introduce a text-audio multimodal model that utilizes metadata of respiratory sounds, which provides useful complementary information for RSC. Specifically, we fine-tune a pretrained text-audio multimodal model using free-text descriptions derived from the sound samples' metadata which includes the gender and age of patients, type of recording devices, and recording location on the patient's body. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the ICBHI dataset, surpassing the previous best result by a notable margin of 1.17%. This result validates the effectiveness of leveraging metadata and respiratory sound samples in enhancing RSC performance. Additionally, we investigate the model performance in the case where metadata is partially unavailable, which may occur in real-world clinical setting.
HyperCLOVA X Technical Report
Apr 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce HyperCLOVA X, a family of large language models (LLMs) tailored to the Korean language and culture, along with competitive capabilities in English, math, and coding. HyperCLOVA X was trained on a balanced mix of Korean, English, and code data, followed by instruction-tuning with high-quality human-annotated datasets while abiding by strict safety guidelines reflecting our commitment to responsible AI. The model is evaluated across various benchmarks, including comprehensive reasoning, knowledge, commonsense, factuality, coding, math, chatting, instruction-following, and harmlessness, in both Korean and English. HyperCLOVA X exhibits strong reasoning capabilities in Korean backed by a deep understanding of the language and cultural nuances. Further analysis of the inherent bilingual nature and its extension to multilingualism highlights the model's cross-lingual proficiency and strong generalization ability to untargeted languages, including machine translation between several language pairs and cross-lingual inference tasks. We believe that HyperCLOVA X can provide helpful guidance for regions or countries in developing their sovereign LLMs.
MED-SE: Medical Entity Definition-based Sentence Embedding
Dec 09, 2022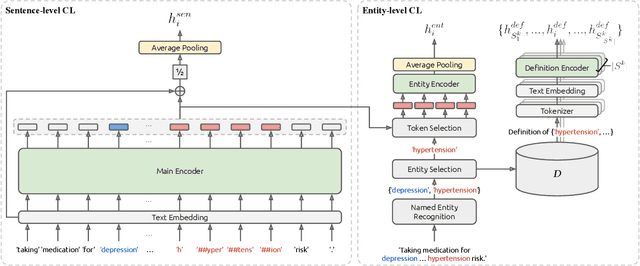
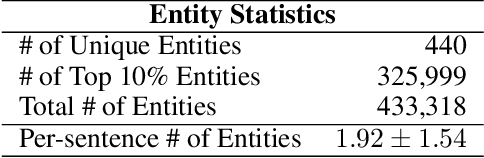
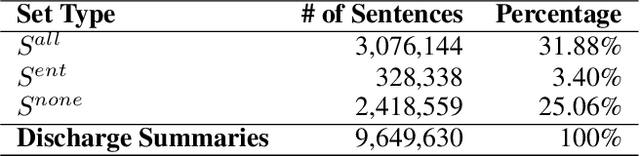
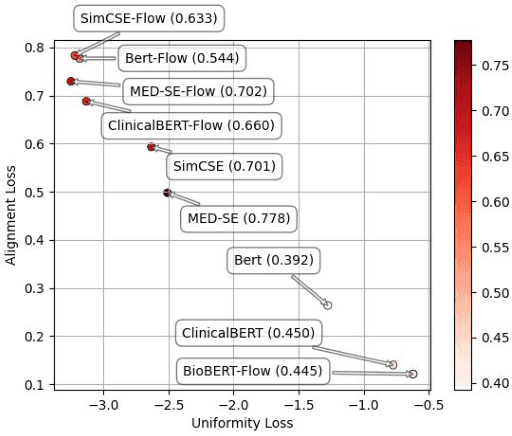
Abstract:We propose Medical Entity Definition-based Sentence Embedding (MED-SE), a novel unsupervised contrastive learning framework designed for clinical texts, which exploits the definitions of medical entities. To this end, we conduct an extensive analysis of multiple sentence embedding techniques in clinical semantic textual similarity (STS) settings. In the entity-centric setting that we have designed, MED-SE achieves significantly better performance, while the existing unsupervised methods including SimCSE show degraded performance. Our experiments elucidate the inherent discrepancies between the general- and clinical-domain texts, and suggest that entity-centric contrastive approaches may help bridge this gap and lead to a better representation of clinical sentences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge