Yasutaka Nishimura
Zero-shot Persuasive Chatbots with LLM-Generated Strategies and Information Retrieval
Jul 04, 2024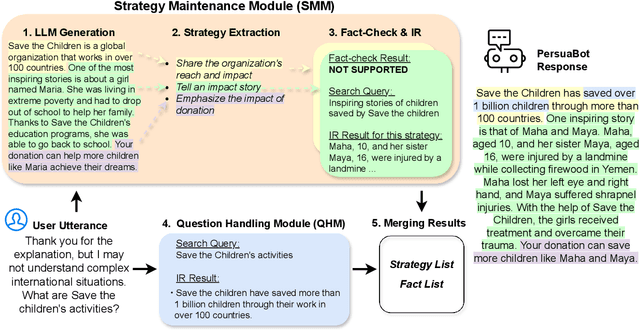
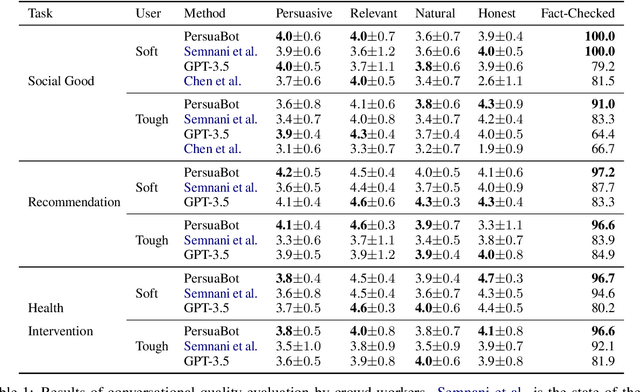
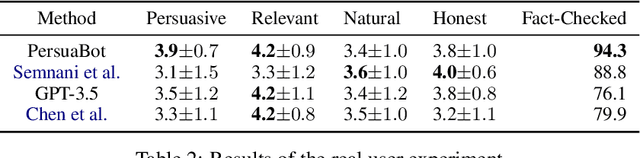
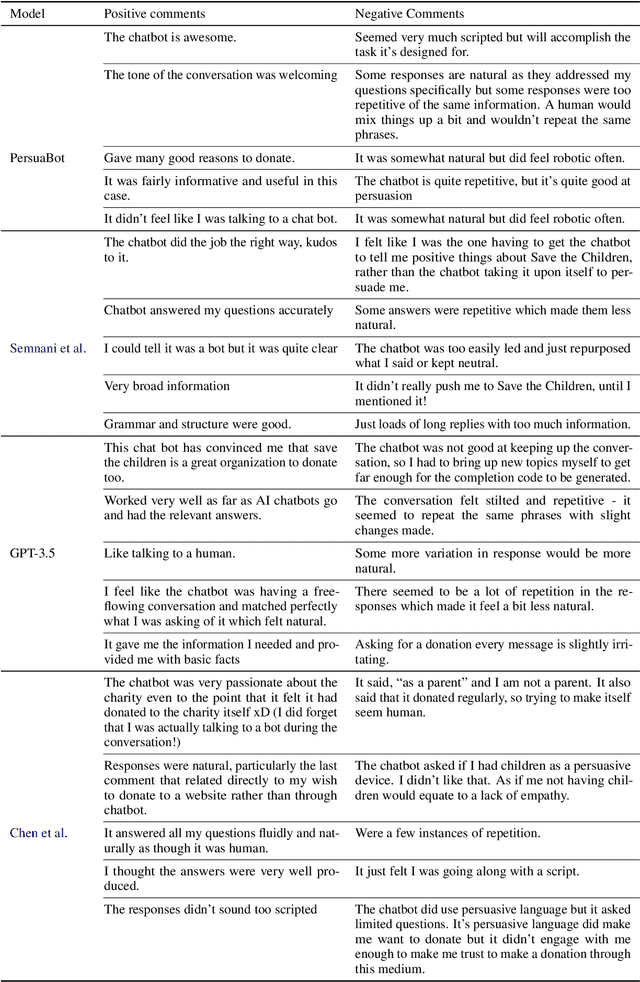
Abstract:Persuasion plays a pivotal role in a wide range of applications from health intervention to the promotion of social good. Persuasive chatbots can accelerate the positive effects of persuasion in such applications. Existing methods rely on fine-tuning persuasive chatbots with task-specific training data which is costly, if not infeasible, to collect. To address this issue, we propose a method to leverage the generalizability and inherent persuasive abilities of large language models (LLMs) in creating effective and truthful persuasive chatbot for any given domain in a zero-shot manner. Unlike previous studies which used pre-defined persuasion strategies, our method first uses an LLM to generate responses, then extracts the strategies used on the fly, and replaces any unsubstantiated claims in the response with retrieved facts supporting the strategies. We applied our chatbot, PersuaBot, to three significantly different domains needing persuasion skills: donation solicitation, recommendations, and health intervention. Our experiments on simulated and human conversations show that our zero-shot approach is more persuasive than prior work, while achieving factual accuracy surpassing state-of-the-art knowledge-oriented chatbots. Our study demonstrated that when persuasive chatbots are employed responsibly for social good, it is an enabler of positive individual and social change.
Explainable Activity Recognition for Smart Home Systems
May 20, 2021



Abstract:Smart home environments are designed to provide services that help improve the quality of life for the occupant via a variety of sensors and actuators installed throughout the space. Many automated actions taken by a smart home are governed by the output of an underlying activity recognition system. However, activity recognition systems may not be perfectly accurate and therefore inconsistencies in smart home operations can lead a user to wonder "why did the smart home do that?" In this work, we build on insights from Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) techniques to contribute computational methods for explainable activity recognition. Specifically, we generate explanations for smart home activity recognition systems that explain what about an activity led to the given classification. To do so, we introduce four computational techniques for generating natural language explanations of smart home data and compare their effectiveness at generating meaningful explanations. Through a study with everyday users, we evaluate user preferences towards the four explanation types. Our results show that the leading approach, SHAP, has a 92% success rate in generating accurate explanations. Moreover, 84% of sampled scenarios users preferred natural language explanations over a simple activity label, underscoring the need for explainable activity recognition systems. Finally, we show that explanations generated by some XAI methods can lead users to lose confidence in the accuracy of the underlying activity recognition model, while others lead users to gain confidence. Taking all studied factors into consideration, we make a recommendation regarding which existing XAI method leads to the best performance in the domain of smart home automation, and discuss a range of topics for future work in this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge