Yash Mahajan
"Santu"
The Pursuit of Empathy: Evaluating Small Language Models for PTSD Dialogue Support
May 21, 2025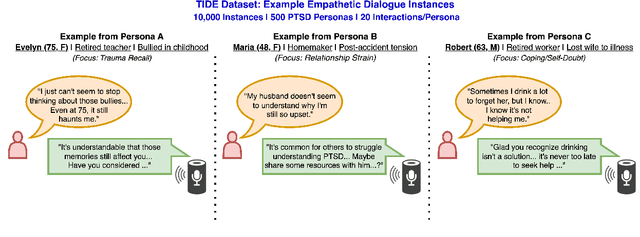
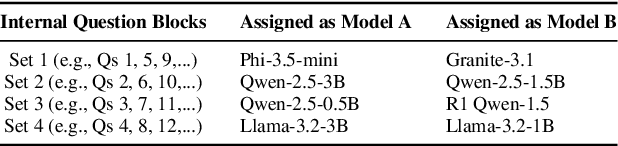
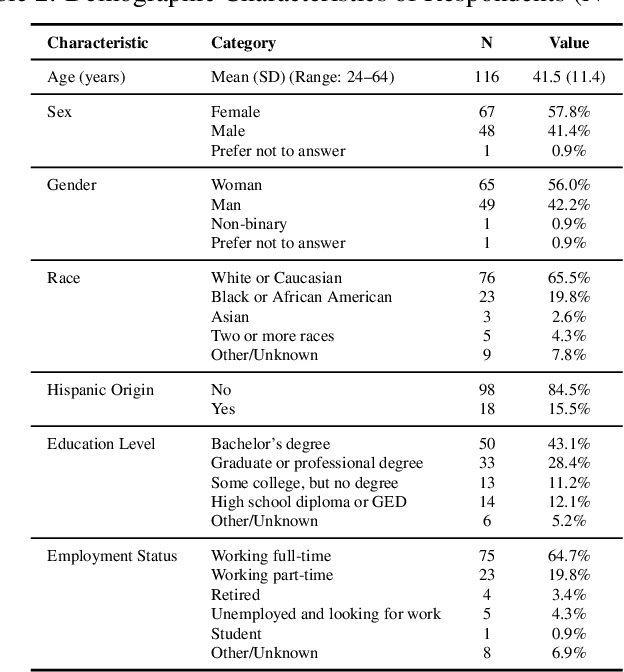
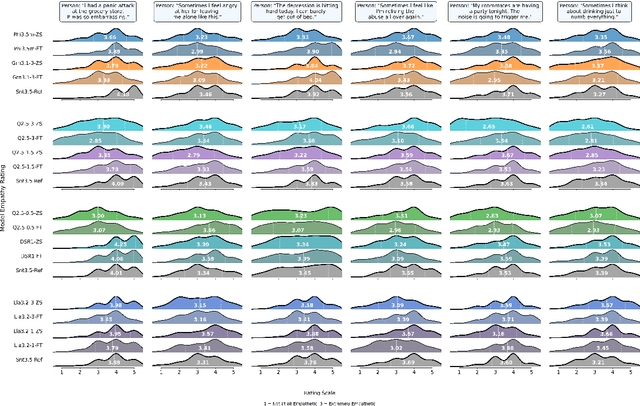
Abstract:Can small language models with 0.5B to 5B parameters meaningfully engage in trauma-informed, empathetic dialogue for individuals with PTSD? We address this question by introducing TIDE, a dataset of 10,000 two-turn dialogues spanning 500 diverse PTSD client personas and grounded in a three-factor empathy model: emotion recognition, distress normalization, and supportive reflection. All scenarios and reference responses were reviewed for realism and trauma sensitivity by a clinical psychologist specializing in PTSD. We evaluate eight small language models before and after fine-tuning, comparing their outputs to a frontier model (Claude Sonnet 3.5). Our IRB-approved human evaluation and automatic metrics show that fine-tuning generally improves perceived empathy, but gains are highly scenario- and user-dependent, with smaller models facing an empathy ceiling. Demographic analysis shows older adults value distress validation and graduate-educated users prefer nuanced replies, while gender effects are minimal. We highlight the limitations of automatic metrics and the need for context- and user-aware system design. Our findings, along with the planned release of TIDE, provide a foundation for building safe, resource-efficient, and ethically sound empathetic AI to supplement, not replace, clinical mental health care.
Revisiting Word Embeddings in the LLM Era
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently shown remarkable advancement in various NLP tasks. As such, a popular trend has emerged lately where NLP researchers extract word/sentence/document embeddings from these large decoder-only models and use them for various inference tasks with promising results. However, it is still unclear whether the performance improvement of LLM-induced embeddings is merely because of scale or whether underlying embeddings they produce significantly differ from classical encoding models like Word2Vec, GloVe, Sentence-BERT (SBERT) or Universal Sentence Encoder (USE). This is the central question we investigate in the paper by systematically comparing classical decontextualized and contextualized word embeddings with the same for LLM-induced embeddings. Our results show that LLMs cluster semantically related words more tightly and perform better on analogy tasks in decontextualized settings. However, in contextualized settings, classical models like SimCSE often outperform LLMs in sentence-level similarity assessment tasks, highlighting their continued relevance for fine-grained semantics.
Prompting LLMs to Compose Meta-Review Drafts from Peer-Review Narratives of Scholarly Manuscripts
Feb 23, 2024Abstract:One of the most important yet onerous tasks in the academic peer-reviewing process is composing meta-reviews, which involves understanding the core contributions, strengths, and weaknesses of a scholarly manuscript based on peer-review narratives from multiple experts and then summarizing those multiple experts' perspectives into a concise holistic overview. Given the latest major developments in generative AI, especially Large Language Models (LLMs), it is very compelling to rigorously study the utility of LLMs in generating such meta-reviews in an academic peer-review setting. In this paper, we perform a case study with three popular LLMs, i.e., GPT-3.5, LLaMA2, and PaLM2, to automatically generate meta-reviews by prompting them with different types/levels of prompts based on the recently proposed TELeR taxonomy. Finally, we perform a detailed qualitative study of the meta-reviews generated by the LLMs and summarize our findings and recommendations for prompting LLMs for this complex task.
The Daunting Dilemma with Sentence Encoders: Success on Standard Benchmarks, Failure in Capturing Basic Semantic Properties
Sep 07, 2023
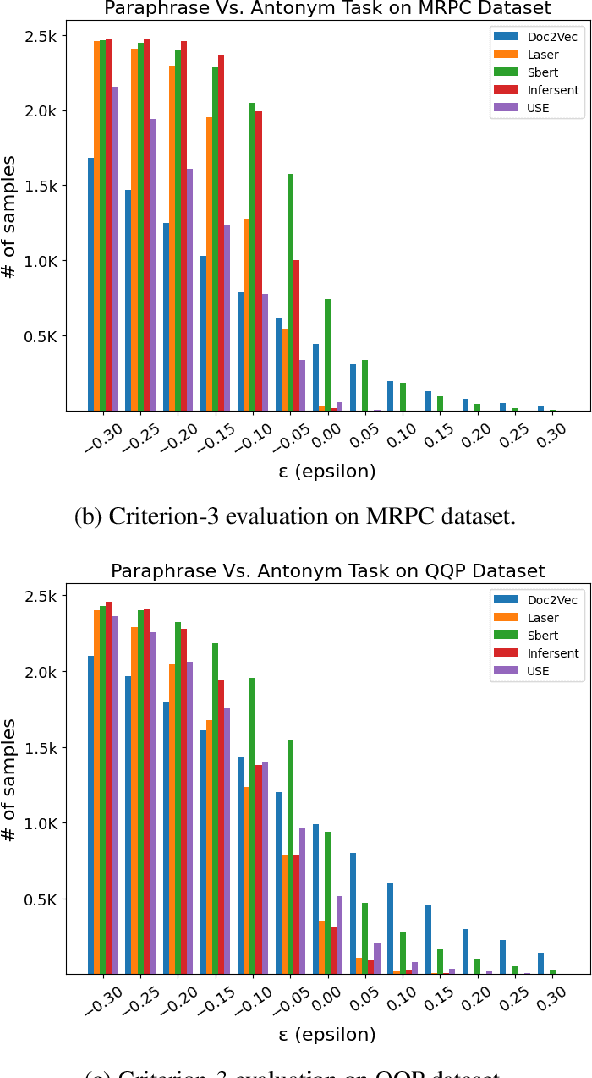
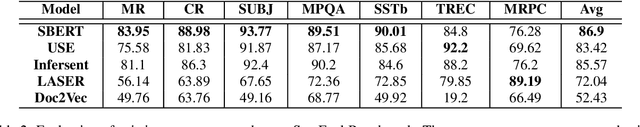
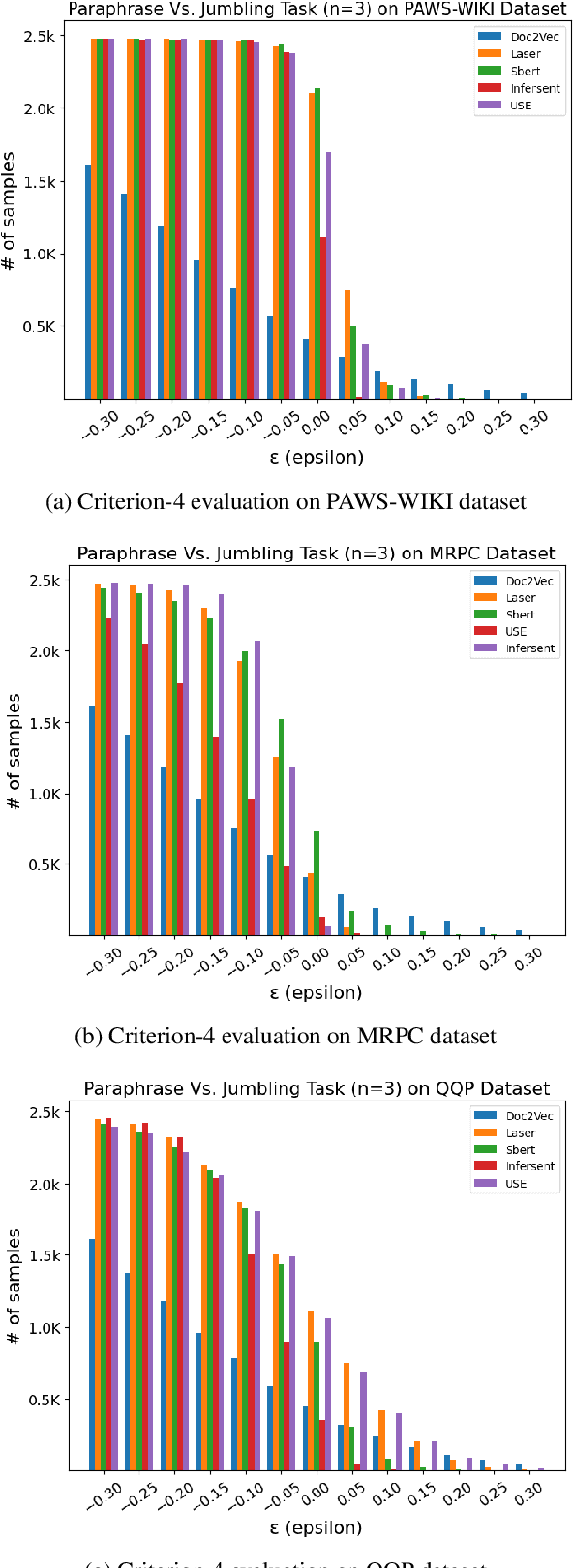
Abstract:In this paper, we adopted a retrospective approach to examine and compare five existing popular sentence encoders, i.e., Sentence-BERT, Universal Sentence Encoder (USE), LASER, InferSent, and Doc2vec, in terms of their performance on downstream tasks versus their capability to capture basic semantic properties. Initially, we evaluated all five sentence encoders on the popular SentEval benchmark and found that multiple sentence encoders perform quite well on a variety of popular downstream tasks. However, being unable to find a single winner in all cases, we designed further experiments to gain a deeper understanding of their behavior. Specifically, we proposed four semantic evaluation criteria, i.e., Paraphrasing, Synonym Replacement, Antonym Replacement, and Sentence Jumbling, and evaluated the same five sentence encoders using these criteria. We found that the Sentence-Bert and USE models pass the paraphrasing criterion, with SBERT being the superior between the two. LASER dominates in the case of the synonym replacement criterion. Interestingly, all the sentence encoders failed the antonym replacement and jumbling criteria. These results suggest that although these popular sentence encoders perform quite well on the SentEval benchmark, they still struggle to capture some basic semantic properties, thus, posing a daunting dilemma in NLP research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge