Yaroslav Kholodov
SCOPE: Smooth Convex Optimization for Planned Evolution of Deformable Linear Objects
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:We present SCOPE, a fast and efficient framework for modeling and manipulating deformable linear objects (DLOs). Unlike conventional energy-based approaches, SCOPE leverages convex approximations to significantly reduce computational cost while maintaining smooth and physically plausible deformations. This trade-off between speed and accuracy makes the method particularly suitable for applications requiring real-time or near-real-time response. The effectiveness of the proposed framework is demonstrated through comprehensive simulation experiments, highlighting its ability to generate smooth shape trajectories under geometric and length constraints.
Quantum-Inspired Episode Selection for Monte Carlo Reinforcement Learning via QUBO Optimization
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Monte Carlo (MC) reinforcement learning suffers from high sample complexity, especially in environments with sparse rewards, large state spaces, and correlated trajectories. We address these limitations by reformulating episode selection as a Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization (QUBO) problem and solving it with quantum-inspired samplers. Our method, MC+QUBO, integrates a combinatorial filtering step into standard MC policy evaluation: from each batch of trajectories, we select a subset that maximizes cumulative reward while promoting state-space coverage. This selection is encoded as a QUBO, where linear terms favor high-reward episodes and quadratic terms penalize redundancy. We explore both Simulated Quantum Annealing (SQA) and Simulated Bifurcation (SB) as black-box solvers within this framework. Experiments in a finite-horizon GridWorld demonstrate that MC+QUBO outperforms vanilla MC in convergence speed and final policy quality, highlighting the potential of quantum-inspired optimization as a decision-making subroutine in reinforcement learning.
Adaptive Backdoor Attacks with Reasonable Constraints on Graph Neural Networks
Mar 12, 2025
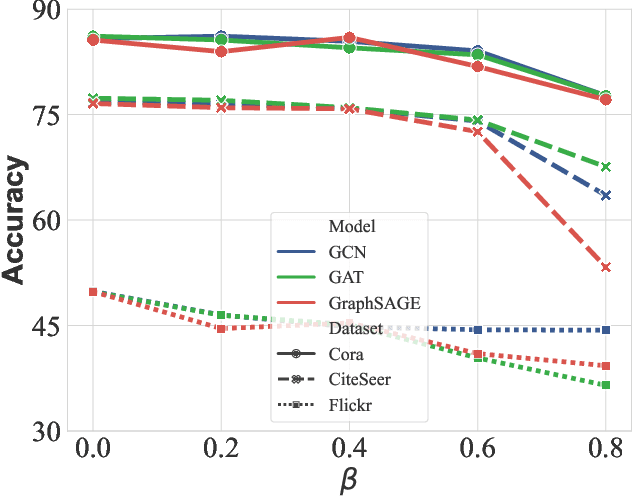
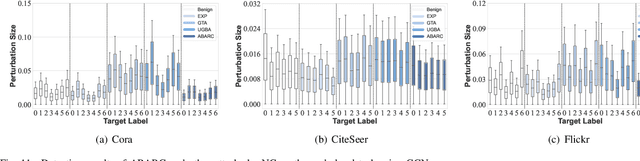
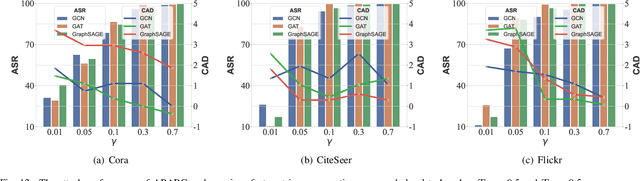
Abstract:Recent studies show that graph neural networks (GNNs) are vulnerable to backdoor attacks. Existing backdoor attacks against GNNs use fixed-pattern triggers and lack reasonable trigger constraints, overlooking individual graph characteristics and rendering insufficient evasiveness. To tackle the above issues, we propose ABARC, the first Adaptive Backdoor Attack with Reasonable Constraints, applying to both graph-level and node-level tasks in GNNs. For graph-level tasks, we propose a subgraph backdoor attack independent of the graph's topology. It dynamically selects trigger nodes for each target graph and modifies node features with constraints based on graph similarity, feature range, and feature type. For node-level tasks, our attack begins with an analysis of node features, followed by selecting and modifying trigger features, which are then constrained by node similarity, feature range, and feature type. Furthermore, an adaptive edge-pruning mechanism is designed to reduce the impact of neighbors on target nodes, ensuring a high attack success rate (ASR). Experimental results show that even with reasonable constraints for attack evasiveness, our attack achieves a high ASR while incurring a marginal clean accuracy drop (CAD). When combined with the state-of-the-art defense randomized smoothing (RS) method, our attack maintains an ASR over 94%, surpassing existing attacks by more than 7%.
Local Methods with Adaptivity via Scaling
Jun 02, 2024

Abstract:The rapid development of machine learning and deep learning has introduced increasingly complex optimization challenges that must be addressed. Indeed, training modern, advanced models has become difficult to implement without leveraging multiple computing nodes in a distributed environment. Distributed optimization is also fundamental to emerging fields such as federated learning. Specifically, there is a need to organize the training process to minimize the time lost due to communication. A widely used and extensively researched technique to mitigate the communication bottleneck involves performing local training before communication. This approach is the focus of our paper. Concurrently, adaptive methods that incorporate scaling, notably led by Adam, have gained significant popularity in recent years. Therefore, this paper aims to merge the local training technique with the adaptive approach to develop efficient distributed learning methods. We consider the classical Local SGD method and enhance it with a scaling feature. A crucial aspect is that the scaling is described generically, allowing us to analyze various approaches, including Adam, RMSProp, and OASIS, in a unified manner. In addition to theoretical analysis, we validate the performance of our methods in practice by training a neural network.
Activations and Gradients Compression for Model-Parallel Training
Jan 15, 2024Abstract:Large neural networks require enormous computational clusters of machines. Model-parallel training, when the model architecture is partitioned sequentially between workers, is a popular approach for training modern models. Information compression can be applied to decrease workers communication time, as it is often a bottleneck in such systems. This work explores how simultaneous compression of activations and gradients in model-parallel distributed training setup affects convergence. We analyze compression methods such as quantization and TopK compression, and also experiment with error compensation techniques. Moreover, we employ TopK with AQ-SGD per-batch error feedback approach. We conduct experiments on image classification and language model fine-tuning tasks. Our findings demonstrate that gradients require milder compression rates than activations. We observe that $K=10\%$ is the lowest TopK compression level, which does not harm model convergence severely. Experiments also show that models trained with TopK perform well only when compression is also applied during inference. We find that error feedback techniques do not improve model-parallel training compared to plain compression, but allow model inference without compression with almost no quality drop. Finally, when applied with the AQ-SGD approach, TopK stronger than with $ K=30\%$ worsens model performance significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge