Aram Avetisyan
Accelerated Methods with Complexity Separation Under Data Similarity for Federated Learning Problems
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Heterogeneity within data distribution poses a challenge in many modern federated learning tasks. We formalize it as an optimization problem involving a computationally heavy composite under data similarity. By employing different sets of assumptions, we present several approaches to develop communication-efficient methods. An optimal algorithm is proposed for the convex case. The constructed theory is validated through a series of experiments across various problems.
Multi-Track Multimodal Learning on iMiGUE: Micro-Gesture and Emotion Recognition
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Micro-gesture recognition and behavior-based emotion prediction are both highly challenging tasks that require modeling subtle, fine-grained human behaviors, primarily leveraging video and skeletal pose data. In this work, we present two multimodal frameworks designed to tackle both problems on the iMiGUE dataset. For micro-gesture classification, we explore the complementary strengths of RGB and 3D pose-based representations to capture nuanced spatio-temporal patterns. To comprehensively represent gestures, video, and skeletal embeddings are extracted using MViTv2-S and 2s-AGCN, respectively. Then, they are integrated through a Cross-Modal Token Fusion module to combine spatial and pose information. For emotion recognition, our framework extends to behavior-based emotion prediction, a binary classification task identifying emotional states based on visual cues. We leverage facial and contextual embeddings extracted using SwinFace and MViTv2-S models and fuse them through an InterFusion module designed to capture emotional expressions and body gestures. Experiments conducted on the iMiGUE dataset, within the scope of the MiGA 2025 Challenge, demonstrate the robust performance and accuracy of our method in the behavior-based emotion prediction task, where our approach secured 2nd place.
Trial and Trust: Addressing Byzantine Attacks with Comprehensive Defense Strategy
May 12, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in machine learning have improved performance while also increasing computational demands. While federated and distributed setups address these issues, their structure is vulnerable to malicious influences. In this paper, we address a specific threat, Byzantine attacks, where compromised clients inject adversarial updates to derail global convergence. We combine the trust scores concept with trial function methodology to dynamically filter outliers. Our methods address the critical limitations of previous approaches, allowing functionality even when Byzantine nodes are in the majority. Moreover, our algorithms adapt to widely used scaled methods like Adam and RMSProp, as well as practical scenarios, including local training and partial participation. We validate the robustness of our methods by conducting extensive experiments on both synthetic and real ECG data collected from medical institutions. Furthermore, we provide a broad theoretical analysis of our algorithms and their extensions to aforementioned practical setups. The convergence guarantees of our methods are comparable to those of classical algorithms developed without Byzantine interference.
SSSD-ECG-nle: New Label Embeddings with Structured State-Space Models for ECG generation
Jul 15, 2024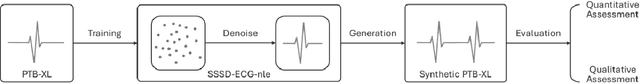
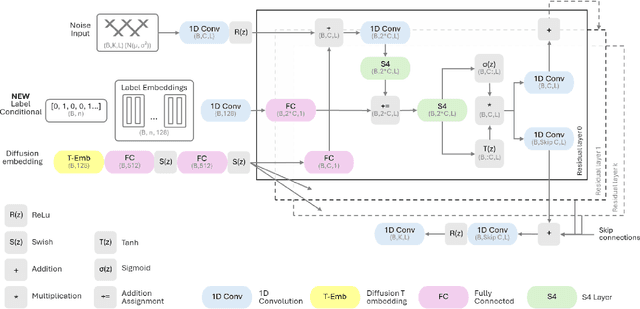
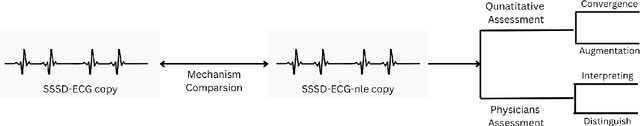
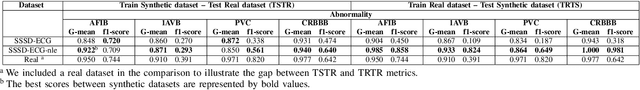
Abstract:An electrocardiogram (ECG) is vital for identifying cardiac diseases, offering crucial insights for diagnosing heart conditions and informing potentially life-saving treatments. However, like other types of medical data, ECGs are subject to privacy concerns when distributed and analyzed. Diffusion models have made significant progress in recent years, creating the possibility for synthesizing data comparable to the real one and allowing their widespread adoption without privacy concerns. In this paper, we use diffusion models with structured state spaces for generating digital 10-second 12-lead ECG signals. We propose the SSSD-ECG-nle architecture based on SSSD-ECG with a modified conditioning mechanism and demonstrate its efficiency on downstream tasks. We conduct quantitative and qualitative evaluations, including analyzing convergence speed, the impact of adding positive samples, and assessment with physicians' expert knowledge. Finally, we share the results of physician evaluations and also make synthetic data available to ensure the reproducibility of the experiments described.
Self-Trained Model for ECG Complex Delineation
Jun 04, 2024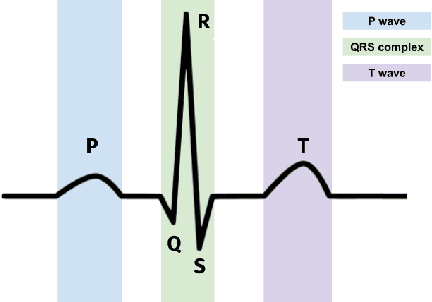
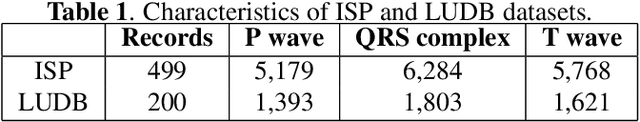
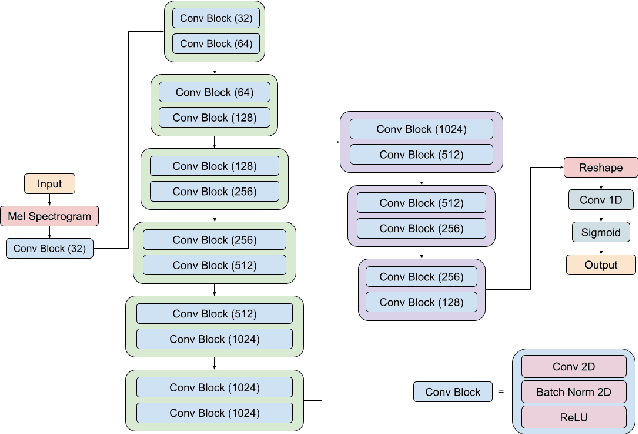
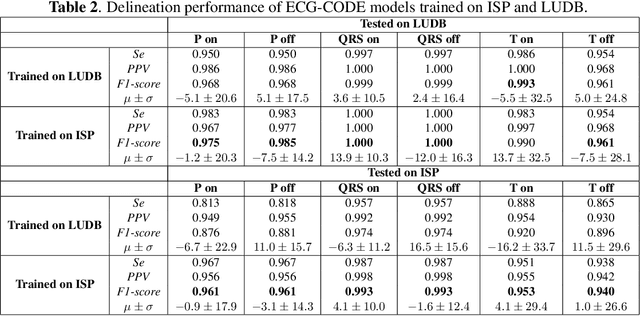
Abstract:Electrocardiogram (ECG) delineation plays a crucial role in assisting cardiologists with accurate diagnoses. Prior research studies have explored various methods, including the application of deep learning techniques, to achieve precise delineation. However, existing approaches face limitations primarily related to dataset size and robustness. In this paper, we introduce a dataset for ECG delineation and propose a novel self-trained method aimed at leveraging a vast amount of unlabeled ECG data. Our approach involves the pseudolabeling of unlabeled data using a neural network trained on our dataset. Subsequently, we train the model on the newly labeled samples to enhance the quality of delineation. We conduct experiments demonstrating that our dataset is a valuable resource for training robust models and that our proposed self-trained method improves the prediction quality of ECG delineation.
Local Methods with Adaptivity via Scaling
Jun 02, 2024

Abstract:The rapid development of machine learning and deep learning has introduced increasingly complex optimization challenges that must be addressed. Indeed, training modern, advanced models has become difficult to implement without leveraging multiple computing nodes in a distributed environment. Distributed optimization is also fundamental to emerging fields such as federated learning. Specifically, there is a need to organize the training process to minimize the time lost due to communication. A widely used and extensively researched technique to mitigate the communication bottleneck involves performing local training before communication. This approach is the focus of our paper. Concurrently, adaptive methods that incorporate scaling, notably led by Adam, have gained significant popularity in recent years. Therefore, this paper aims to merge the local training technique with the adaptive approach to develop efficient distributed learning methods. We consider the classical Local SGD method and enhance it with a scaling feature. A crucial aspect is that the scaling is described generically, allowing us to analyze various approaches, including Adam, RMSProp, and OASIS, in a unified manner. In addition to theoretical analysis, we validate the performance of our methods in practice by training a neural network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge