Yannian Gu
EHRWorld: A Patient-Centric Medical World Model for Long-Horizon Clinical Trajectories
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:World models offer a principled framework for simulating future states under interventions, but realizing such models in complex, high-stakes domains like medicine remains challenging. Recent large language models (LLMs) have achieved strong performance on static medical reasoning tasks, raising the question of whether they can function as dynamic medical world models capable of simulating disease progression and treatment outcomes over time. In this work, we show that LLMs only incorporating medical knowledge struggle to maintain consistent patient states under sequential interventions, leading to error accumulation in long-horizon clinical simulation. To address this limitation, we introduce EHRWorld, a patient-centric medical world model trained under a causal sequential paradigm, together with EHRWorld-110K, a large-scale longitudinal clinical dataset derived from real-world electronic health records. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that EHRWorld significantly outperforms naive LLM-based baselines, achieving more stable long-horizon simulation, improved modeling of clinically sensitive events, and favorable reasoning efficiency, highlighting the necessity of training on causally grounded, temporally evolving clinical data for reliable and robust medical world modeling.
MedCEG: Reinforcing Verifiable Medical Reasoning with Critical Evidence Graph
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Large language models with reasoning capabilities have demonstrated impressive performance across a wide range of domains. In clinical applications, a transparent, step-by-step reasoning process provides physicians with strong evidence to support decision-making. While reinforcement learning has effectively enhanced reasoning performance in medical contexts, the clinical reliability of these reasoning processes remains limited because their accuracy and validity are often overlooked during training. To address this gap, we propose MedCEG, a framework that augments medical language models with clinically valid reasoning pathways by explicitly supervising the reasoning process through a Critical Evidence Graph (CEG). We curate a dataset of challenging clinical cases and algorithmically construct a CEG for each sample to represent a high-quality verifiable reasoning pathway. To guide the reasoning process, we introduce a Clinical Reasoning Procedure Reward, which evaluates Node Coverage, Structural Correctness, and Chain Completeness, thereby providing a holistic assessment of reasoning quality. Experimental results show that MedCEG surpasses existing methods in performance while producing clinically valid reasoning chains, representing a solid advancement in reliable medical AI reasoning. The code and models are available at https://github.com/LinjieMu/MedCEG.
CP-Env: Evaluating Large Language Models on Clinical Pathways in a Controllable Hospital Environment
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Medical care follows complex clinical pathways that extend beyond isolated physician-patient encounters, emphasizing decision-making and transitions between different stages. Current benchmarks focusing on static exams or isolated dialogues inadequately evaluate large language models (LLMs) in dynamic clinical scenarios. We introduce CP-Env, a controllable agentic hospital environment designed to evaluate LLMs across end-to-end clinical pathways. CP-Env simulates a hospital ecosystem with patient and physician agents, constructing scenarios ranging from triage and specialist consultation to diagnostic testing and multidisciplinary team meetings for agent interaction. Following real hospital adaptive flow of healthcare, it enables branching, long-horizon task execution. We propose a three-tiered evaluation framework encompassing Clinical Efficacy, Process Competency, and Professional Ethics. Results reveal that most models struggle with pathway complexity, exhibiting hallucinations and losing critical diagnostic details. Interestingly, excessive reasoning steps can sometimes prove counterproductive, while top models tend to exhibit reduced tool dependency through internalized knowledge. CP-Env advances medical AI agents development through comprehensive end-to-end clinical evaluation. We provide the benchmark and evaluation tools for further research and development at https://github.com/SPIRAL-MED/CP_ENV.
Interactive Segmentation and Report Generation for CT Images
Mar 05, 2025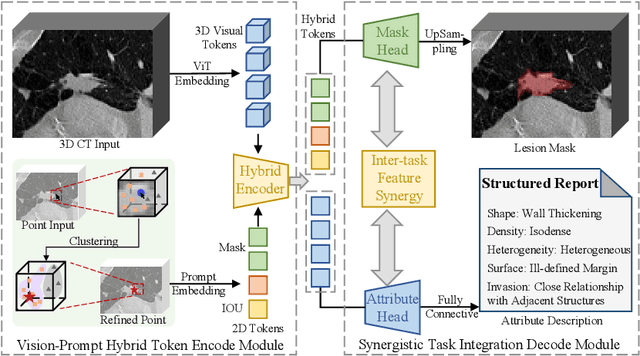
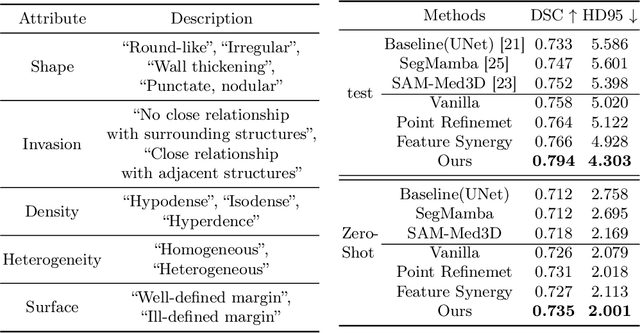

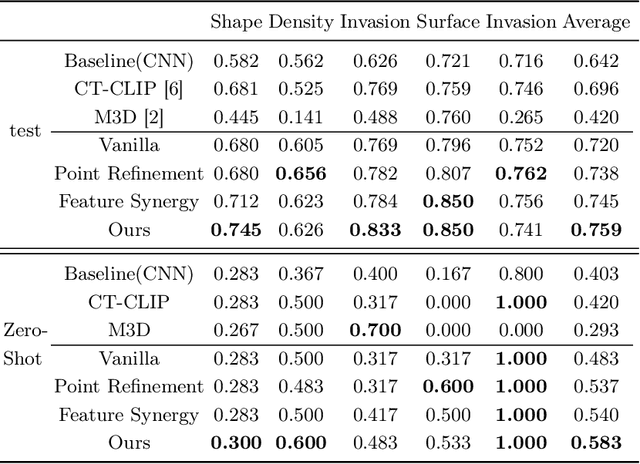
Abstract:Automated CT report generation plays a crucial role in improving diagnostic accuracy and clinical workflow efficiency. However, existing methods lack interpretability and impede patient-clinician understanding, while their static nature restricts radiologists from dynamically adjusting assessments during image review. Inspired by interactive segmentation techniques, we propose a novel interactive framework for 3D lesion morphology reporting that seamlessly generates segmentation masks with comprehensive attribute descriptions, enabling clinicians to generate detailed lesion profiles for enhanced diagnostic assessment. To our best knowledge, we are the first to integrate the interactive segmentation and structured reports in 3D CT medical images. Experimental results across 15 lesion types demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in providing a more comprehensive and reliable reporting system for lesion segmentation and capturing. The source code will be made publicly available following paper acceptance.
A Data-Efficient Pan-Tumor Foundation Model for Oncology CT Interpretation
Feb 10, 2025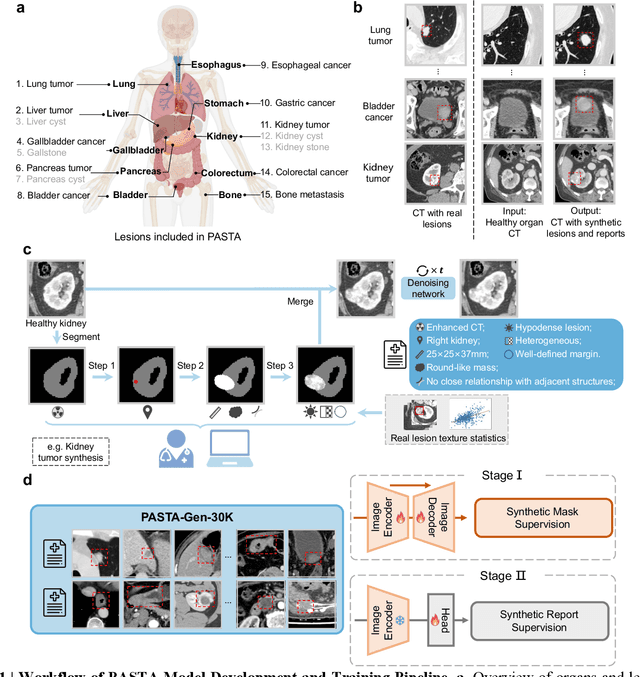
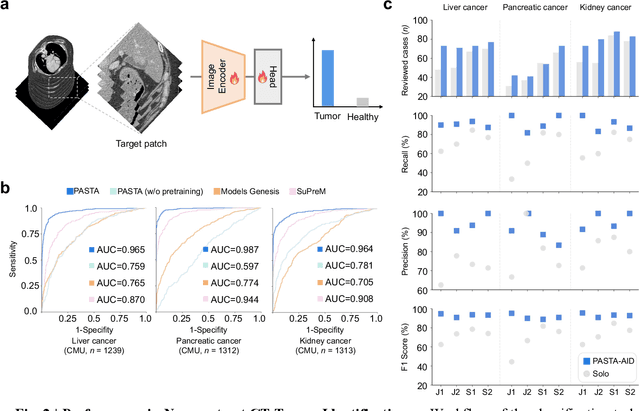
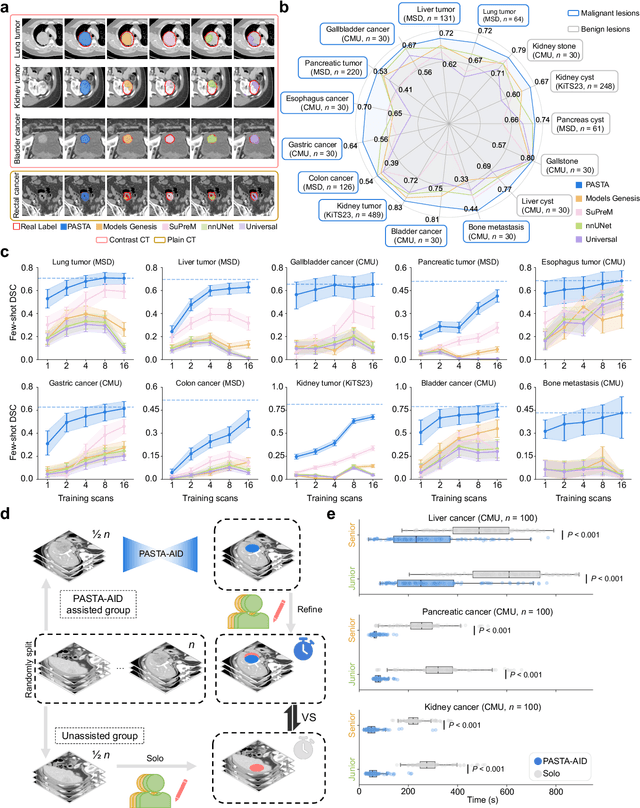
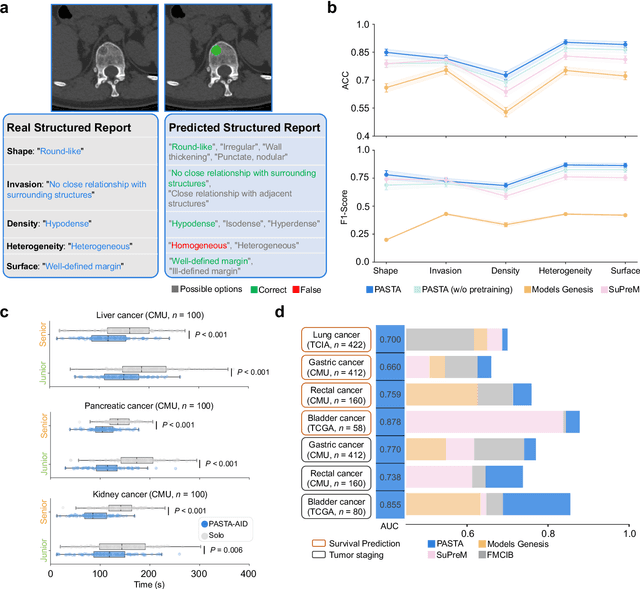
Abstract:Artificial intelligence-assisted imaging analysis has made substantial strides in tumor diagnosis and management. Here we present PASTA, a pan-tumor CT foundation model that achieves state-of-the-art performance on 45 of 46 representative oncology tasks -- including lesion segmentation, tumor detection in plain CT, tumor staging, survival prediction, structured report generation, and cross-modality transfer learning, significantly outperforming the second-best models on 35 tasks. This remarkable advancement is driven by our development of PASTA-Gen, an innovative synthetic tumor generation framework that produces a comprehensive dataset of 30,000 CT scans with pixel-level annotated lesions and paired structured reports, encompassing malignancies across ten organs and five benign lesion types. By leveraging this rich, high-quality synthetic data, we overcome a longstanding bottleneck in the development of CT foundation models -- specifically, the scarcity of publicly available, high-quality annotated datasets due to privacy constraints and the substantial labor required for scaling precise data annotation. Encouragingly, PASTA demonstrates exceptional data efficiency with promising practical value, markedly improving performance on various tasks with only a small amount of real-world data. The open release of both the synthetic dataset and PASTA foundation model effectively addresses the challenge of data scarcity, thereby advancing oncological research and clinical translation.
MedDiff-FM: A Diffusion-based Foundation Model for Versatile Medical Image Applications
Oct 20, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved significant success in both the natural image and medical image domains, encompassing a wide range of applications. Previous investigations in medical images have often been constrained to specific anatomical regions, particular applications, and limited datasets, resulting in isolated diffusion models. This paper introduces a diffusion-based foundation model to address a diverse range of medical image tasks, namely MedDiff-FM. MedDiff-FM leverages 3D CT images from multiple publicly available datasets, covering anatomical regions from head to abdomen, to pre-train a diffusion foundation model, and explores the capabilities of the diffusion foundation model across a variety of application scenarios. The diffusion foundation model handles multi-level image processing both at the image-level and patch-level, and utilizes position embedding to establish multi-level spatial relationships as well as anatomical structures and region classes to control certain anatomical regions. MedDiff-FM manages several downstream tasks seamlessly, including image denoising, anomaly detection, and image synthesis. MedDiff-FM is also capable of performing lesion generation and lesion inpainting by rapidly fine-tuning the diffusion foundation model using ControlNet with task-specific conditions. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of MedDiff-FM in addressing diverse downstream medical image tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge