Yanlong Wang
FinZero: Launching Multi-modal Financial Time Series Forecast with Large Reasoning Model
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Financial time series forecasting is both highly significant and challenging. Previous approaches typically standardized time series data before feeding it into forecasting models, but this encoding process inherently leads to a loss of important information. Moreover, past time series models generally require fixed numbers of variables or lookback window lengths, which further limits the scalability of time series forecasting. Besides, the interpretability and the uncertainty in forecasting remain areas requiring further research, as these factors directly impact the reliability and practical value of predictions. To address these issues, we first construct a diverse financial image-text dataset (FVLDB) and develop the Uncertainty-adjusted Group Relative Policy Optimization (UARPO) method to enable the model not only output predictions but also analyze the uncertainty of those predictions. We then proposed FinZero, a multimodal pre-trained model finetuned by UARPO to perform reasoning, prediction, and analytical understanding on the FVLDB financial time series. Extensive experiments validate that FinZero exhibits strong adaptability and scalability. After fine-tuning with UARPO, FinZero achieves an approximate 13.48\% improvement in prediction accuracy over GPT-4o in the high-confidence group, demonstrating the effectiveness of reinforcement learning fine-tuning in multimodal large model, including in financial time series forecasting tasks.
Assessing Uncertainty in Stock Returns: A Gaussian Mixture Distribution-Based Method
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:This study seeks to advance the understanding and prediction of stock market return uncertainty through the application of advanced deep learning techniques. We introduce a novel deep learning model that utilizes a Gaussian mixture distribution to capture the complex, time-varying nature of asset return distributions in the Chinese stock market. By incorporating the Gaussian mixture distribution, our approach effectively characterizes short-term fluctuations and non-traditional features of stock returns, such as skewness and heavy tails, that are often overlooked by traditional models. Compared to GARCH models and their variants, our method demonstrates superior performance in volatility estimation, particularly during periods of heightened market volatility. It provides more accurate volatility forecasts and offers unique risk insights for different assets, thereby deepening the understanding of return uncertainty. Additionally, we propose a novel use of Code embedding which utilizes a bag-of-words approach to train hidden representations of stock codes and transforms the uncertainty attributes of stocks into high-dimensional vectors. These vectors are subsequently reduced to two dimensions, allowing the observation of similarity among different stocks. This visualization facilitates the identification of asset clusters with similar risk profiles, offering valuable insights for portfolio management and risk mitigation. Since we predict the uncertainty of returns by estimating their latent distribution, it is challenging to evaluate the return distribution when the true distribution is unobservable. However, we can measure it through the CRPS to assess how well the predicted distribution matches the true returns, and through MSE and QLIKE metrics to evaluate the error between the volatility level of the predicted distribution and proxy measures of true volatility.
FinTSBridge: A New Evaluation Suite for Real-world Financial Prediction with Advanced Time Series Models
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Despite the growing attention to time series forecasting in recent years, many studies have proposed various solutions to address the challenges encountered in time series prediction, aiming to improve forecasting performance. However, effectively applying these time series forecasting models to the field of financial asset pricing remains a challenging issue. There is still a need for a bridge to connect cutting-edge time series forecasting models with financial asset pricing. To bridge this gap, we have undertaken the following efforts: 1) We constructed three datasets from the financial domain; 2) We selected over ten time series forecasting models from recent studies and validated their performance in financial time series; 3) We developed new metrics, msIC and msIR, in addition to MSE and MAE, to showcase the time series correlation captured by the models; 4) We designed financial-specific tasks for these three datasets and assessed the practical performance and application potential of these forecasting models in important financial problems. We hope the developed new evaluation suite, FinTSBridge, can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and robustness of advanced forecasting models in finanical domains.
PSformer: Parameter-efficient Transformer with Segment Attention for Time Series Forecasting
Nov 03, 2024



Abstract:Time series forecasting remains a critical challenge across various domains, often complicated by high-dimensional data and long-term dependencies. This paper presents a novel transformer architecture for time series forecasting, incorporating two key innovations: parameter sharing (PS) and Spatial-Temporal Segment Attention (SegAtt). We also define the time series segment as the concatenation of sequence patches from the same positions across different variables. The proposed model, PSformer, reduces the number of training parameters through the parameter sharing mechanism, thereby improving model efficiency and scalability. The introduction of SegAtt could enhance the capability of capturing local spatio-temporal dependencies by computing attention over the segments, and improve global representation by integrating information across segments. The combination of parameter sharing and SegAtt significantly improves the forecasting performance. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that PSformer outperforms popular baselines and other transformer-based approaches in terms of accuracy and scalability, establishing itself as an accurate and scalable tool for time series forecasting.
MultiColor: Image Colorization by Learning from Multiple Color Spaces
Aug 08, 2024Abstract:Deep networks have shown impressive performance in the image restoration tasks, such as image colorization. However, we find that previous approaches rely on the digital representation from single color model with a specific mapping function, a.k.a., color space, during the colorization pipeline. In this paper, we first investigate the modeling of different color spaces, and find each of them exhibiting distinctive characteristics with unique distribution of colors. The complementarity among multiple color spaces leads to benefits for the image colorization task. We present MultiColor, a new learning-based approach to automatically colorize grayscale images that combines clues from multiple color spaces. Specifically, we employ a set of dedicated colorization modules for individual color space. Within each module, a transformer decoder is first employed to refine color query embeddings and then a color mapper produces color channel prediction using the embeddings and semantic features. With these predicted color channels representing various color spaces, a complementary network is designed to exploit the complementarity and generate pleasing and reasonable colorized images. We conduct extensive experiments on real-world datasets, and the results demonstrate superior performance over the state-of-the-arts.
Design and Implementation of Global Path Planning System for Unmanned Surface Vehicle among Multiple Task Points
Jul 21, 2018
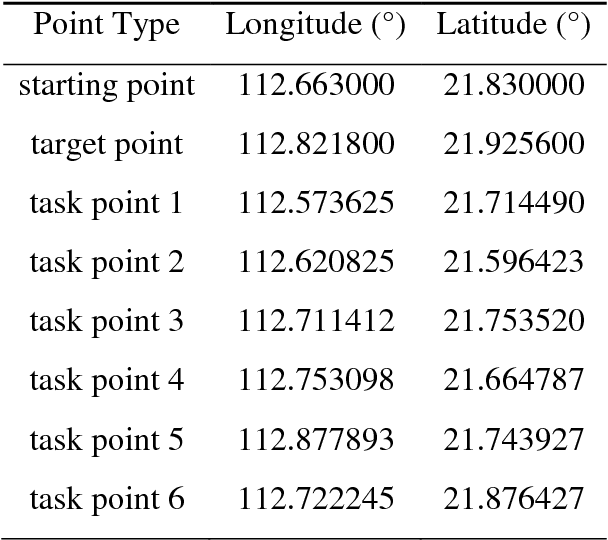


Abstract:Global path planning is the key technology in the design of unmanned surface vehicles. This paper establishes global environment modelling based on electronic charts and hexagonal grids which are proved to be better than square grids in validity, safety and rapidity. Besides, we introduce Cube coordinate system to simplify hexagonal algorithms. Furthermore, we propose an improved A* algorithm to realize the path planning between two points. Based on that, we build the global path planning modelling for multiple task points and present an improved ant colony optimization to realize it accurately. The simulation results show that the global path planning system can plan an optimal path to tour multiple task points safely and quickly, which is superior to traditional methods in safety, rapidity and path length. Besides, the planned path can directly apply to actual applications of USVs.
* 28 pages, 15 figures
Research and Implementation of Global Path Planning for Unmanned Surface Vehicle Based on Electronic Chart
Feb 09, 2018
Abstract:Unmanned Surface Vehicle (USV) is a new type of intelligent surface craft, and global path planning is the key technology of USV research, which can reflect the intelligent level of USV. In order to solve the problem of global path planning of USV, this paper proposes an improved A* algorithm for sailing cost optimization based on electronic charts. This paper uses the S-57 electronic chart to realize the establishment of the octree grid environment model, and proposes an improved A* algorithm based on sailing safety weight, pilot quantity and path curve smoothing to ensure the safety of the route, reduce the planning time, and improve path smoothness. The simulation results show that the environmental model construction method and the improved A* algorithm can generate safe and reasonable global path.
* 7 pages, 3 figures, conference
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge