Yanfeng Jiang
DeltaDQ: Ultra-High Delta Compression for Fine-Tuned LLMs via Group-wise Dropout and Separate Quantization
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:Large language models achieve exceptional performance on various downstream tasks through supervised fine-tuning. However, the diversity of downstream tasks and practical requirements makes deploying multiple full-parameter fine-tuned models challenging. Current methods that compress the delta weight struggle to achieve ultra-high compression, failing to minimize the deployment overhead. To address the above issue, we propose a novel distribution-driven delta compression framework DeltaDQ, which utilizes Group-wise Dropout and Separate Quantization to achieve ultra-high compression for the delta weight. We have observed that the matrix-computed intermediate results for the delta weight exhibit extremely small variance and min-max range characteristics, referred to as Balanced Intermediate Results. Exploiting this phenomenon, we introduce Group-wise Dropout to perform dropout on the delta weight using an optimal group size. Furthermore, using Separate Quantization, sparse weights are quantized and decomposed to achieve a lower bit. Experimental results show that DeltaDQ achieves 16x compression with improved accuracy compared to baselines for WizardMath and WizardCoder models across different parameter scales. Moreover, DeltaDQ demonstrates the ability for ultra-high compression ratio, achieving 128x compression for the WizardMath-7B model and 512x compression for the WizardMath-70B model.
ADFQ-ViT: Activation-Distribution-Friendly Post-Training Quantization for Vision Transformers
Jul 03, 2024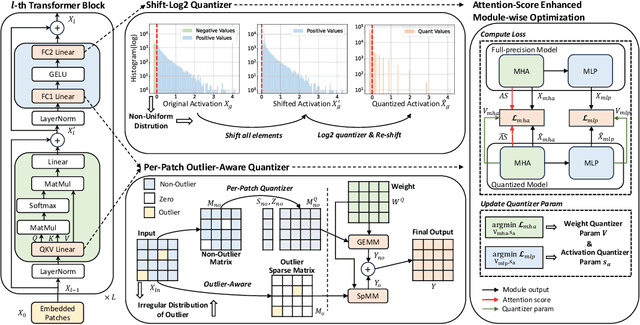
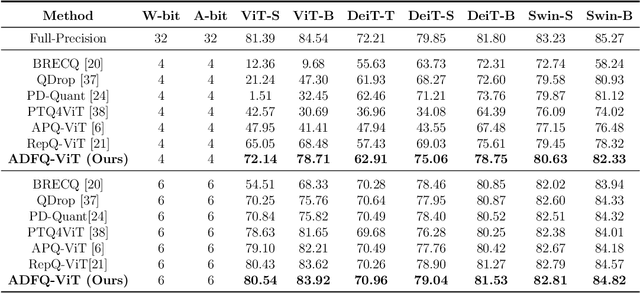
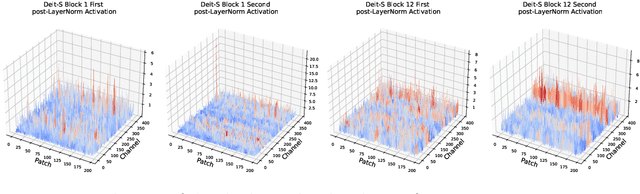
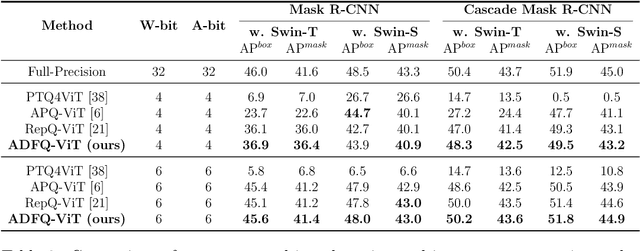
Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have exhibited exceptional performance across diverse computer vision tasks, while their substantial parameter size incurs significantly increased memory and computational demands, impeding effective inference on resource-constrained devices. Quantization has emerged as a promising solution to mitigate these challenges, yet existing methods still suffer from significant accuracy loss at low-bit. We attribute this issue to the distinctive distributions of post-LayerNorm and post-GELU activations within ViTs, rendering conventional hardware-friendly quantizers ineffective, particularly in low-bit scenarios. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework called Activation-Distribution-Friendly post-training Quantization for Vision Transformers, ADFQ-ViT. Concretely, we introduce the Per-Patch Outlier-aware Quantizer to tackle irregular outliers in post-LayerNorm activations. This quantizer refines the granularity of the uniform quantizer to a per-patch level while retaining a minimal subset of values exceeding a threshold at full-precision. To handle the non-uniform distributions of post-GELU activations between positive and negative regions, we design the Shift-Log2 Quantizer, which shifts all elements to the positive region and then applies log2 quantization. Moreover, we present the Attention-score enhanced Module-wise Optimization which adjusts the parameters of each quantizer by reconstructing errors to further mitigate quantization error. Extensive experiments demonstrate ADFQ-ViT provides significant improvements over various baselines in image classification, object detection, and instance segmentation tasks at 4-bit. Specifically, when quantizing the ViT-B model to 4-bit, we achieve a 10.23% improvement in Top-1 accuracy on the ImageNet dataset.
Exploring Post-Training Quantization of Protein Language Models
Oct 30, 2023



Abstract:Recent advancements in unsupervised protein language models (ProteinLMs), like ESM-1b and ESM-2, have shown promise in different protein prediction tasks. However, these models face challenges due to their high computational demands, significant memory needs, and latency, restricting their usage on devices with limited resources. To tackle this, we explore post-training quantization (PTQ) for ProteinLMs, focusing on ESMFold, a simplified version of AlphaFold based on ESM-2 ProteinLM. Our study is the first attempt to quantize all weights and activations of ProteinLMs. We observed that the typical uniform quantization method performs poorly on ESMFold, causing a significant drop in TM-Score when using 8-bit quantization. We conducted extensive quantization experiments, uncovering unique challenges associated with ESMFold, particularly highly asymmetric activation ranges before Layer Normalization, making representation difficult using low-bit fixed-point formats. To address these challenges, we propose a new PTQ method for ProteinLMs, utilizing piecewise linear quantization for asymmetric activation values to ensure accurate approximation. We demonstrated the effectiveness of our method in protein structure prediction tasks, demonstrating that ESMFold can be accurately quantized to low-bit widths without compromising accuracy. Additionally, we applied our method to the contact prediction task, showcasing its versatility. In summary, our study introduces an innovative PTQ method for ProteinLMs, addressing specific quantization challenges and potentially leading to the development of more efficient ProteinLMs with significant implications for various protein-related applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge