Yan Chai Hum
Vehicle Detection Performance in Nordic Region
Mar 22, 2024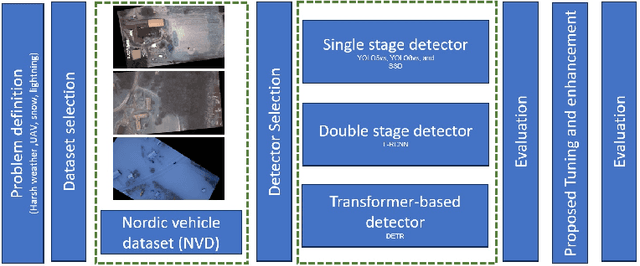

Abstract:This paper addresses the critical challenge of vehicle detection in the harsh winter conditions in the Nordic regions, characterized by heavy snowfall, reduced visibility, and low lighting. Due to their susceptibility to environmental distortions and occlusions, traditional vehicle detection methods have struggled in these adverse conditions. The advanced proposed deep learning architectures brought promise, yet the unique difficulties of detecting vehicles in Nordic winters remain inadequately addressed. This study uses the Nordic Vehicle Dataset (NVD), which has UAV images from northern Sweden, to evaluate the performance of state-of-the-art vehicle detection algorithms under challenging weather conditions. Our methodology includes a comprehensive evaluation of single-stage, two-stage, and transformer-based detectors against the NVD. We propose a series of enhancements tailored to each detection framework, including data augmentation, hyperparameter tuning, transfer learning, and novel strategies designed explicitly for the DETR model. Our findings not only highlight the limitations of current detection systems in the Nordic environment but also offer promising directions for enhancing these algorithms for improved robustness and accuracy in vehicle detection amidst the complexities of winter landscapes. The code and the dataset are available at https://nvd.ltu-ai.dev
Robust and Fast Vehicle Detection using Augmented Confidence Map
Apr 27, 2023



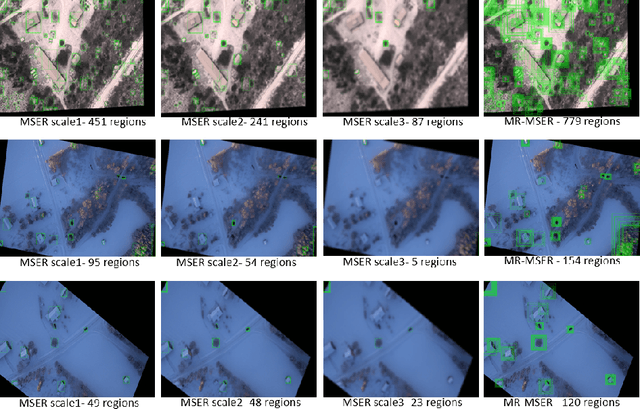
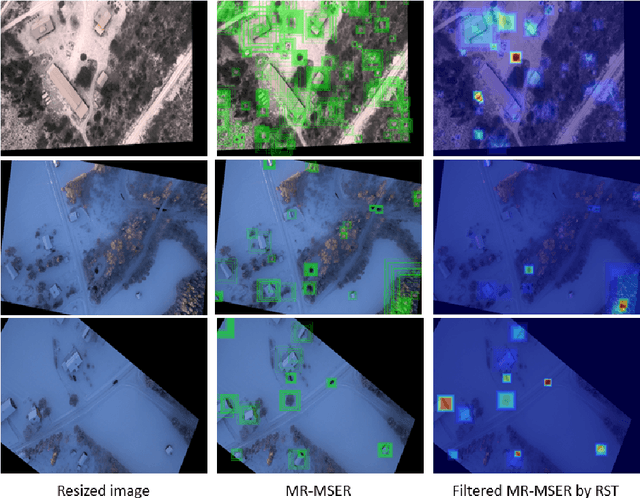
Abstract:Vehicle detection in real-time scenarios is challenging because of the time constraints and the presence of multiple types of vehicles with different speeds, shapes, structures, etc. This paper presents a new method relied on generating a confidence map-for robust and faster vehicle detection. To reduce the adverse effect of different speeds, shapes, structures, and the presence of several vehicles in a single image, we introduce the concept of augmentation which highlights the region of interest containing the vehicles. The augmented map is generated by exploring the combination of multiresolution analysis and maximally stable extremal regions (MR-MSER). The output of MR-MSER is supplied to fast CNN to generate a confidence map, which results in candidate regions. Furthermore, unlike existing models that implement complicated models for vehicle detection, we explore the combination of a rough set and fuzzy-based models for robust vehicle detection. To show the effectiveness of the proposed method, we conduct experiments on our dataset captured by drones and on several vehicle detection benchmark datasets, namely, KITTI and UA-DETRAC. The results on our dataset and the benchmark datasets show that the proposed method outperforms the existing methods in terms of time efficiency and achieves a good detection rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge