Yadi Zhou
Repurpose Open Data to Discover Therapeutics for COVID-19 using Deep Learning
May 21, 2020Abstract:There have been more than 850,000 confirmed cases and over 48,000 deaths from the human coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), in the United States alone. However, there are currently no proven effective medications against COVID-19. Drug repurposing offers a promising way for the development of prevention and treatment strategies for COVID-19. This study reports an integrative, network-based deep learning methodology to identify repurposable drugs for COVID-19 (termed CoV-KGE). Specifically, we built a comprehensive knowledge graph that includes 15 million edges across 39 types of relationships connecting drugs, diseases, genes, pathways, and expressions, from a large scientific corpus of 24 million PubMed publications. Using Amazon AWS computing resources, we identified 41 repurposable drugs (including indomethacin, toremifene and niclosamide) whose therapeutic association with COVID-19 were validated by transcriptomic and proteomic data in SARS-CoV-2 infected human cells and data from ongoing clinical trials. While this study, by no means recommends specific drugs, it demonstrates a powerful deep learning methodology to prioritize existing drugs for further investigation, which holds the potential of accelerating therapeutic development for COVID-19.
Galaxy morphology prediction using capsule networks
Sep 22, 2018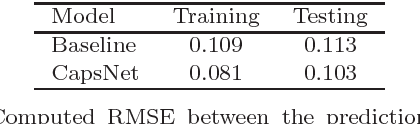
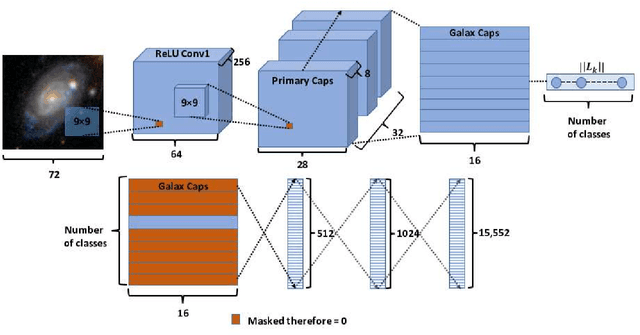
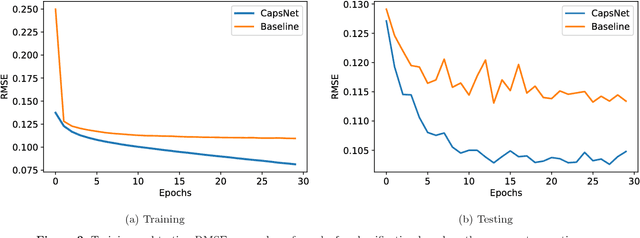

Abstract:Understanding morphological types of galaxies is a key parameter for studying their formation and evolution. Neural networks that have been used previously for galaxy morphology classification have some disadvantages, such as not being invariant under rotation. In this work, we studied the performance of Capsule Network, a recently introduced neural network architecture that is rotationally invariant and spatially aware, on the task of galaxy morphology classification. We designed two evaluation scenarios based on the answers from the question tree in the Galaxy Zoo project. In the first scenario, we used Capsule Network for regression and predicted probabilities for all of the questions. In the second scenario, we chose the answer to the first morphology question that had the highest user agreement as the class of the object and trained a Capsule Network classifier, where we also reconstructed galaxy images. We achieved promising results in both of these scenarios. Automated approaches such as the one introduced here will greatly decrease the workload of astronomers and will play a critical role in the upcoming large sky surveys.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge