Yachuan Li
AVIR: Adaptive Visual In-Document Retrieval for Efficient Multi-Page Document Question Answering
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Multi-page Document Visual Question Answering (MP-DocVQA) remains challenging because long documents not only strain computational resources but also reduce the effectiveness of the attention mechanism in large vision-language models (LVLMs). We tackle these issues with an Adaptive Visual In-document Retrieval (AVIR) framework. A lightweight retrieval model first scores each page for question relevance. Pages are then clustered according to the score distribution to adaptively select relevant content. The clustered pages are screened again by Top-K to keep the context compact. However, for short documents, clustering reliability decreases, so we use a relevance probability threshold to select pages. The selected pages alone are fed to a frozen LVLM for answer generation, eliminating the need for model fine-tuning. The proposed AVIR framework reduces the average page count required for question answering by 70%, while achieving an ANLS of 84.58% on the MP-DocVQA dataset-surpassing previous methods with significantly lower computational cost. The effectiveness of the proposed AVIR is also verified on the SlideVQA and DUDE benchmarks. The code is available at https://github.com/Li-yachuan/AVIR.
EDMB: Edge Detector with Mamba
Jan 08, 2025Abstract:Transformer-based models have made significant progress in edge detection, but their high computational cost is prohibitive. Recently, vision Mamba have shown excellent ability in efficiently capturing long-range dependencies. Drawing inspiration from this, we propose a novel edge detector with Mamba, termed EDMB, to efficiently generate high-quality multi-granularity edges. In EDMB, Mamba is combined with a global-local architecture, therefore it can focus on both global information and fine-grained cues. The fine-grained cues play a crucial role in edge detection, but are usually ignored by ordinary Mamba. We design a novel decoder to construct learnable Gaussian distributions by fusing global features and fine-grained features. And the multi-grained edges are generated by sampling from the distributions. In order to make multi-granularity edges applicable to single-label data, we introduce Evidence Lower Bound loss to supervise the learning of the distributions. On the multi-label dataset BSDS500, our proposed EDMB achieves competitive single-granularity ODS 0.837 and multi-granularity ODS 0.851 without multi-scale test or extra PASCAL-VOC data. Remarkably, EDMB can be extended to single-label datasets such as NYUDv2 and BIPED. The source code is available at https://github.com/Li-yachuan/EDMB.
Tiny and Efficient Model for the Edge Detection Generalization
Aug 12, 2023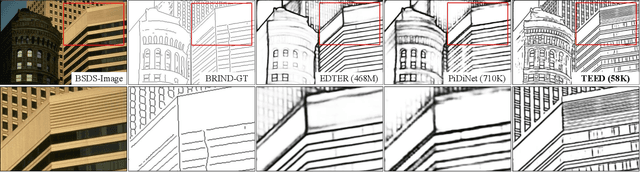
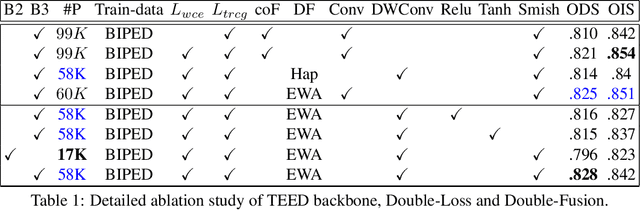
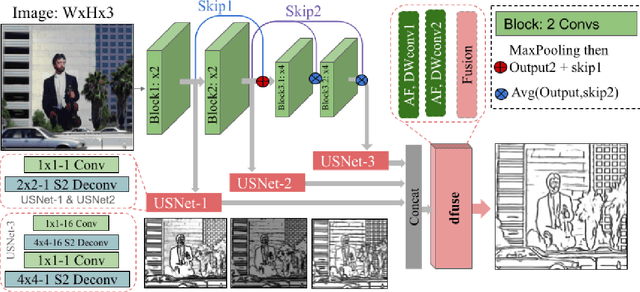

Abstract:Most high-level computer vision tasks rely on low-level image operations as their initial processes. Operations such as edge detection, image enhancement, and super-resolution, provide the foundations for higher level image analysis. In this work we address the edge detection considering three main objectives: simplicity, efficiency, and generalization since current state-of-the-art (SOTA) edge detection models are increased in complexity for better accuracy. To achieve this, we present Tiny and Efficient Edge Detector (TEED), a light convolutional neural network with only $58K$ parameters, less than $0.2$% of the state-of-the-art models. Training on the BIPED dataset takes $less than 30 minutes$, with each epoch requiring $less than 5 minutes$. Our proposed model is easy to train and it quickly converges within very first few epochs, while the predicted edge-maps are crisp and of high quality. Additionally, we propose a new dataset to test the generalization of edge detection, which comprises samples from popular images used in edge detection and image segmentation. The source code is available in https://github.com/xavysp/TEED.
Compact Twice Fusion Network for Edge Detection
Jul 11, 2023Abstract:The significance of multi-scale features has been gradually recognized by the edge detection community. However, the fusion of multi-scale features increases the complexity of the model, which is not friendly to practical application. In this work, we propose a Compact Twice Fusion Network (CTFN) to fully integrate multi-scale features while maintaining the compactness of the model. CTFN includes two lightweight multi-scale feature fusion modules: a Semantic Enhancement Module (SEM) that can utilize the semantic information contained in coarse-scale features to guide the learning of fine-scale features, and a Pseudo Pixel-level Weighting (PPW) module that aggregate the complementary merits of multi-scale features by assigning weights to all features. Notwithstanding all this, the interference of texture noise makes the correct classification of some pixels still a challenge. For these hard samples, we propose a novel loss function, coined Dynamic Focal Loss, which reshapes the standard cross-entropy loss and dynamically adjusts the weights to correct the distribution of hard samples. We evaluate our method on three datasets, i.e., BSDS500, NYUDv2, and BIPEDv2. Compared with state-of-the-art methods, CTFN achieves competitive accuracy with less parameters and computational cost. Apart from the backbone, CTFN requires only 0.1M additional parameters, which reduces its computation cost to just 60% of other state-of-the-art methods. The codes are available at https://github.com/Li-yachuan/CTFN-pytorch-master.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge