Xuchu Xu
Self-Supervised Visual Place Recognition by Mining Temporal and Feature Neighborhoods
Aug 19, 2022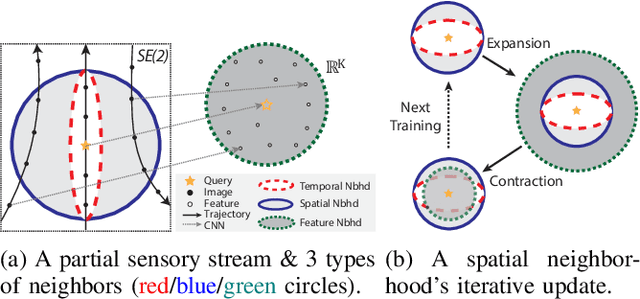
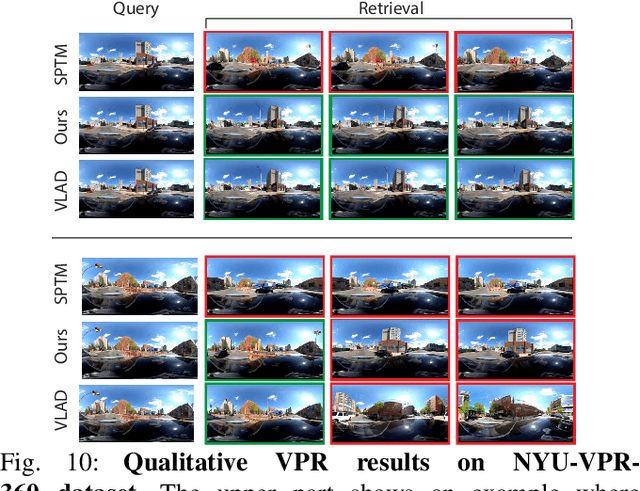
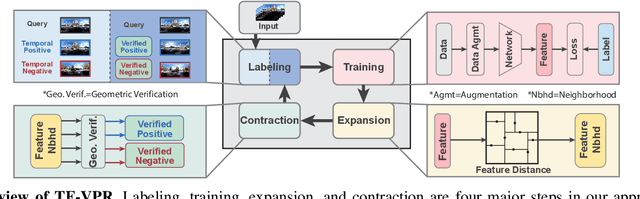
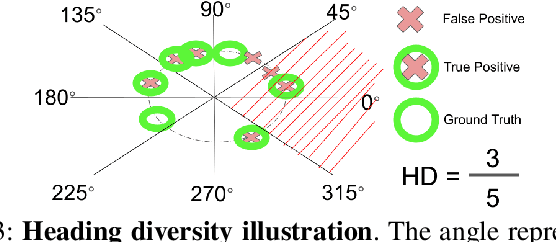
Abstract:Visual place recognition (VPR) using deep networks has achieved state-of-the-art performance. However, most of them require a training set with ground truth sensor poses to obtain positive and negative samples of each observation's spatial neighborhood for supervised learning. When such information is unavailable, temporal neighborhoods from a sequentially collected data stream could be exploited for self-supervised training, although we find its performance suboptimal. Inspired by noisy label learning, we propose a novel self-supervised framework named \textit{TF-VPR} that uses temporal neighborhoods and learnable feature neighborhoods to discover unknown spatial neighborhoods. Our method follows an iterative training paradigm which alternates between: (1) representation learning with data augmentation, (2) positive set expansion to include the current feature space neighbors, and (3) positive set contraction via geometric verification. We conduct comprehensive experiments on both simulated and real datasets, with either RGB images or point clouds as inputs. The results show that our method outperforms our baselines in recall rate, robustness, and heading diversity, a novel metric we propose for VPR. Our code and datasets can be found at https://ai4ce.github.io/TF-VPR/.
Projector-Guided Non-Holonomic Mobile 3D Printing
May 19, 2021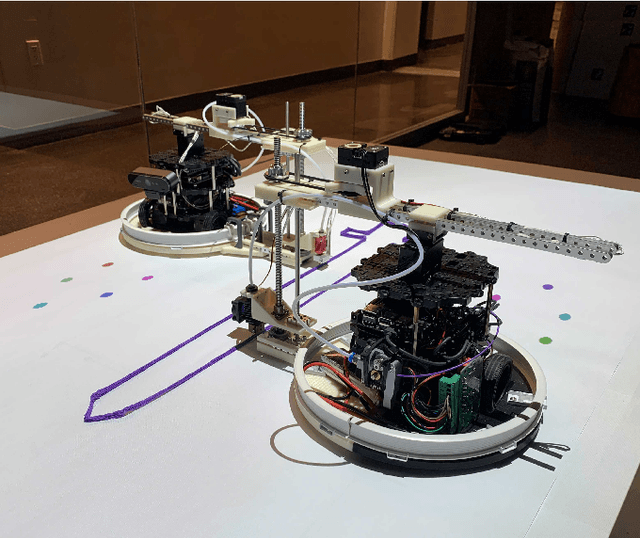
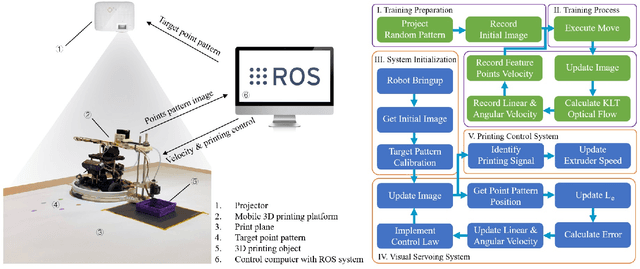
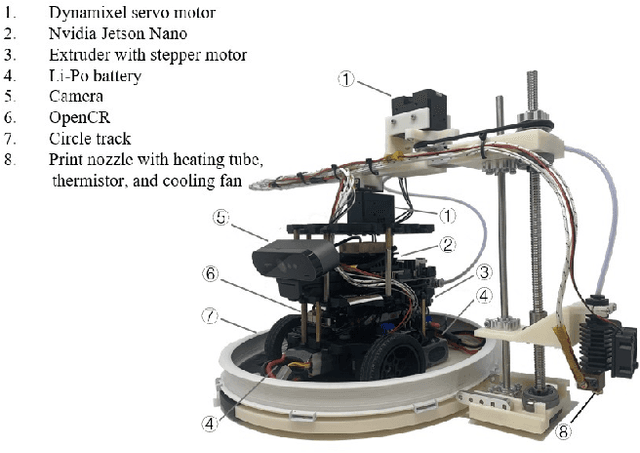
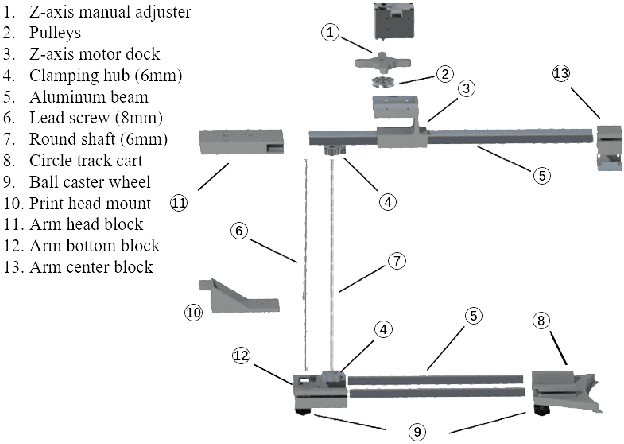
Abstract:Fused deposition modeling (FDM) using mobile robots instead of the gantry-based 3D printer enables additive manufacturing at a larger scale with higher speed. This introduces challenges including accurate localization, control of the printhead, and design of a stable mobile manipulator with low vibrations and proper degrees of freedom. We proposed and developed a low-cost non-holonomic mobile 3D printing system guided by a projector via learning-based visual servo-ing. It requires almost no manual calibration of the system parameters. Using a regular top-down projector without any expensive external localization device for pose feedback, this system enabled mobile robots to accurately follow pre-designed millimeter-level printing trajectories with speed control. We evaluate the system in terms of its trajectory accuracy and printing quality compared with original 3D designs. We further demonstrated the potential of this system using two such mobile robots to collaboratively print a 3D object with dimensions of 80cm x 30cm size, which exceeds the limitation of common desktop FDM 3D printers.
Deep Weakly Supervised Positioning
Apr 10, 2021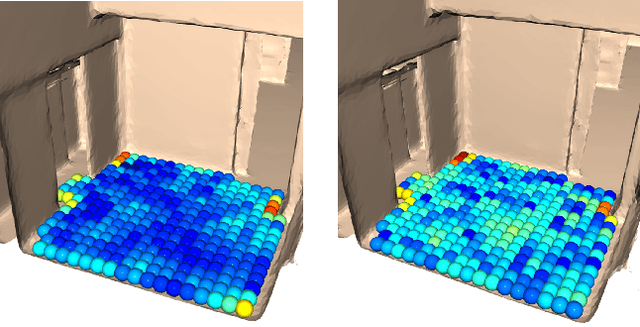

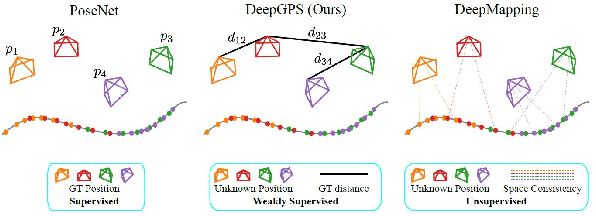
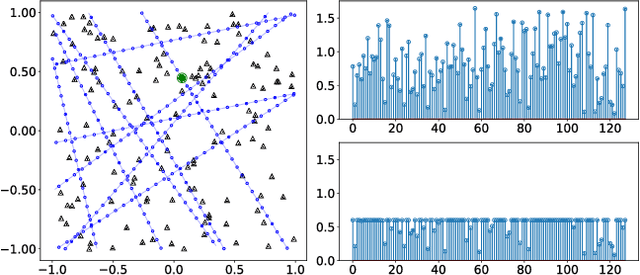
Abstract:PoseNet can map a photo to the position where it is taken, which is appealing in robotics. However, training PoseNet requires full supervision, where ground truth positions are non-trivial to obtain. Can we train PoseNet without knowing the ground truth positions for each observation? We show that this is possible via constraint-based weak-supervision, leading to the proposed framework: DeepGPS. Particularly, using wheel-encoder-estimated distances traveled by a robot along random straight line segments as constraints between PoseNet outputs, DeepGPS can achieve a relative positioning error of less than 2%. Moreover, training DeepGPS can be done as auto-calibration with almost no human attendance, which is more attractive than its competing methods that typically require careful and expert-level manual calibration. We conduct various experiments on simulated and real datasets to demonstrate the general applicability, effectiveness, and accuracy of DeepGPS, and perform a comprehensive analysis of its robustness. Our code is available at https://ai4ce.github.io/DeepGPS/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge