Xuan Ren
Agentic Proposing: Enhancing Large Language Model Reasoning via Compositional Skill Synthesis
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Advancing complex reasoning in large language models relies on high-quality, verifiable datasets, yet human annotation remains cost-prohibitive and difficult to scale. Current synthesis paradigms often face a recurring trade-off: maintaining structural validity typically restricts problem complexity, while relaxing constraints to increase difficulty frequently leads to inconsistent or unsolvable instances. To address this, we propose Agentic Proposing, a framework that models problem synthesis as a goal-driven sequential decision process where a specialized agent dynamically selects and composes modular reasoning skills. Through an iterative workflow of internal reflection and tool-use, we develop the Agentic-Proposer-4B using Multi-Granularity Policy Optimization (MGPO) to generate high-precision, verifiable training trajectories across mathematics, coding, and science. Empirical results demonstrate that downstream solvers trained on agent-synthesized data significantly outperform leading baselines and exhibit robust cross-domain generalization. Notably, a 30B solver trained on only 11,000 synthesized trajectories achieves a state-of-the-art 91.6% accuracy on AIME25, rivaling frontier-scale proprietary models such as GPT-5 and proving that a small volume of high-quality synthetic signals can effectively substitute for massive human-curated datasets.
Unmasking Reasoning Processes: A Process-aware Benchmark for Evaluating Structural Mathematical Reasoning in LLMs
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Recent large language models (LLMs) achieve near-saturation accuracy on many established mathematical reasoning benchmarks, raising concerns about their ability to diagnose genuine reasoning competence. This saturation largely stems from the dominance of template-based computation and shallow arithmetic decomposition in existing datasets, which underrepresent reasoning skills such as multi-constraint coordination, constructive logical synthesis, and spatial inference. To address this gap, we introduce ReasoningMath-Plus, a benchmark of 150 carefully curated problems explicitly designed to evaluate structural reasoning. Each problem emphasizes reasoning under interacting constraints, constructive solution formation, or non-trivial structural insight, and is annotated with a minimal reasoning skeleton to support fine-grained process-level evaluation. Alongside the dataset, we introduce HCRS (Hazard-aware Chain-based Rule Score), a deterministic step-level scoring function, and train a Process Reward Model (PRM) on the annotated reasoning traces. Empirically, while leading models attain relatively high final-answer accuracy (up to 5.8/10), HCRS-based holistic evaluation yields substantially lower scores (average 4.36/10, best 5.14/10), showing that answer-only metrics can overestimate reasoning robustness.
Efficient Response Generation Method Selection for Fine-Tuning Large Language Models
Feb 17, 2025



Abstract:The training data for fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) is typically structured as input-output pairs. However, for many tasks, there can be multiple equally valid output variations for the same input. Recent studies have observed that the choice of output variation used in training can affect the model's performance. This raises an important question: how can we generate the most effective output from the many possible response generation strategy options? Rather than relying on the traditional but resource-intensive train-and-evaluate approach, this paper proposes a scalable, approximate method for estimating the quality of a small subset of generated training data derived from the same input. We then evaluate how well this small subset of generated output fits the target model we are trying to train. We present a large-scale benchmark covering diverse reasoning-based datasets to support our study. The central idea is that a good output should closely resemble the output generated by the target LLM. We formalize this 'closeness' as the expected alignment score between a candidate output and the output sampled from the target LLM. We connect this measurement to the perplexity metric used in previous literature and demonstrate that leveraging an alignment-based metric can provide better predictions of model performance. Using this strategy, we can evaluate a small subset of the generated output from each response generation strategy option, then select the most effective strategy. We show that an LLM trained on data generated by the selected strategy could lead to a significant performance gain in many cases.
I Learn Better If You Speak My Language: Enhancing Large Language Model Fine-Tuning with Style-Aligned Response Adjustments
Feb 17, 2024
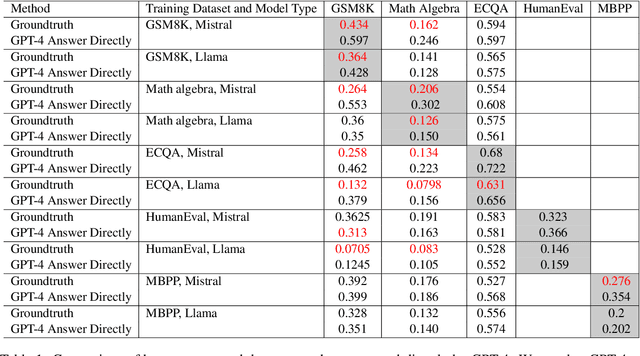
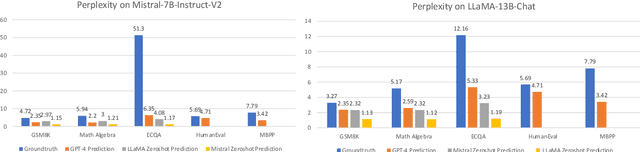
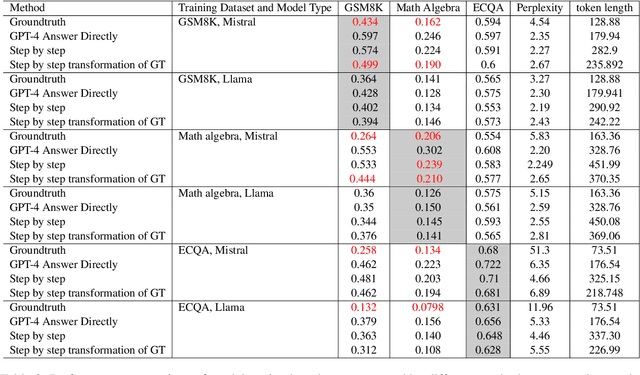
Abstract:Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) with a small data set for particular tasks is a widely encountered yet complex challenge. The potential for overfitting on a limited number of examples can negatively impact the model's ability to generalize and retain its original skills. Our research explores the impact of the style of ground-truth responses during the fine-tuning process. We found that matching the ground-truth response style with the LLM's inherent style results in better learning outcomes. Building on this insight, we developed a method that minimally alters the LLM's pre-existing responses to correct errors, using these adjusted responses as training targets. This technique enables precise corrections in line with the model's native response style, safeguarding the model's core capabilities and thus avoid overfitting. Our findings show that this approach not only improves the LLM's task-specific accuracy but also crucially maintains its original competencies and effectiveness.
You Can Generate It Again: Data-to-text Generation with Verification and Correction Prompting
Jun 28, 2023



Abstract:Despite significant advancements in existing models, generating text descriptions from structured data input, known as data-to-text generation, remains a challenging task. In this paper, we propose a novel approach that goes beyond traditional one-shot generation methods by introducing a multi-step process consisting of generation, verification, and correction stages. Our approach, VCP(Verification and Correction Prompting), begins with the model generating an initial output. We then proceed to verify the correctness of different aspects of the generated text. The observations from the verification step are converted into a specialized error-indication prompt, which instructs the model to regenerate the output while considering the identified errors. To enhance the model's correction ability, we have developed a carefully designed training procedure. This procedure enables the model to incorporate feedback from the error-indication prompt, resulting in improved output generation. Through experimental results, we demonstrate that our approach effectively reduces slot error rates while maintaining the overall quality of the generated text.
Out-of-Distribution Generalization in Text Classification: Past, Present, and Future
May 23, 2023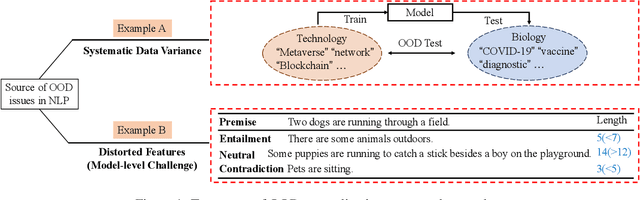
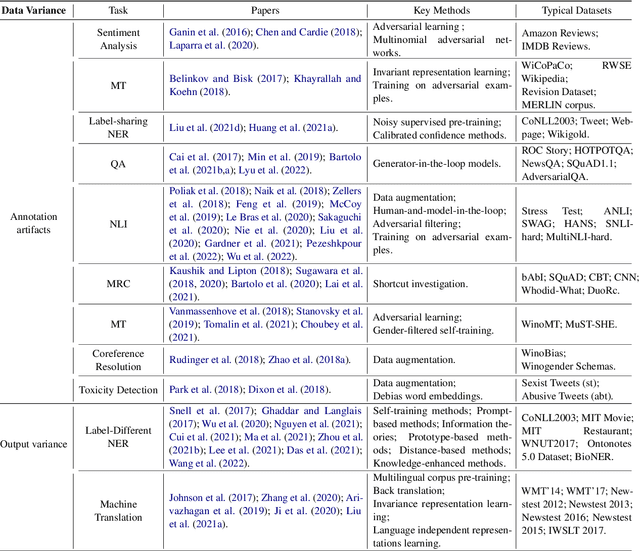
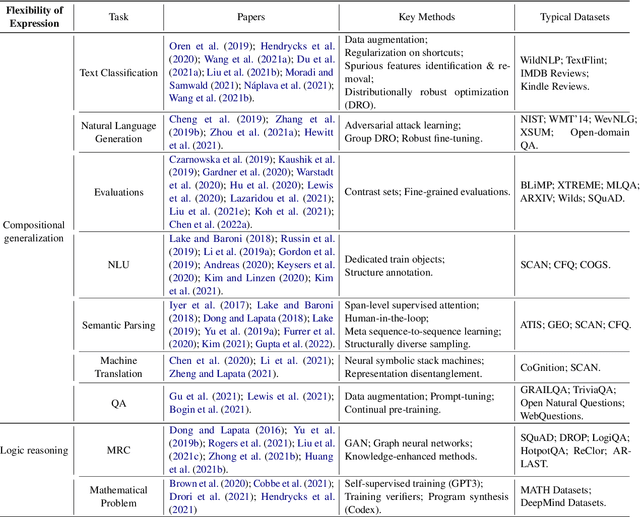
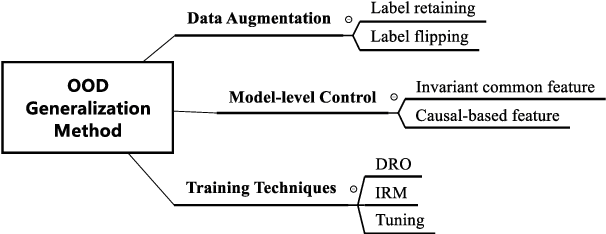
Abstract:Machine learning (ML) systems in natural language processing (NLP) face significant challenges in generalizing to out-of-distribution (OOD) data, where the test distribution differs from the training data distribution. This poses important questions about the robustness of NLP models and their high accuracy, which may be artificially inflated due to their underlying sensitivity to systematic biases. Despite these challenges, there is a lack of comprehensive surveys on the generalization challenge from an OOD perspective in text classification. Therefore, this paper aims to fill this gap by presenting the first comprehensive review of recent progress, methods, and evaluations on this topic. We furth discuss the challenges involved and potential future research directions. By providing quick access to existing work, we hope this survey will encourage future research in this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge