Xiucheng Guo
Spatiotemporal Prediction of Secondary Crashes by Rebalancing Dynamic and Static Data with Generative Adversarial Networks
Jan 17, 2025



Abstract:Data imbalance is a common issue in analyzing and predicting sudden traffic events. Secondary crashes constitute only a small proportion of all crashes. These secondary crashes, triggered by primary crashes, significantly exacerbate traffic congestion and increase the severity of incidents. However, the severe imbalance of secondary crash data poses significant challenges for prediction models, affecting their generalization ability and prediction accuracy. Existing methods fail to fully address the complexity of traffic crash data, particularly the coexistence of dynamic and static features, and often struggle to effectively handle data samples of varying lengths. Furthermore, most current studies predict the occurrence probability and spatiotemporal distribution of secondary crashes separately, lacking an integrated solution. To address these challenges, this study proposes a hybrid model named VarFusiGAN-Transformer, aimed at improving the fidelity of secondary crash data generation and jointly predicting the occurrence and spatiotemporal distribution of secondary crashes. The VarFusiGAN-Transformer model employs Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks to enhance the generation of multivariate long-time series data, incorporating a static data generator and an auxiliary discriminator to model the joint distribution of dynamic and static features. In addition, the model's prediction module achieves simultaneous prediction of both the occurrence and spatiotemporal distribution of secondary crashes. Compared to existing methods, the proposed model demonstrates superior performance in generating high-fidelity data and improving prediction accuracy.
A Generative Deep Learning Approach for Crash Severity Modeling with Imbalanced Data
Apr 02, 2024Abstract:Crash data is often greatly imbalanced, with the majority of crashes being non-fatal crashes, and only a small number being fatal crashes due to their rarity. Such data imbalance issue poses a challenge for crash severity modeling since it struggles to fit and interpret fatal crash outcomes with very limited samples. Usually, such data imbalance issues are addressed by data resampling methods, such as under-sampling and over-sampling techniques. However, most traditional and deep learning-based data resampling methods, such as synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE) and generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) are designed dedicated to processing continuous variables. Though some resampling methods have improved to handle both continuous and discrete variables, they may have difficulties in dealing with the collapse issue associated with sparse discrete risk factors. Moreover, there is a lack of comprehensive studies that compare the performance of various resampling methods in crash severity modeling. To address the aforementioned issues, the current study proposes a crash data generation method based on the Conditional Tabular GAN. After data balancing, a crash severity model is employed to estimate the performance of classification and interpretation. A comparative study is conducted to assess classification accuracy and distribution consistency of the proposed generation method using a 4-year imbalanced crash dataset collected in Washington State, U.S. Additionally, Monte Carlo simulation is employed to estimate the performance of parameter and probability estimation in both two- and three-class imbalance scenarios. The results indicate that using synthetic data generated by CTGAN-RU for crash severity modeling outperforms using original data or synthetic data generated by other resampling methods.
Inferring Heterogeneous Treatment Effects of Crashes on Highway Traffic: A Doubly Robust Causal Machine Learning Approach
Jan 01, 2024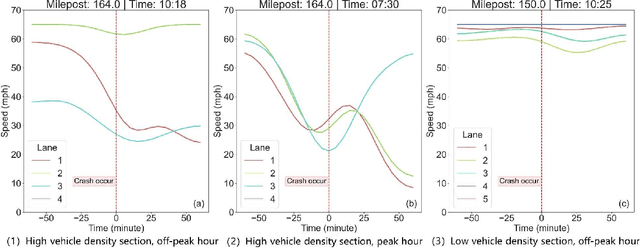
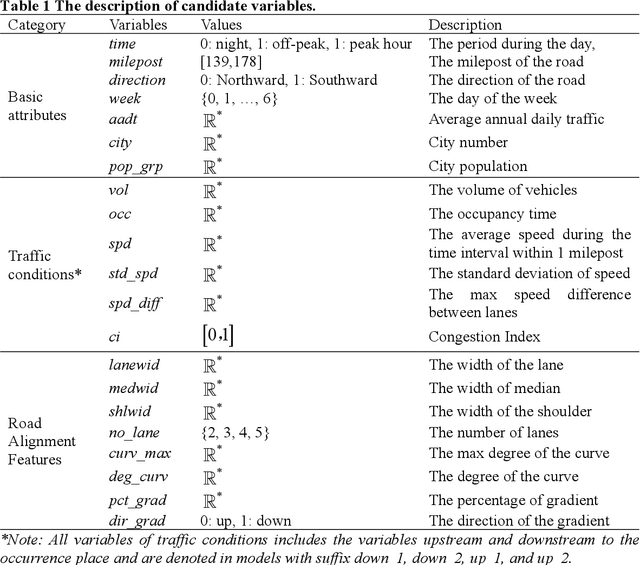
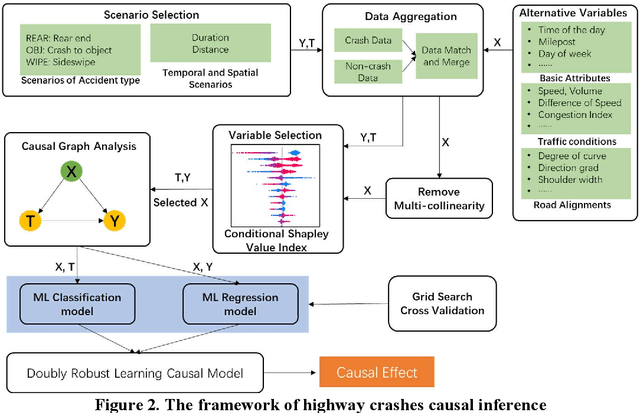
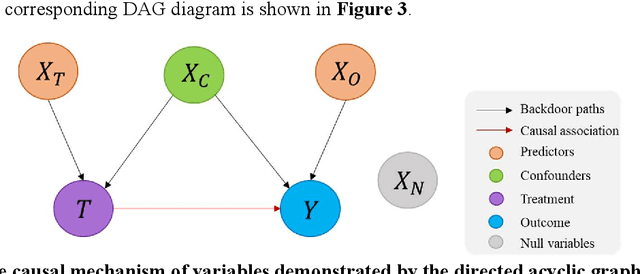
Abstract:Highway traffic crashes exert a considerable impact on both transportation systems and the economy. In this context, accurate and dependable emergency responses are crucial for effective traffic management. However, the influence of crashes on traffic status varies across diverse factors and may be biased due to selection bias. Therefore, there arises a necessity to accurately estimate the heterogeneous causal effects of crashes, thereby providing essential insights to facilitate individual-level emergency decision-making. This paper proposes a novel causal machine learning framework to estimate the causal effect of different types of crashes on highway speed. The Neyman-Rubin Causal Model (RCM) is employed to formulate this problem from a causal perspective. The Conditional Shapley Value Index (CSVI) is proposed based on causal graph theory to filter adverse variables, and the Structural Causal Model (SCM) is then adopted to define the statistical estimand for causal effects. The treatment effects are estimated by Doubly Robust Learning (DRL) methods, which combine doubly robust causal inference with classification and regression machine learning models. Experimental results from 4815 crashes on Highway Interstate 5 in Washington State reveal the heterogeneous treatment effects of crashes at varying distances and durations. The rear-end crashes cause more severe congestion and longer durations than other types of crashes, and the sideswipe crashes have the longest delayed impact. Additionally, the findings show that rear-end crashes affect traffic greater at night, while crash to objects has the most significant influence during peak hours. Statistical hypothesis tests, error metrics based on matched "counterfactual outcomes", and sensitive analyses are employed for assessment, and the results validate the accuracy and effectiveness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge