Xinxuan Wu
SE-MoE: A Scalable and Efficient Mixture-of-Experts Distributed Training and Inference System
May 20, 2022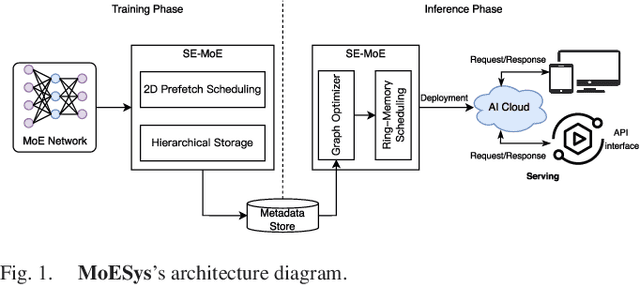
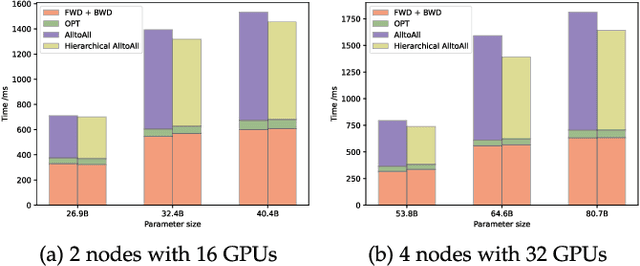
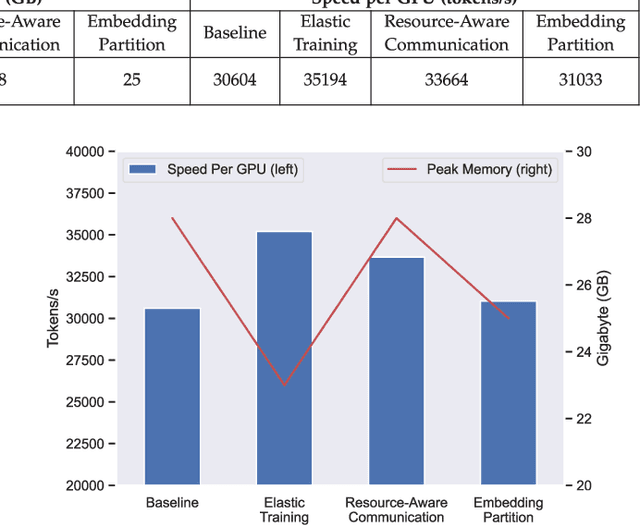
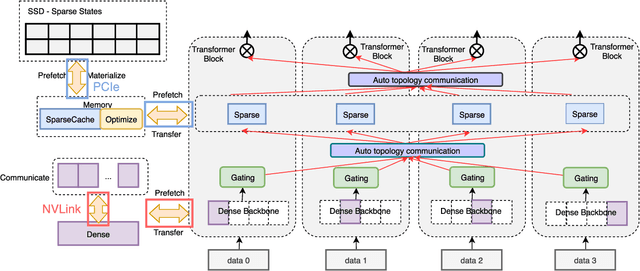
Abstract:With the increasing diversity of ML infrastructures nowadays, distributed training over heterogeneous computing systems is desired to facilitate the production of big models. Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models have been proposed to lower the cost of training subject to the overall size of models/data through gating and parallelism in a divide-and-conquer fashion. While DeepSpeed has made efforts in carrying out large-scale MoE training over heterogeneous infrastructures, the efficiency of training and inference could be further improved from several system aspects, including load balancing, communication/computation efficiency, and memory footprint limits. In this work, we present SE-MoE that proposes Elastic MoE training with 2D prefetch and Fusion communication over Hierarchical storage, so as to enjoy efficient parallelisms in various types. For scalable inference in a single node, especially when the model size is larger than GPU memory, SE-MoE forms the CPU-GPU memory jointly into a ring of sections to load the model, and executes the computation tasks across the memory sections in a round-robin manner for efficient inference. We carried out extensive experiments to evaluate SE-MoE, where SE-MoE successfully trains a Unified Feature Optimization (UFO) model with a Sparsely-Gated Mixture-of-Experts model of 12B parameters in 8 days on 48 A100 GPU cards. The comparison against the state-of-the-art shows that SE-MoE outperformed DeepSpeed with 33% higher throughput (tokens per second) in training and 13% higher throughput in inference in general. Particularly, under unbalanced MoE Tasks, e.g., UFO, SE-MoE achieved 64% higher throughput with 18% lower memory footprints. The code of the framework will be released on: https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.
HeterPS: Distributed Deep Learning With Reinforcement Learning Based Scheduling in Heterogeneous Environments
Nov 20, 2021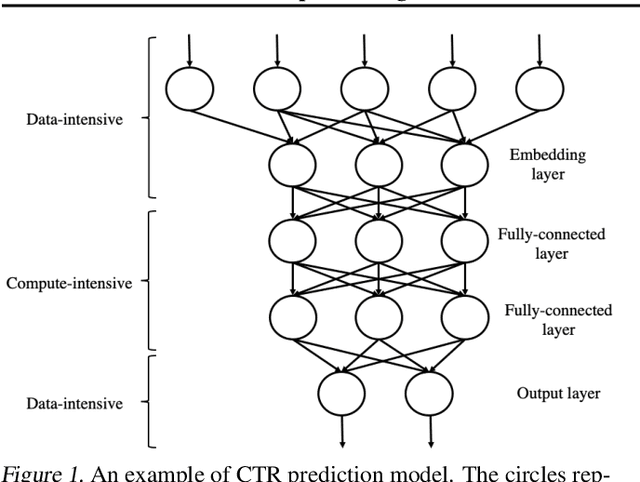

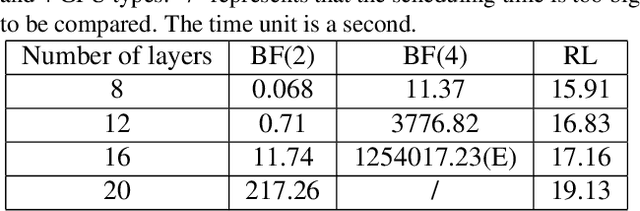
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) exploit many layers and a large number of parameters to achieve excellent performance. The training process of DNN models generally handles large-scale input data with many sparse features, which incurs high Input/Output (IO) cost, while some layers are compute-intensive. The training process generally exploits distributed computing resources to reduce training time. In addition, heterogeneous computing resources, e.g., CPUs, GPUs of multiple types, are available for the distributed training process. Thus, the scheduling of multiple layers to diverse computing resources is critical for the training process. To efficiently train a DNN model using the heterogeneous computing resources, we propose a distributed framework, i.e., Paddle-Heterogeneous Parameter Server (Paddle-HeterPS), composed of a distributed architecture and a Reinforcement Learning (RL)-based scheduling method. The advantages of Paddle-HeterPS are three-fold compared with existing frameworks. First, Paddle-HeterPS enables efficient training process of diverse workloads with heterogeneous computing resources. Second, Paddle-HeterPS exploits an RL-based method to efficiently schedule the workload of each layer to appropriate computing resources to minimize the cost while satisfying throughput constraints. Third, Paddle-HeterPS manages data storage and data communication among distributed computing resources. We carry out extensive experiments to show that Paddle-HeterPS significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in terms of throughput (14.5 times higher) and monetary cost (312.3% smaller). The codes of the framework are publicly available at: https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge