Xindi Tong
Learning to Optimize by Differentiable Programming
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Solving massive-scale optimization problems requires scalable first-order methods with low per-iteration cost. This tutorial highlights a shift in optimization: using differentiable programming not only to execute algorithms but to learn how to design them. Modern frameworks such as PyTorch, TensorFlow, and JAX enable this paradigm through efficient automatic differentiation. Embedding first-order methods within these systems allows end-to-end training that improves convergence and solution quality. Guided by Fenchel-Rockafellar duality, the tutorial demonstrates how duality-informed iterative schemes such as ADMM and PDHG can be learned and adapted. Case studies across LP, OPF, Laplacian regularization, and neural network verification illustrate these gains.
Certifying the Right to Be Forgotten: Primal-Dual Optimization for Sample and Label Unlearning in Vertical Federated Learning
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Federated unlearning has become an attractive approach to address privacy concerns in collaborative machine learning, for situations when sensitive data is remembered by AI models during the machine learning process. It enables the removal of specific data influences from trained models, aligning with the growing emphasis on the "right to be forgotten." While extensively studied in horizontal federated learning, unlearning in vertical federated learning (VFL) remains challenging due to the distributed feature architecture. VFL unlearning includes sample unlearning that removes specific data points' influence and label unlearning that removes entire classes. Since different parties hold complementary features of the same samples, unlearning tasks require cross-party coordination, creating computational overhead and complexities from feature interdependencies. To address such challenges, we propose FedORA (Federated Optimization for data Removal via primal-dual Algorithm), designed for sample and label unlearning in VFL. FedORA formulates the removal of certain samples or labels as a constrained optimization problem solved using a primal-dual framework. Our approach introduces a new unlearning loss function that promotes classification uncertainty rather than misclassification. An adaptive step size enhances stability, while an asymmetric batch design, considering the prior influence of the remaining data on the model, handles unlearning and retained data differently to efficiently reduce computational costs. We provide theoretical analysis proving that the model difference between FedORA and Train-from-scratch is bounded, establishing guarantees for unlearning effectiveness. Experiments on tabular and image datasets demonstrate that FedORA achieves unlearning effectiveness and utility preservation comparable to Train-from-scratch with reduced computation and communication overhead.
* Published in the IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security
Efficient Federated Unlearning with Adaptive Differential Privacy Preservation
Nov 17, 2024



Abstract:Federated unlearning (FU) offers a promising solution to effectively address the need to erase the impact of specific clients' data on the global model in federated learning (FL), thereby granting individuals the ``Right to be Forgotten". The most straightforward approach to achieve unlearning is to train the model from scratch, excluding clients who request data removal, but it is resource-intensive. Current state-of-the-art FU methods extend traditional FL frameworks by leveraging stored historical updates, enabling more efficient unlearning than training from scratch. However, the use of stored updates introduces significant privacy risks. Adversaries with access to these updates can potentially reconstruct clients' local data, a well-known vulnerability in the privacy domain. While privacy-enhanced techniques exist, their applications to FU scenarios that balance unlearning efficiency with privacy protection remain underexplored. To address this gap, we propose FedADP, a method designed to achieve both efficiency and privacy preservation in FU. Our approach incorporates an adaptive differential privacy (DP) mechanism, carefully balancing privacy and unlearning performance through a novel budget allocation strategy tailored for FU. FedADP also employs a dual-layered selection process, focusing on global models with significant changes and client updates closely aligned with the global model, reducing storage and communication costs. Additionally, a novel calibration method is introduced to facilitate effective unlearning. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that FedADP effectively manages the trade-off between unlearning efficiency and privacy protection.
T3: A Novel Zero-shot Transfer Learning Framework Iteratively Training on an Assistant Task for a Target Task
Sep 26, 2024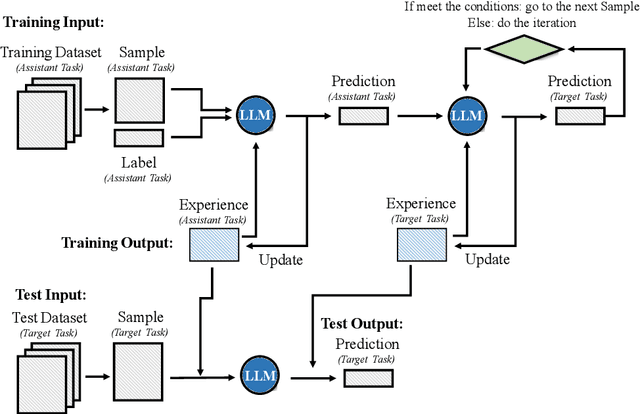
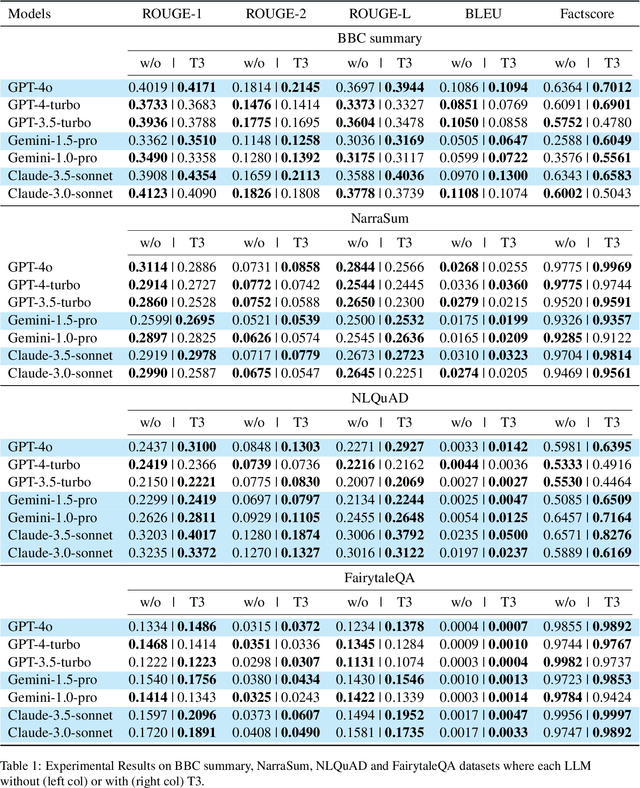
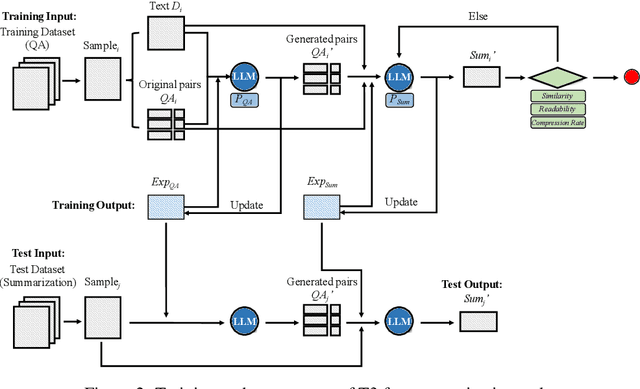
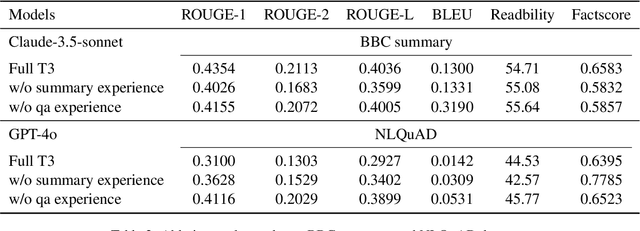
Abstract:Long text summarization, gradually being essential for efficiently processing large volumes of information, stays challenging for Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT and LLaMA families because of the insufficient open-sourced training datasets and the high requirement of contextual details dealing. To address the issue, we design a novel zero-shot transfer learning framework, abbreviated as T3, to iteratively training a baseline LLM on an assistant task for the target task, where the former should own richer data resources and share structural or semantic similarity with the latter. In practice, T3 is approached to deal with the long text summarization task by utilizing question answering as the assistant task, and further validated its effectiveness on the BBC summary, NarraSum, FairytaleQA, and NLQuAD datasets, with up to nearly 14% improvement in ROUGE, 35% improvement in BLEU, and 16% improvement in Factscore compared to three baseline LLMs, demonstrating its potential for more assistant-target task combinations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge