Xiaoyue Zhang
Online Resource Allocation with Non-Stationary Customers
Jan 30, 2024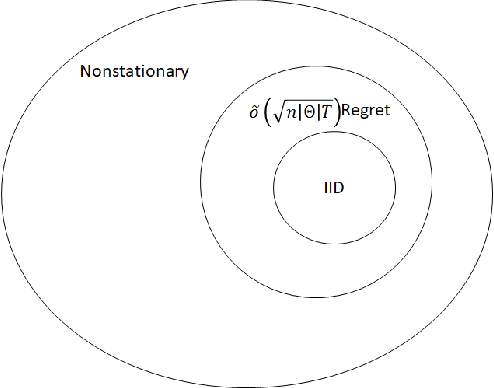
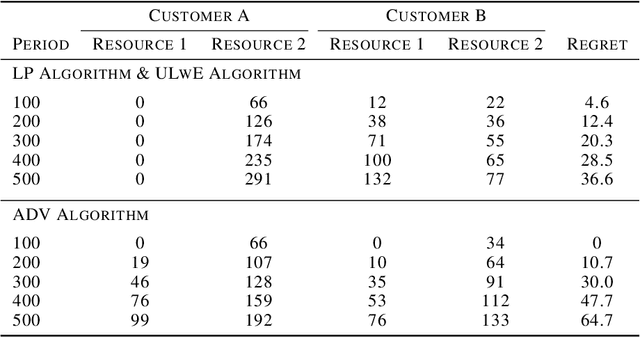
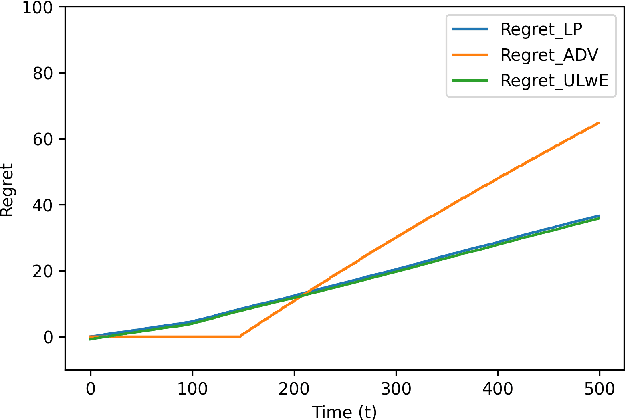
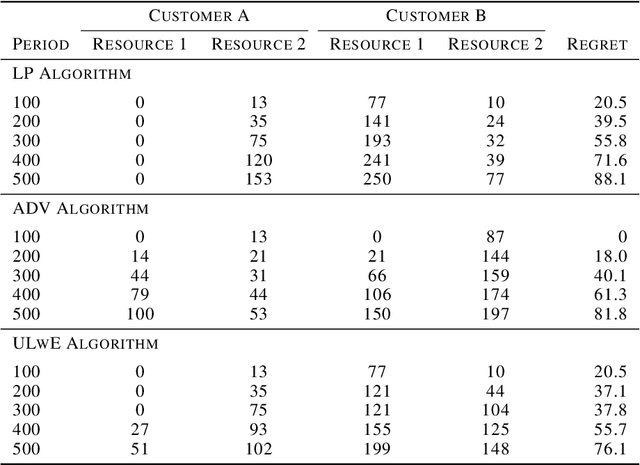
Abstract:We propose a novel algorithm for online resource allocation with non-stationary customer arrivals and unknown click-through rates. We assume multiple types of customers arrive in a nonstationary stochastic fashion, with unknown arrival rates in each period, and that customers' click-through rates are unknown and can only be learned online. By leveraging results from the stochastic contextual bandit with knapsack and online matching with adversarial arrivals, we develop an online scheme to allocate the resources to nonstationary customers. We prove that under mild conditions, our scheme achieves a ``best-of-both-world'' result: the scheme has a sublinear regret when the customer arrivals are near-stationary, and enjoys an optimal competitive ratio under general (non-stationary) customer arrival distributions. Finally, we conduct extensive numerical experiments to show our approach generates near-optimal revenues for all different customer scenarios.
Cross-domain Detection Transformer based on Spatial-aware and Semantic-aware Token Alignment
Jun 01, 2022
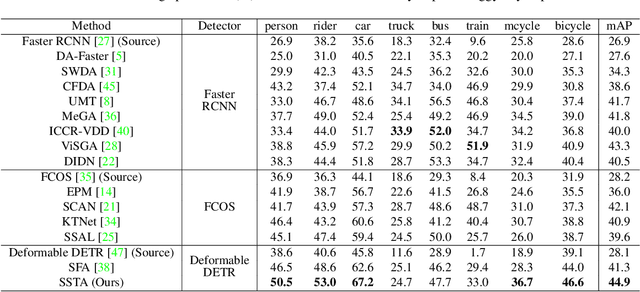
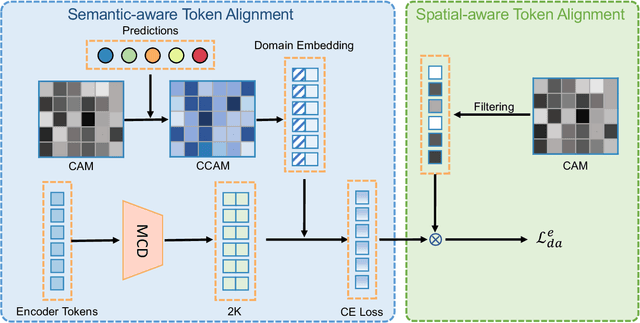
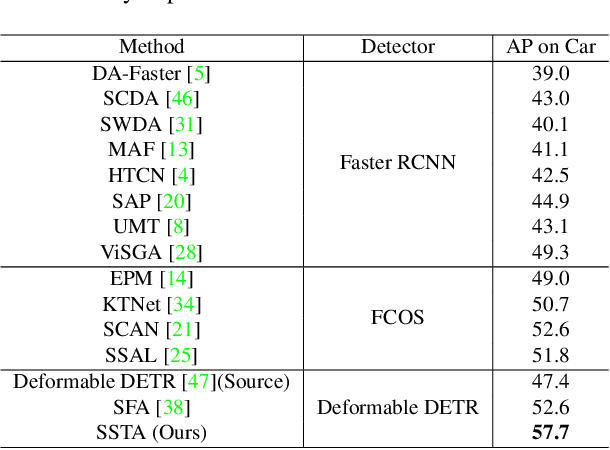
Abstract:Detection transformers like DETR have recently shown promising performance on many object detection tasks, but the generalization ability of those methods is still quite challenging for cross-domain adaptation scenarios. To address the cross-domain issue, a straightforward way is to perform token alignment with adversarial training in transformers. However, its performance is often unsatisfactory as the tokens in detection transformers are quite diverse and represent different spatial and semantic information. In this paper, we propose a new method called Spatial-aware and Semantic-aware Token Alignment (SSTA) for cross-domain detection transformers. In particular, we take advantage of the characteristics of cross-attention as used in detection transformer and propose the spatial-aware token alignment (SpaTA) and the semantic-aware token alignment (SemTA) strategies to guide the token alignment across domains. For spatial-aware token alignment, we can extract the information from the cross-attention map (CAM) to align the distribution of tokens according to their attention to object queries. For semantic-aware token alignment, we inject the category information into the cross-attention map and construct domain embedding to guide the learning of a multi-class discriminator so as to model the category relationship and achieve category-level token alignment during the entire adaptation process. We conduct extensive experiments on several widely-used benchmarks, and the results clearly show the effectiveness of our proposed method over existing state-of-the-art baselines.
Deform-GAN:An Unsupervised Learning Model for Deformable Registration
Feb 26, 2020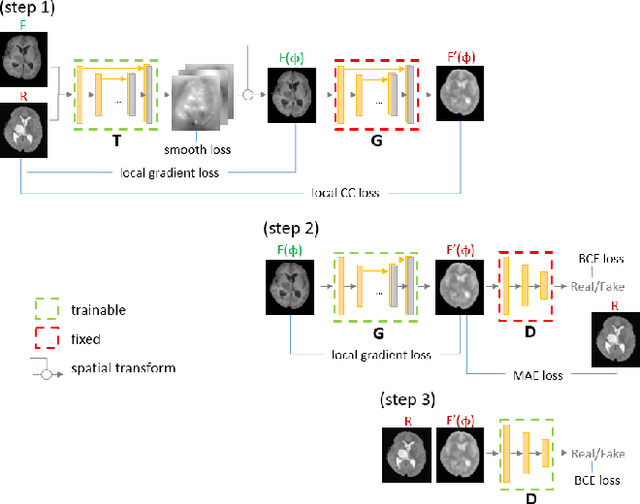
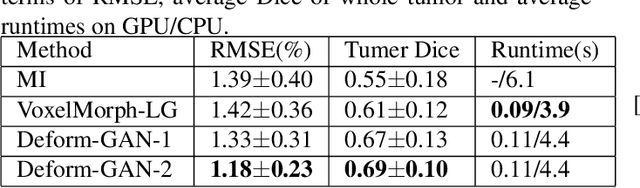
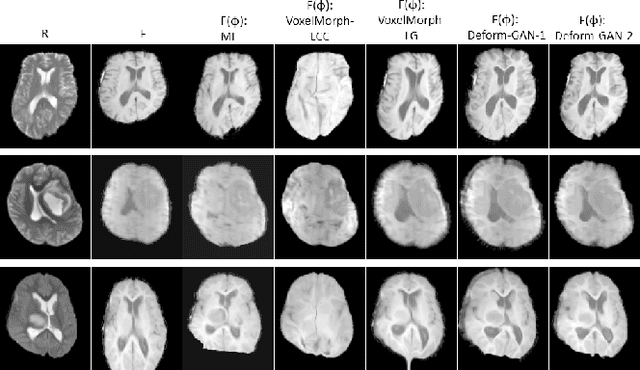
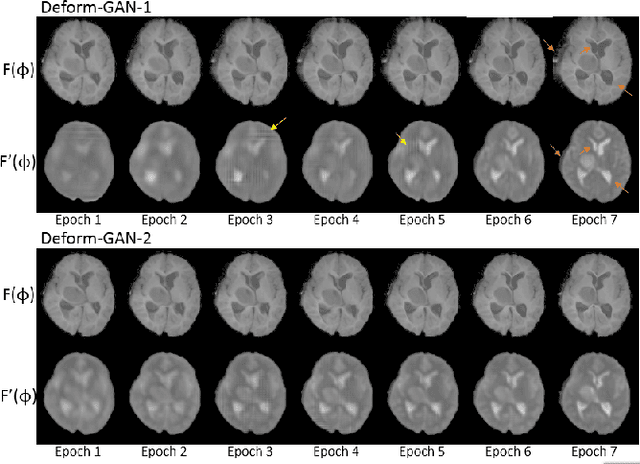
Abstract:Deformable registration is one of the most challenging task in the field of medical image analysis, especially for the alignment between different sequences and modalities. In this paper, a non-rigid registration method is proposed for 3D medical images leveraging unsupervised learning. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to introduce gradient loss into deep-learning-based registration. The proposed gradient loss is robust across sequences and modals for large deformation. Besides, adversarial learning approach is used to transfer multi-modal similarity to mono-modal similarity and improve the precision. Neither ground-truth nor manual labeling is required during training. We evaluated our network on a 3D brain registration task comprehensively. The experiments demonstrate that the proposed method can cope with the data which has non-functional intensity relations, noise and blur. Our approach outperforms other methods especially in accuracy and speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge