Xiaolu Kang
Enhanced Contrastive Learning with Multi-view Longitudinal Data for Chest X-ray Report Generation
Feb 27, 2025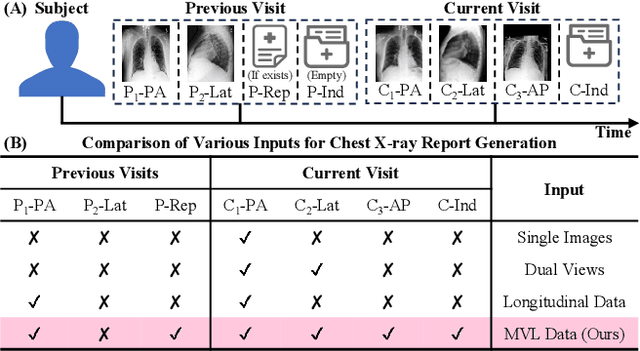
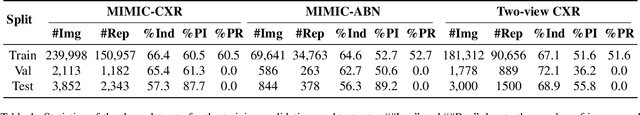
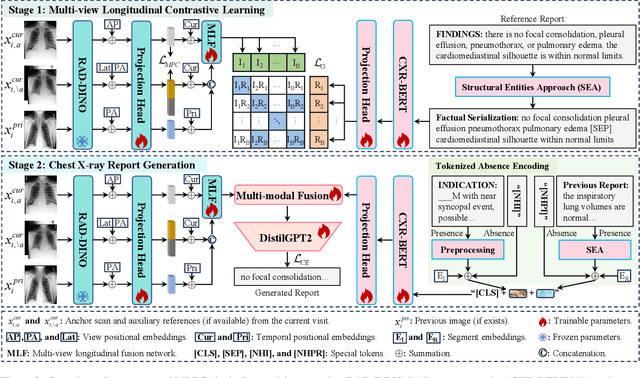
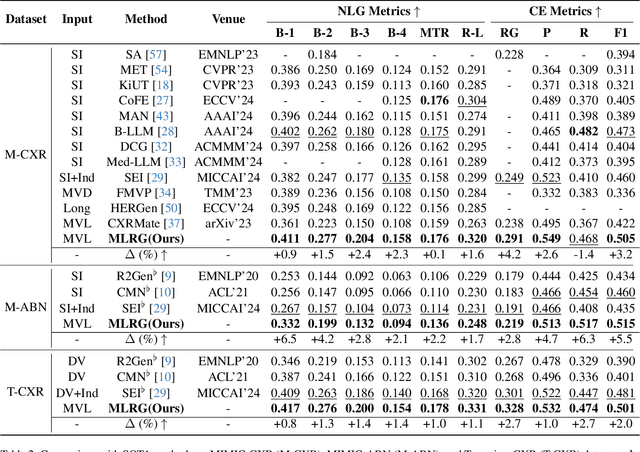
Abstract:Automated radiology report generation offers an effective solution to alleviate radiologists' workload. However, most existing methods focus primarily on single or fixed-view images to model current disease conditions, which limits diagnostic accuracy and overlooks disease progression. Although some approaches utilize longitudinal data to track disease progression, they still rely on single images to analyze current visits. To address these issues, we propose enhanced contrastive learning with Multi-view Longitudinal data to facilitate chest X-ray Report Generation, named MLRG. Specifically, we introduce a multi-view longitudinal contrastive learning method that integrates spatial information from current multi-view images and temporal information from longitudinal data. This method also utilizes the inherent spatiotemporal information of radiology reports to supervise the pre-training of visual and textual representations. Subsequently, we present a tokenized absence encoding technique to flexibly handle missing patient-specific prior knowledge, allowing the model to produce more accurate radiology reports based on available prior knowledge. Extensive experiments on MIMIC-CXR, MIMIC-ABN, and Two-view CXR datasets demonstrate that our MLRG outperforms recent state-of-the-art methods, achieving a 2.3% BLEU-4 improvement on MIMIC-CXR, a 5.5% F1 score improvement on MIMIC-ABN, and a 2.7% F1 RadGraph improvement on Two-view CXR.
Structural Entities Extraction and Patient Indications Incorporation for Chest X-ray Report Generation
May 23, 2024



Abstract:The automated generation of imaging reports proves invaluable in alleviating the workload of radiologists. A clinically applicable reports generation algorithm should demonstrate its effectiveness in producing reports that accurately describe radiology findings and attend to patient-specific indications. In this paper, we introduce a novel method, \textbf{S}tructural \textbf{E}ntities extraction and patient indications \textbf{I}ncorporation (SEI) for chest X-ray report generation. Specifically, we employ a structural entities extraction (SEE) approach to eliminate presentation-style vocabulary in reports and improve the quality of factual entity sequences. This reduces the noise in the following cross-modal alignment module by aligning X-ray images with factual entity sequences in reports, thereby enhancing the precision of cross-modal alignment and further aiding the model in gradient-free retrieval of similar historical cases. Subsequently, we propose a cross-modal fusion network to integrate information from X-ray images, similar historical cases, and patient-specific indications. This process allows the text decoder to attend to discriminative features of X-ray images, assimilate historical diagnostic information from similar cases, and understand the examination intention of patients. This, in turn, assists in triggering the text decoder to produce high-quality reports. Experiments conducted on MIMIC-CXR validate the superiority of SEI over state-of-the-art approaches on both natural language generation and clinical efficacy metrics.
Multi-scale Information Sharing and Selection Network with Boundary Attention for Polyp Segmentation
May 18, 2024Abstract:Polyp segmentation for colonoscopy images is of vital importance in clinical practice. It can provide valuable information for colorectal cancer diagnosis and surgery. While existing methods have achieved relatively good performance, polyp segmentation still faces the following challenges: (1) Varying lighting conditions in colonoscopy and differences in polyp locations, sizes, and morphologies. (2) The indistinct boundary between polyps and surrounding tissue. To address these challenges, we propose a Multi-scale information sharing and selection network (MISNet) for polyp segmentation task. We design a Selectively Shared Fusion Module (SSFM) to enforce information sharing and active selection between low-level and high-level features, thereby enhancing model's ability to capture comprehensive information. We then design a Parallel Attention Module (PAM) to enhance model's attention to boundaries, and a Balancing Weight Module (BWM) to facilitate the continuous refinement of boundary segmentation in the bottom-up process. Experiments on five polyp segmentation datasets demonstrate that MISNet successfully improved the accuracy and clarity of segmentation result, outperforming state-of-the-art methods.
Factual Serialization Enhancement: A Key Innovation for Chest X-ray Report Generation
May 15, 2024Abstract:The automation of writing imaging reports is a valuable tool for alleviating the workload of radiologists. Crucial steps in this process involve the cross-modal alignment between medical images and reports, as well as the retrieval of similar historical cases. However, the presence of presentation-style vocabulary (e.g., sentence structure and grammar) in reports poses challenges for cross-modal alignment. Additionally, existing methods for similar historical cases retrieval face suboptimal performance owing to the modal gap issue. In response, this paper introduces a novel method, named Factual Serialization Enhancement (FSE), for chest X-ray report generation. FSE begins with the structural entities approach to eliminate presentation-style vocabulary in reports, providing specific input for our model. Then, uni-modal features are learned through cross-modal alignment between images and factual serialization in reports. Subsequently, we present a novel approach to retrieve similar historical cases from the training set, leveraging aligned image features. These features implicitly preserve semantic similarity with their corresponding reference reports, enabling us to calculate similarity solely among aligned features. This effectively eliminates the modal gap issue for knowledge retrieval without the requirement for disease labels. Finally, the cross-modal fusion network is employed to query valuable information from these cases, enriching image features and aiding the text decoder in generating high-quality reports. Experiments on MIMIC-CXR and IU X-ray datasets from both specific and general scenarios demonstrate the superiority of FSE over state-of-the-art approaches in both natural language generation and clinical efficacy metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge