Xiangyang Yang
Learning Occlusion-Robust Vision Transformers for Real-Time UAV Tracking
Apr 12, 2025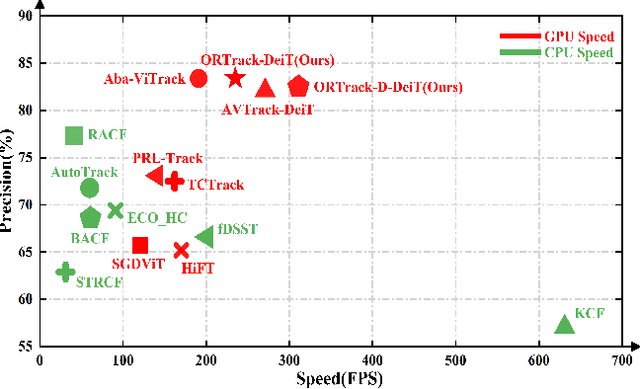
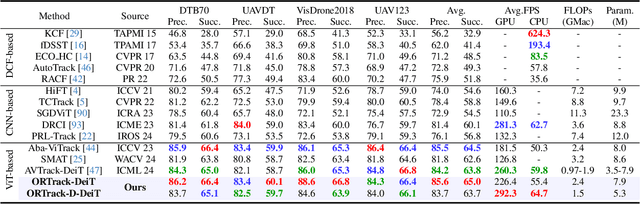
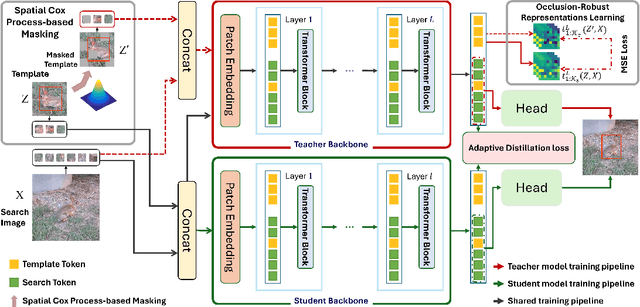
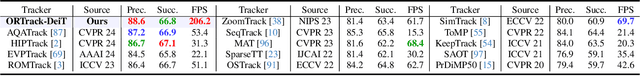
Abstract:Single-stream architectures using Vision Transformer (ViT) backbones show great potential for real-time UAV tracking recently. However, frequent occlusions from obstacles like buildings and trees expose a major drawback: these models often lack strategies to handle occlusions effectively. New methods are needed to enhance the occlusion resilience of single-stream ViT models in aerial tracking. In this work, we propose to learn Occlusion-Robust Representations (ORR) based on ViTs for UAV tracking by enforcing an invariance of the feature representation of a target with respect to random masking operations modeled by a spatial Cox process. Hopefully, this random masking approximately simulates target occlusions, thereby enabling us to learn ViTs that are robust to target occlusion for UAV tracking. This framework is termed ORTrack. Additionally, to facilitate real-time applications, we propose an Adaptive Feature-Based Knowledge Distillation (AFKD) method to create a more compact tracker, which adaptively mimics the behavior of the teacher model ORTrack according to the task's difficulty. This student model, dubbed ORTrack-D, retains much of ORTrack's performance while offering higher efficiency. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks validate the effectiveness of our method, demonstrating its state-of-the-art performance. Codes is available at https://github.com/wuyou3474/ORTrack.
Learning Adaptive and View-Invariant Vision Transformer with Multi-Teacher Knowledge Distillation for Real-Time UAV Tracking
Dec 28, 2024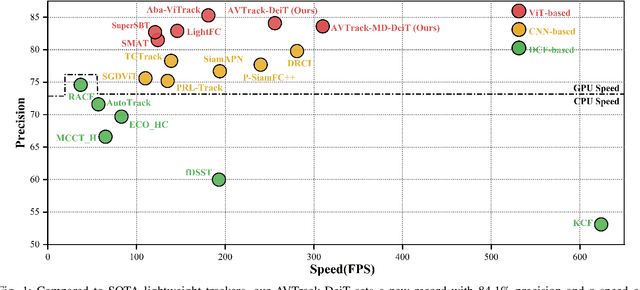
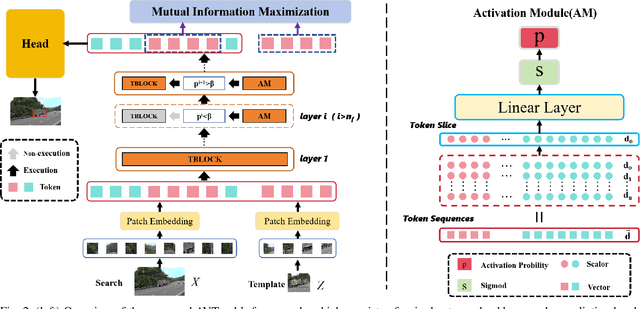
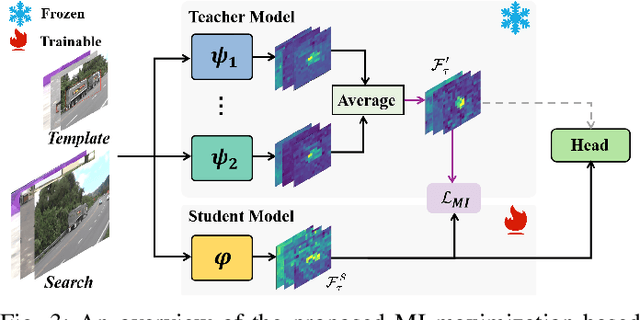
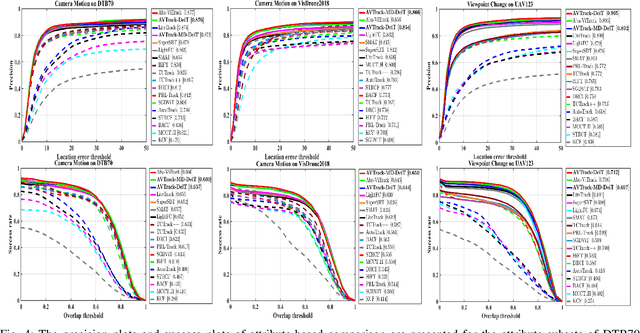
Abstract:Visual tracking has made significant strides due to the adoption of transformer-based models. Most state-of-the-art trackers struggle to meet real-time processing demands on mobile platforms with constrained computing resources, particularly for real-time unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) tracking. To achieve a better balance between performance and efficiency, we introduce AVTrack, an adaptive computation framework designed to selectively activate transformer blocks for real-time UAV tracking. The proposed Activation Module (AM) dynamically optimizes the ViT architecture by selectively engaging relevant components, thereby enhancing inference efficiency without significant compromise to tracking performance. Furthermore, to tackle the challenges posed by extreme changes in viewing angles often encountered in UAV tracking, the proposed method enhances ViTs' effectiveness by learning view-invariant representations through mutual information (MI) maximization. Two effective design principles are proposed in the AVTrack. Building on it, we propose an improved tracker, dubbed AVTrack-MD, which introduces the novel MI maximization-based multi-teacher knowledge distillation (MD) framework. It harnesses the benefits of multiple teachers, specifically the off-the-shelf tracking models from the AVTrack, by integrating and refining their outputs, thereby guiding the learning process of the compact student network. Specifically, we maximize the MI between the softened feature representations from the multi-teacher models and the student model, leading to improved generalization and performance of the student model, particularly in noisy conditions. Extensive experiments on multiple UAV tracking benchmarks demonstrate that AVTrack-MD not only achieves performance comparable to the AVTrack baseline but also reduces model complexity, resulting in a significant 17\% increase in average tracking speed.
MambaNUT: Nighttime UAV Tracking via Mamba and Adaptive Curriculum Learning
Dec 01, 2024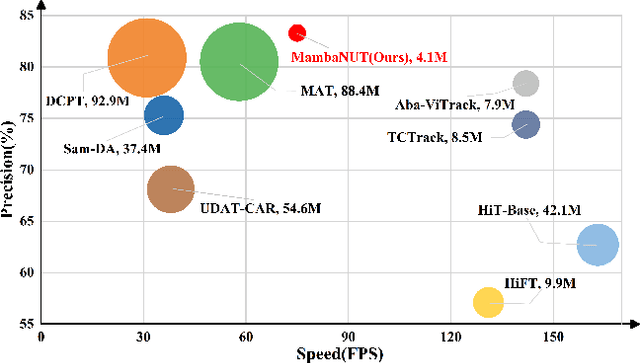
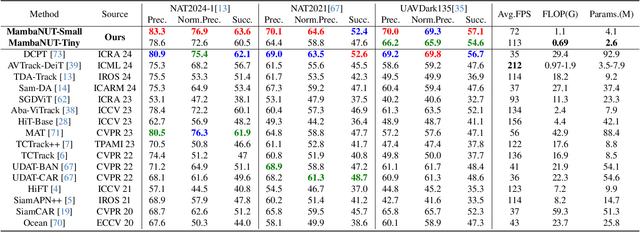

Abstract:Harnessing low-light enhancement and domain adaptation, nighttime UAV tracking has made substantial strides. However, over-reliance on image enhancement, scarcity of high-quality nighttime data, and neglecting the relationship between daytime and nighttime trackers, which hinders the development of an end-to-end trainable framework. Moreover, current CNN-based trackers have limited receptive fields, leading to suboptimal performance, while ViT-based trackers demand heavy computational resources due to their reliance on the self-attention mechanism. In this paper, we propose a novel pure Mamba-based tracking framework (\textbf{MambaNUT}) that employs a state space model with linear complexity as its backbone, incorporating a single-stream architecture that integrates feature learning and template-search coupling within Vision Mamba. We introduce an adaptive curriculum learning (ACL) approach that dynamically adjusts sampling strategies and loss weights, thereby improving the model's ability of generalization. Our ACL is composed of two levels of curriculum schedulers: (1) sampling scheduler that transforms the data distribution from imbalanced to balanced, as well as from easier (daytime) to harder (nighttime) samples; (2) loss scheduler that dynamically assigns weights based on data frequency and the IOU. Exhaustive experiments on multiple nighttime UAV tracking benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed MambaNUT achieves state-of-the-art performance while requiring lower computational costs. The code will be available.
Adaptively Bypassing Vision Transformer Blocks for Efficient Visual Tracking
Jun 12, 2024
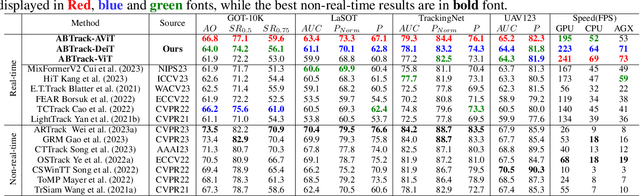
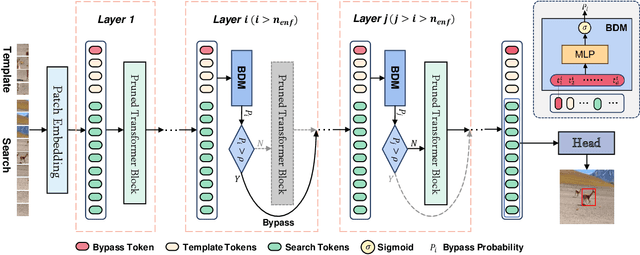
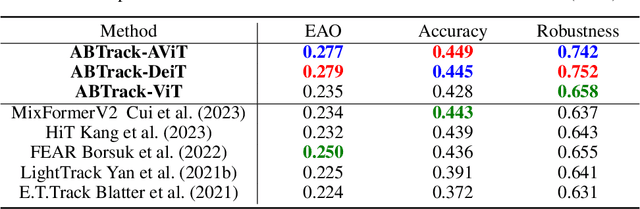
Abstract:Empowered by transformer-based models, visual tracking has advanced significantly. However, the slow speed of current trackers limits their applicability on devices with constrained computational resources. To address this challenge, we introduce ABTrack, an adaptive computation framework that adaptively bypassing transformer blocks for efficient visual tracking. The rationale behind ABTrack is rooted in the observation that semantic features or relations do not uniformly impact the tracking task across all abstraction levels. Instead, this impact varies based on the characteristics of the target and the scene it occupies. Consequently, disregarding insignificant semantic features or relations at certain abstraction levels may not significantly affect the tracking accuracy. We propose a Bypass Decision Module (BDM) to determine if a transformer block should be bypassed, which adaptively simplifies the architecture of ViTs and thus speeds up the inference process. To counteract the time cost incurred by the BDMs and further enhance the efficiency of ViTs, we innovatively adapt a pruning technique to reduce the dimension of the latent representation of tokens in each transformer block. Extensive experiments on multiple tracking benchmarks validate the effectiveness and generality of the proposed method and show that it achieves state-of-the-art performance. Code is released at: \href{https://github.com/1HykhqV3rU/ABTrack}
Learning Disentangled Representation with Mutual Information Maximization for Real-Time UAV Tracking
Aug 20, 2023Abstract:Efficiency has been a critical problem in UAV tracking due to limitations in computation resources, battery capacity, and unmanned aerial vehicle maximum load. Although discriminative correlation filters (DCF)-based trackers prevail in this field for their favorable efficiency, some recently proposed lightweight deep learning (DL)-based trackers using model compression demonstrated quite remarkable CPU efficiency as well as precision. Unfortunately, the model compression methods utilized by these works, though simple, are still unable to achieve satisfying tracking precision with higher compression rates. This paper aims to exploit disentangled representation learning with mutual information maximization (DR-MIM) to further improve DL-based trackers' precision and efficiency for UAV tracking. The proposed disentangled representation separates the feature into an identity-related and an identity-unrelated features. Only the latter is used, which enhances the effectiveness of the feature representation for subsequent classification and regression tasks. Extensive experiments on four UAV benchmarks, including UAV123@10fps, DTB70, UAVDT and VisDrone2018, show that our DR-MIM tracker significantly outperforms state-of-the-art UAV tracking methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge