Xiangchi Chen
Compliance while resisting: a shear-thickening fluid controller for physical human-robot interaction
Feb 03, 2025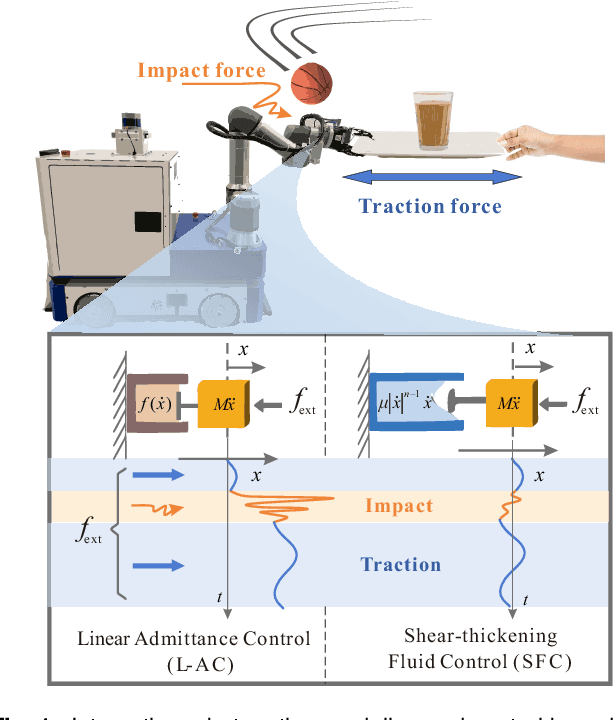

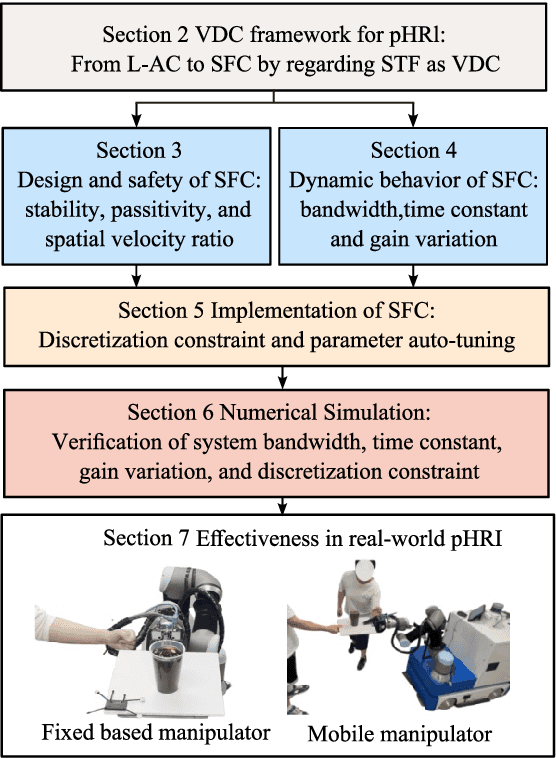
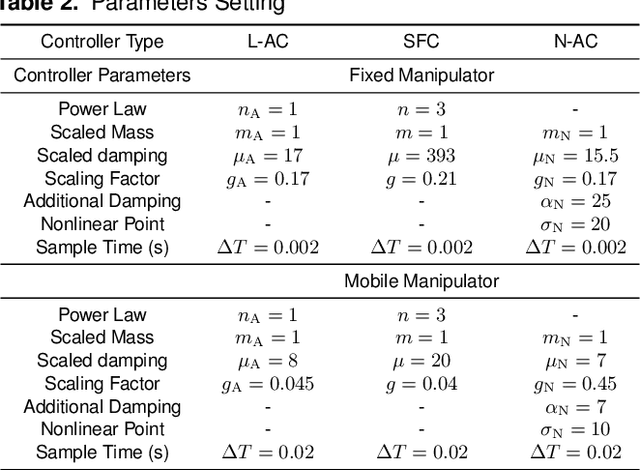
Abstract:Physical human-robot interaction (pHRI) is widely needed in many fields, such as industrial manipulation, home services, and medical rehabilitation, and puts higher demands on the safety of robots. Due to the uncertainty of the working environment, the pHRI may receive unexpected impact interference, which affects the safety and smoothness of the task execution. The commonly used linear admittance control (L-AC) can cope well with high-frequency small-amplitude noise, but for medium-frequency high-intensity impact, the effect is not as good. Inspired by the solid-liquid phase change nature of shear-thickening fluid, we propose a Shear-thickening Fluid Control (SFC) that can achieve both an easy human-robot collaboration and resistance to impact interference. The SFC's stability, passivity, and phase trajectory are analyzed in detail, the frequency and time domain properties are quantified, and parameter constraints in discrete control and coupled stability conditions are provided. We conducted simulations to compare the frequency and time domain characteristics of L-AC, nonlinear admittance controller (N-AC), and SFC, and validated their dynamic properties. In real-world experiments, we compared the performance of L-AC, N-AC, and SFC in both fixed and mobile manipulators. L-AC exhibits weak resistance to impact. N-AC can resist moderate impacts but not high-intensity ones, and may exhibit self-excited oscillations. In contrast, SFC demonstrated superior impact resistance and maintained stable collaboration, enhancing comfort in cooperative water delivery tasks. Additionally, a case study was conducted in a factory setting, further affirming the SFC's capability in facilitating human-robot collaborative manipulation and underscoring its potential in industrial applications.
Improving Redundancy Availability: Dynamic Subtasks Modulation for Robots with Redundancy Insufficiency
Dec 10, 2020



Abstract:This work presents an approach for robots to suitably carry out complex applications characterized by the presence of multiple additional constraints or subtasks (e.g. obstacle and self-collision avoidance) but subject to redundancy insufficiency. The proposed approach, based on a novel subtask merging strategy, enforces all subtasks in due course by dynamically modulating a virtual secondary task, where the task status and soft priority are incorporated to improve the overall efficiency of redundancy resolution. The proposed approach greatly improves the redundancy availability by unitizing and deploying subtasks in a fine-grained and compact manner. We build up our control framework on the null space projection, which guarantees the execution of subtasks does not interfere with the primary task. Experimental results on two case studies are presented to show the performance of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge