William Theisen
N-Modal Contrastive Losses with Applications to Social Media Data in Trimodal Space
Mar 18, 2024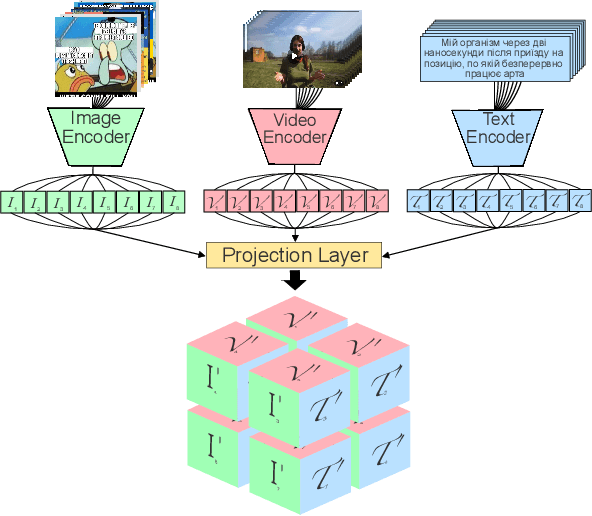
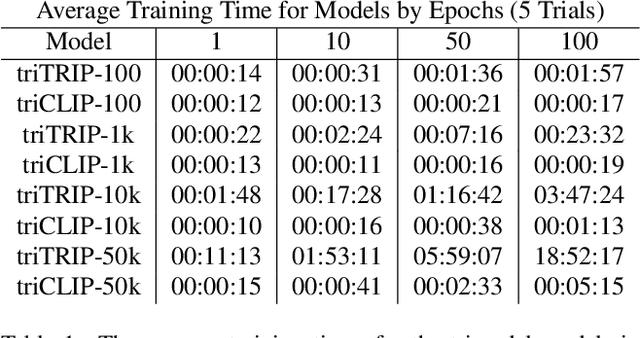
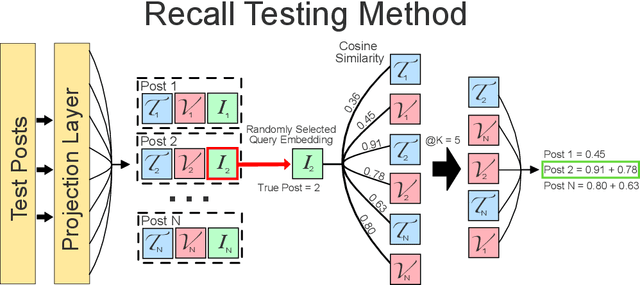
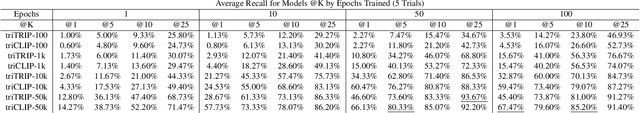
Abstract:The social media landscape of conflict dynamics has grown increasingly multi-modal. Recent advancements in model architectures such as CLIP have enabled researchers to begin studying the interplay between the modalities of text and images in a shared latent space. However, CLIP models fail to handle situations on social media when modalities present in a post expand above two. Social media dynamics often require understanding the interplay between not only text and images, but video as well. In this paper we explore an extension of the contrastive loss function to allow for any number of modalities, and demonstrate its usefulness in trimodal spaces on social media. By extending CLIP into three dimensions we can further aide understanding social media landscapes where all three modalities are present (an increasingly common situation). We use a newly collected public data set of Telegram posts containing all three modalities to train, and then demonstrate the usefulness of, a trimodal model in two OSINT scenarios: classifying a social media artifact post as either pro-Russian or pro-Ukrainian and identifying which account a given artifact originated from. While trimodal CLIP models have been explored before (though not on social media data), we also display a novel quadmodal CLIP model. This model can learn the interplay between text, image, video, and audio. We demonstrate new state-of-the-art baseline results on retrieval for quadmodel models moving forward.
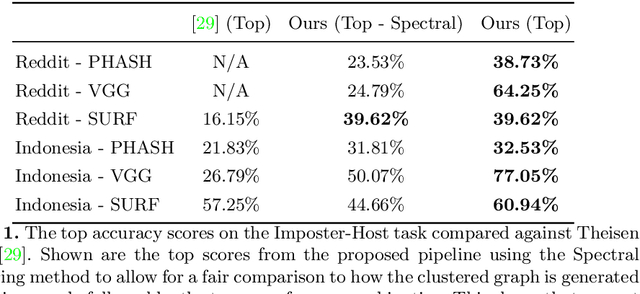
C-CLIP: Contrastive Image-Text Encoders to Close the Descriptive-Commentative Gap
Sep 06, 2023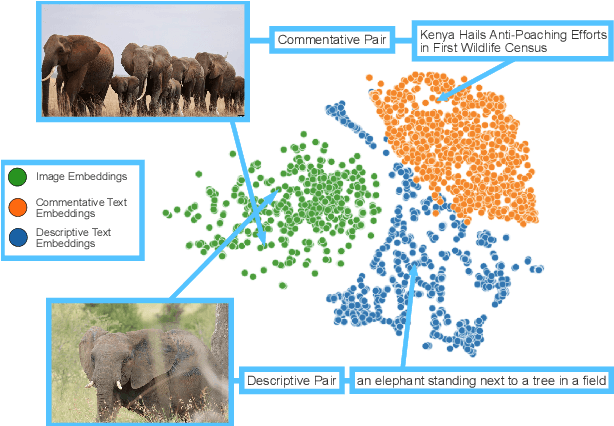
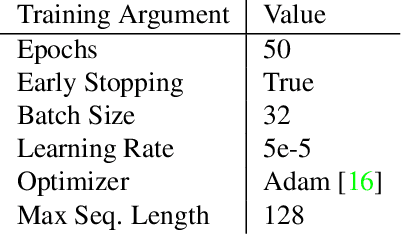

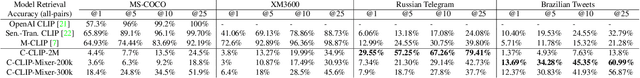
Abstract:The interplay between the image and comment on a social media post is one of high importance for understanding its overall message. Recent strides in multimodal embedding models, namely CLIP, have provided an avenue forward in relating image and text. However the current training regime for CLIP models is insufficient for matching content found on social media, regardless of site or language. Current CLIP training data is based on what we call ``descriptive'' text: text in which an image is merely described. This is something rarely seen on social media, where the vast majority of text content is ``commentative'' in nature. The captions provide commentary and broader context related to the image, rather than describing what is in it. Current CLIP models perform poorly on retrieval tasks where image-caption pairs display a commentative relationship. Closing this gap would be beneficial for several important application areas related to social media. For instance, it would allow groups focused on Open-Source Intelligence Operations (OSINT) to further aid efforts during disaster events, such as the ongoing Russian invasion of Ukraine, by easily exposing data to non-technical users for discovery and analysis. In order to close this gap we demonstrate that training contrastive image-text encoders on explicitly commentative pairs results in large improvements in retrieval results, with the results extending across a variety of non-English languages.
MEWS: Real-time Social Media Manipulation Detection and Analysis
May 13, 2022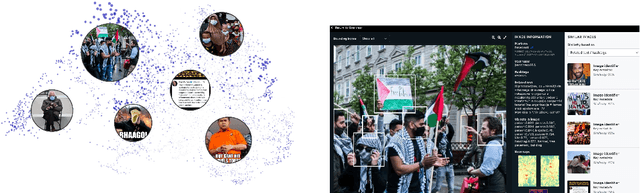
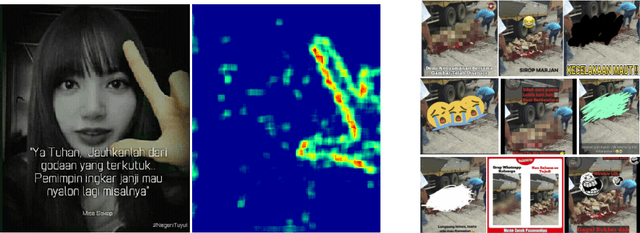

Abstract:This article presents a beta-version of MEWS (Misinformation Early Warning System). It describes the various aspects of the ingestion, manipulation detection, and graphing algorithms employed to determine--in near real-time--the relationships between social media images as they emerge and spread on social media platforms. By combining these various technologies into a single processing pipeline, MEWS can identify manipulated media items as they arise and identify when these particular items begin trending on individual social media platforms or even across multiple platforms. The emergence of a novel manipulation followed by rapid diffusion of the manipulated content suggests a disinformation campaign.
Motif Mining: Finding and Summarizing Remixed Image Content
Mar 17, 2022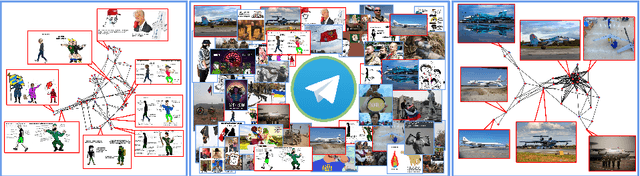
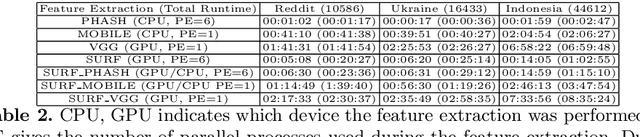
Abstract:On the internet, images are no longer static; they have become dynamic content. Thanks to the availability of smartphones with cameras and easy-to-use editing software, images can be remixed (i.e., redacted, edited, and recombined with other content) on-the-fly and with a world-wide audience that can repeat the process. From digital art to memes, the evolution of images through time is now an important topic of study for digital humanists, social scientists, and media forensics specialists. However, because typical data sets in computer vision are composed of static content, the development of automated algorithms to analyze remixed content has been limited. In this paper, we introduce the idea of Motif Mining - the process of finding and summarizing remixed image content in large collections of unlabeled and unsorted data. In this paper, this idea is formalized and a reference implementation is introduced. Experiments are conducted on three meme-style data sets, including a newly collected set associated with the information war in the Russo-Ukrainian conflict. The proposed motif mining approach is able to identify related remixed content that, when compared to similar approaches, more closely aligns with the preferences and expectations of human observers.
Automatic Discovery of Political Meme Genres with Diverse Appearances
Jan 17, 2020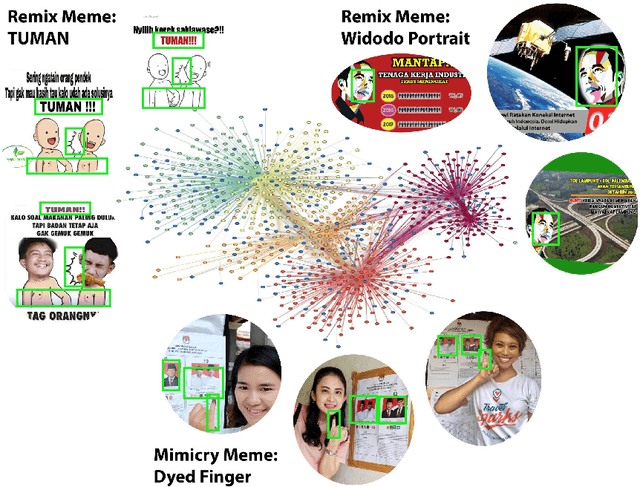
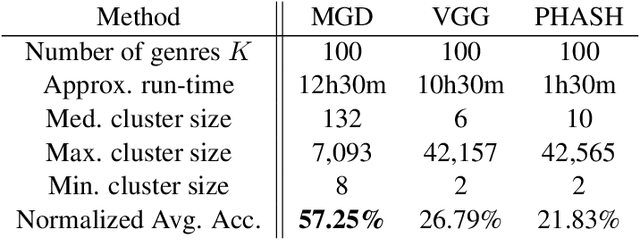
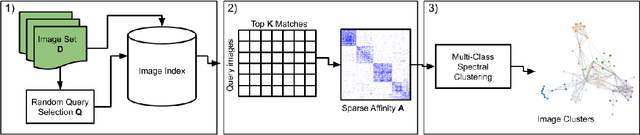

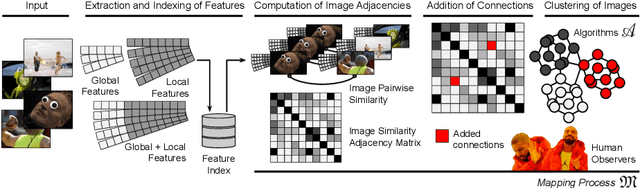
Abstract:Forms of human communication are not static --- we expect some evolution in the way information is conveyed over time because of advances in technology. One example of this phenomenon is the image-based meme, which has emerged as a dominant form of political messaging in the past decade. While originally used to spread jokes on social media, memes are now having an outsized impact on public perception of world events. A significant challenge in automatic meme analysis has been the development of a strategy to match memes from within a single genre when the appearances of the images vary. Such variation is especially common in memes exhibiting mimicry. For example, when voters perform a common hand gesture to signal their support for a candidate. In this paper we introduce a scalable automated visual recognition pipeline for discovering political meme genres of diverse appearance. This pipeline can ingest meme images from a social network, apply computer vision-based techniques to extract local features and index new images into a database, and then organize the memes into related genres. To validate this approach, we perform a large case study on the 2019 Indonesian Presidential Election using a new dataset of over two million images collected from Twitter and Instagram. Results show that this approach can discover new meme genres with visually diverse images that share common stylistic elements, paving the way forward for further work in semantic analysis and content attribution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge