William Adorno
HMIC: Hierarchical Medical Image Classification, A Deep Learning Approach
Jun 23, 2020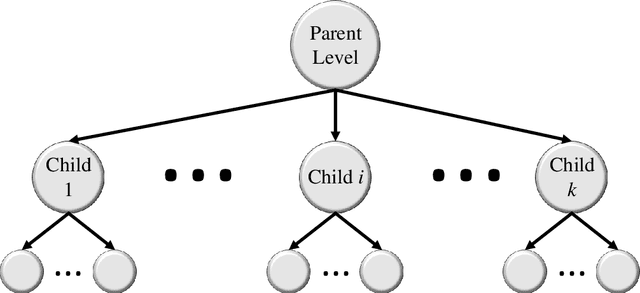
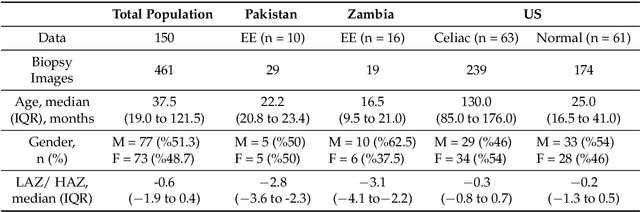
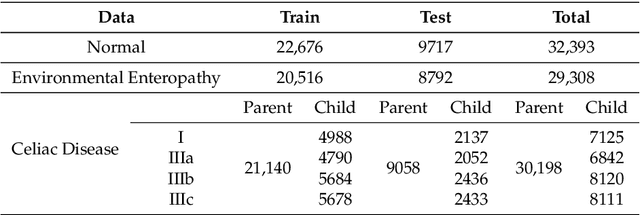
Abstract:Image classification is central to the big data revolution in medicine. Improved information processing methods for diagnosis and classification of digital medical images have shown to be successful via deep learning approaches. As this field is explored, there are limitations to the performance of traditional supervised classifiers. This paper outlines an approach that is different from the current medical image classification tasks that view the issue as multi-class classification. We performed a hierarchical classification using our Hierarchical Medical Image classification (HMIC) approach. HMIC uses stacks of deep learning models to give particular comprehension at each level of the clinical picture hierarchy. For testing our performance, we use biopsy of the small bowel images that contain three categories in the parent level (Celiac Disease, Environmental Enteropathy, and histologically normal controls). For the child level, Celiac Disease Severity is classified into 4 classes (I, IIIa, IIIb, and IIIC).
Diagnosis of Celiac Disease and Environmental Enteropathy on Biopsy Images Using Color Balancing on Convolutional Neural Networks
Apr 24, 2019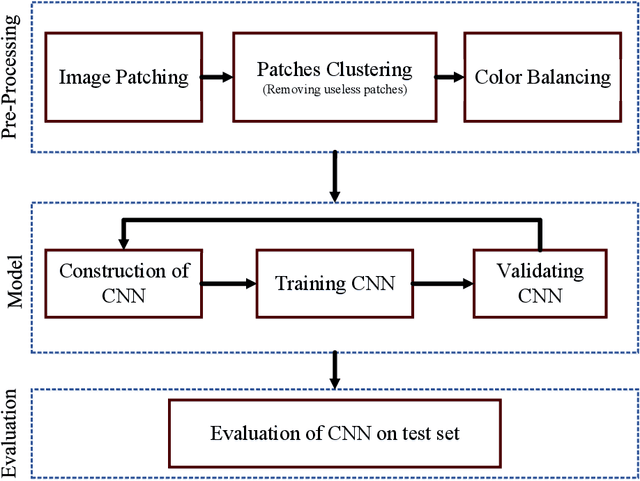
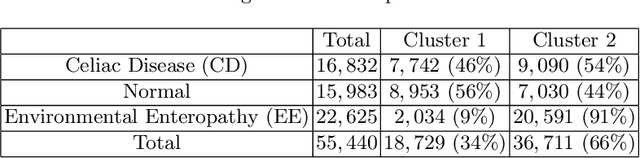
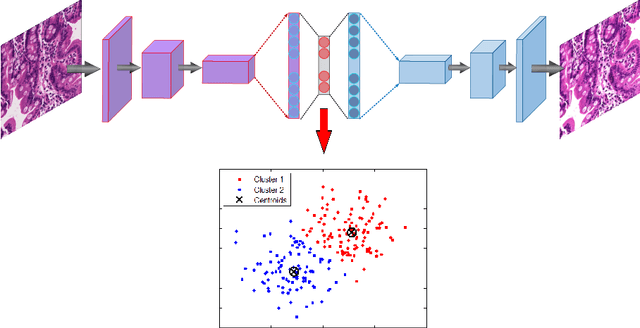
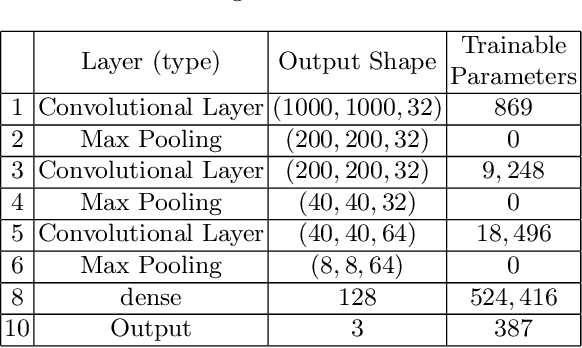
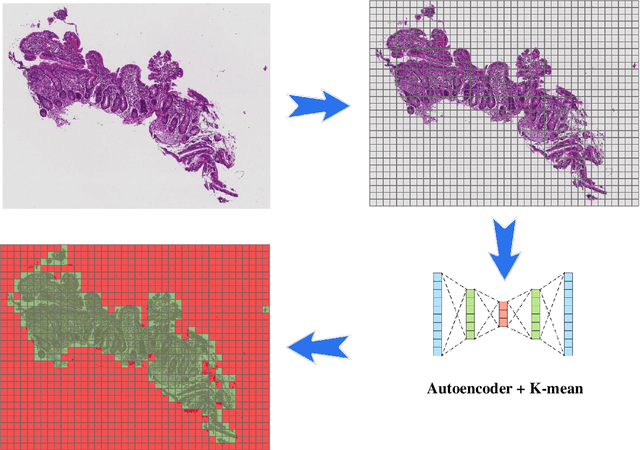
Abstract:Celiac Disease (CD) and Environmental Enteropathy (EE) are common causes of malnutrition and adversely impact normal childhood development. CD is an autoimmune disorder that is prevalent worldwide and is caused by an increased sensitivity to gluten. Gluten exposure destructs the small intestinal epithelial barrier, resulting in nutrient mal-absorption and childhood under-nutrition. EE also results in barrier dysfunction but is thought to be caused by an increased vulnerability to infections. EE has been implicated as the predominant cause of under-nutrition, oral vaccine failure, and impaired cognitive development in low-and-middle-income countries. Both conditions require a tissue biopsy for diagnosis, and a major challenge of interpreting clinical biopsy images to differentiate between these gastrointestinal diseases is striking histopathologic overlap between them. In the current study, we propose a convolutional neural network (CNN) to classify duodenal biopsy images from subjects with CD, EE, and healthy controls. We evaluated the performance of our proposed model using a large cohort containing 1000 biopsy images. Our evaluations show that the proposed model achieves an area under ROC of 0.99, 1.00, and 0.97 for CD, EE, and healthy controls, respectively. These results demonstrate the discriminative power of the proposed model in duodenal biopsies classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge