S. Asad Ali
Self-Attentive Adversarial Stain Normalization
Sep 04, 2019
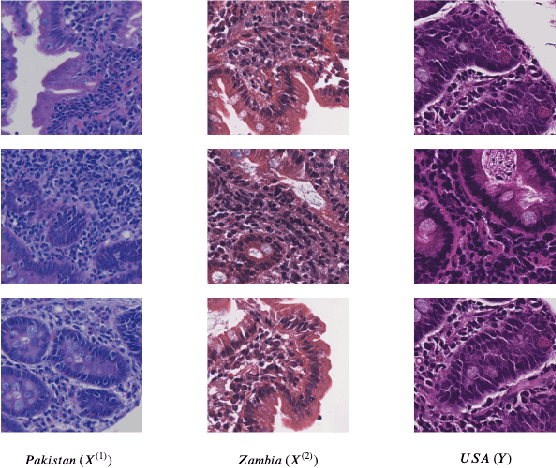
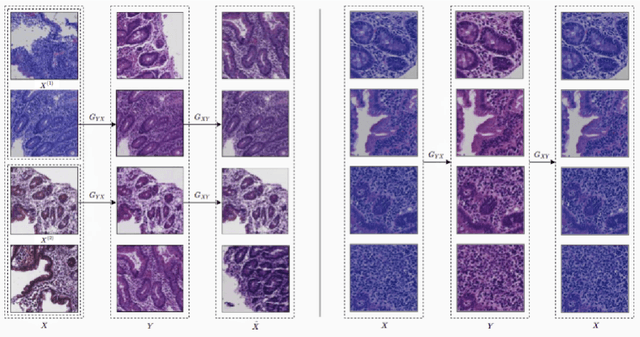

Abstract:Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stained Whole Slide Images (WSIs) are utilized for biopsy visualization-based diagnostic and prognostic assessment of diseases. Variation in the H&E staining process across different lab sites can lead to significant variations in biopsy image appearance. These variations introduce an undesirable bias when the slides are examined by pathologists or used for training deep learning models. To reduce this bias, slides need to be translated to a common domain of stain appearance before analysis. We propose a Self-Attentive Adversarial Stain Normalization (SAASN) approach for the normalization of multiple stain appearances to a common domain. This unsupervised generative adversarial approach includes self-attention mechanism for synthesizing images with finer detail while preserving the structural consistency of the biopsy features during translation. SAASN demonstrates consistent and superior performance compared to other popular stain normalization techniques on H&E stained duodenal biopsy image data.
Diagnosis of Celiac Disease and Environmental Enteropathy on Biopsy Images Using Color Balancing on Convolutional Neural Networks
Apr 24, 2019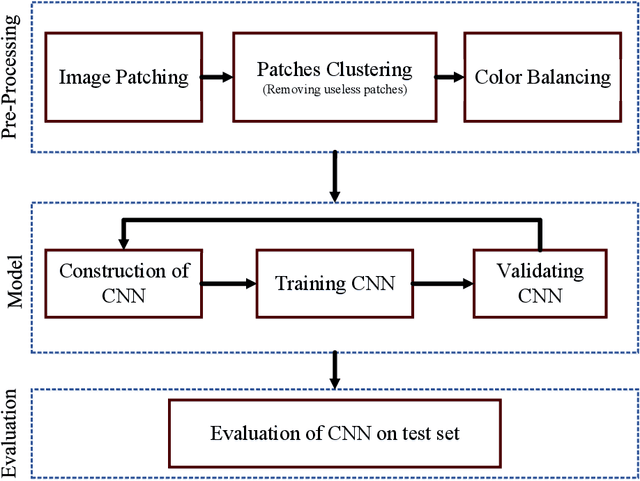
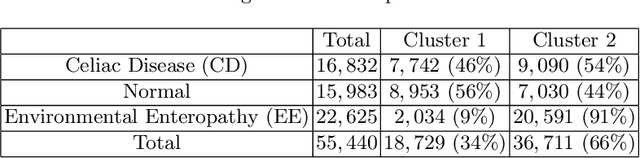
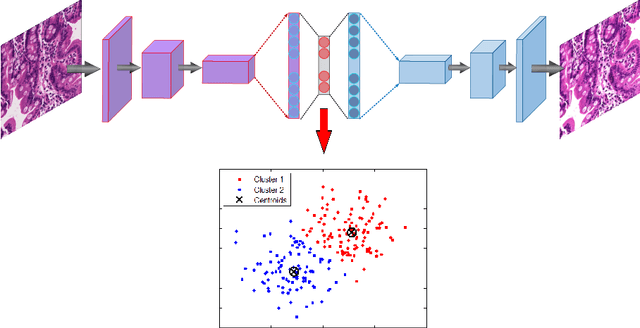
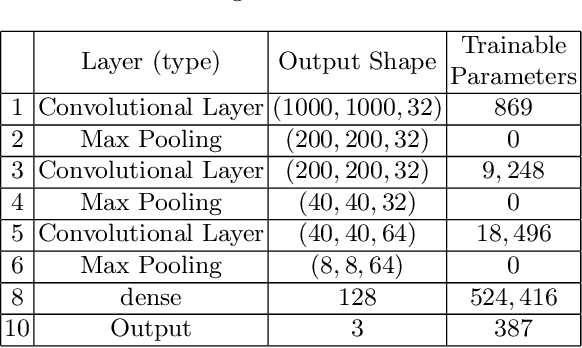
Abstract:Celiac Disease (CD) and Environmental Enteropathy (EE) are common causes of malnutrition and adversely impact normal childhood development. CD is an autoimmune disorder that is prevalent worldwide and is caused by an increased sensitivity to gluten. Gluten exposure destructs the small intestinal epithelial barrier, resulting in nutrient mal-absorption and childhood under-nutrition. EE also results in barrier dysfunction but is thought to be caused by an increased vulnerability to infections. EE has been implicated as the predominant cause of under-nutrition, oral vaccine failure, and impaired cognitive development in low-and-middle-income countries. Both conditions require a tissue biopsy for diagnosis, and a major challenge of interpreting clinical biopsy images to differentiate between these gastrointestinal diseases is striking histopathologic overlap between them. In the current study, we propose a convolutional neural network (CNN) to classify duodenal biopsy images from subjects with CD, EE, and healthy controls. We evaluated the performance of our proposed model using a large cohort containing 1000 biopsy images. Our evaluations show that the proposed model achieves an area under ROC of 0.99, 1.00, and 0.97 for CD, EE, and healthy controls, respectively. These results demonstrate the discriminative power of the proposed model in duodenal biopsies classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge