Wenchao Zhai
6G Downlink Transmission via Rate Splitting Space Division Multiple Access Based on Grouped Code Index Modulation
Mar 01, 2021


Abstract:A novel rate splitting space division multiple access (SDMA) scheme based on grouped code index modulation (GrCIM) is proposed for the sixth generation (6G) downlink transmission. The proposed RSMA-GrCIM scheme transmits information to multiple user equipments (UEs) through the space division multiple access (SDMA) technique, and exploits code index modulation for rate splitting. Since the CIM scheme conveys information bits via the index of the selected Walsh code and binary phase shift keying (BPSK) signal, our RSMA scheme transmits the private messages of each user through the indices, and the common messages via the BPSK signal. Moreover, the Walsh code set is grouped into several orthogonal subsets to eliminate the interference from other users. A maximum likelihood (ML) detector is used to recovery the source bits, and a mathematical analysis is provided for the upper bound bit error ratio (BER) of each user. Comparisons are also made between our proposed scheme and the traditional SDMA scheme in spectrum utilization, number of available UEs, etc. Numerical results are given to verify the effectiveness of the proposed SDMA-GrCIM scheme.
Smart City Enabled by 5G/6G Networks: An Intelligent Hybrid Random Access Scheme
Jan 16, 2021



Abstract:The Internet of Things (IoT) is the enabler for smart city to achieve the envision of the "Internet of Everything" by intelligently connecting devices without human interventions. The explosive growth of IoT devices makes the amount of business data generated by machine-type communications (MTC) account for a great proportion in all communication services. The fifth-generation (5G) specification for cellular networks defines two types of application scenarios for MTC: One is massive machine type communications (mMTC) requiring massive connections, while the other is ultra-reliable low latency communications (URLLC) requiring high reliability and low latency communications. 6G, as the next generation beyond 5G, will have even stronger scales of mMTC and URLLC. mMTC and URLLC will co-exist in MTC networks for 5G 6G-enabled smart city. To enable massive and reliable LLC access to such heterogeneous MTC networks where mMTC and URLLC co-exist, in this article, we introduce the network architecture of heterogeneous MTC networks, and propose an intelligent hybrid random access scheme for 5G/6G-enabled smart city. Numerical results show that, compared to the benchmark schemes, the proposed scheme significantly improves the successful access probability, and satisfies the diverse quality of services requirements of URLLC and mMTC devices.
A GCICA Grant-Free Random Access Scheme for M2M Communications in Crowded Massive MIMO Systems
Dec 25, 2020



Abstract:A high success rate of grant-free random access scheme is proposed to support massive access for machine-to-machine communications in massive multipleinput multiple-output systems. This scheme allows active user equipments (UEs) to transmit their modulated uplink messages along with super pilots consisting of multiple sub-pilots to a base station (BS). Then, the BS performs channel state information (CSI) estimation and uplink message decoding by utilizing a proposed graph combined clustering independent component analysis (GCICA) decoding algorithm, and then employs the estimated CSIs to detect active UEs by utilizing the characteristic of asymptotic favorable propagation of massive MIMO channel. We call this proposed scheme as GCICA based random access (GCICA-RA) scheme. We analyze the successful access probability, missed detection probability, and uplink throughput of the GCICA-RA scheme. Numerical results show that, the GCICA-RA scheme significantly improves the successful access probability and uplink throughput, decreases missed detection probability, and provides low CSI estimation error at the same time.
LSTM-Aided Hybrid Random Access Scheme for 6G Heterogeneous MTC Networks
Dec 25, 2020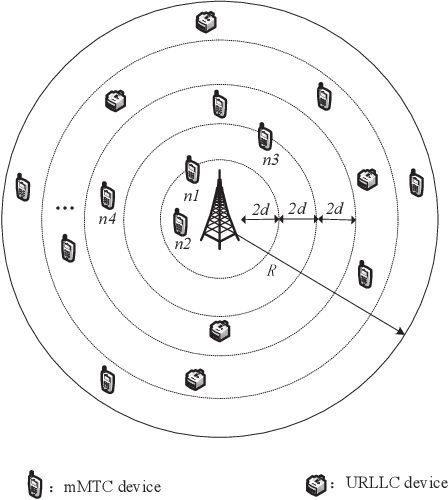
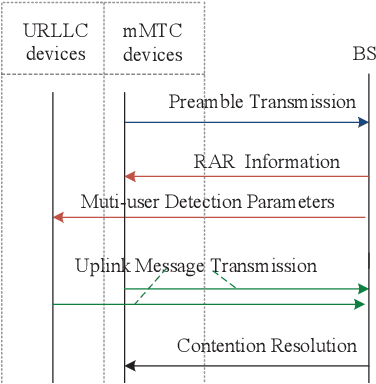
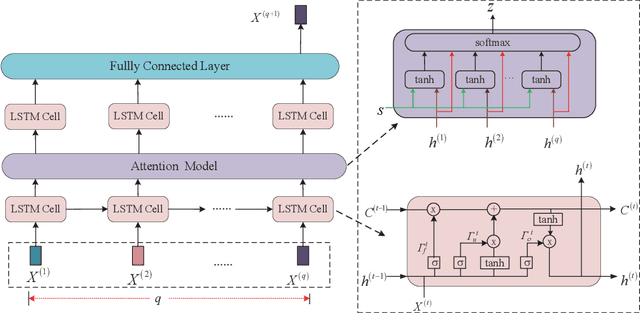

Abstract:An LSTM-aided hybrid random access scheme (LSTMH-RA) is proposed to support diverse quality of service (QoS) requirements in 6G MTC heterogeneous networks where URLLC and mMTC devices coexist. This scheme employs an attention-based LSTM prediction model to predict the number of active URLLC devices, determines the parameters of the multi-user detection algorithm dynamically, and then allows URLLC devices to access the network via a two-step contention-free access procedure, to meet latency and reliability access requirements; mMTC devices access the network via a contentionbased TA-aided access mechanism to meet massive access requirement. We analyze the successful access probability of the LSTMH-RA scheme. Numerical results show that, compared to the benchmark schemes, the LSTMH-RA scheme significantly improves the successful access probability, and satisfies the diverse QoS requirements of URLLC and mMTC devices
A Comprehensive Survey of 6G Wireless Communications
Dec 21, 2020



Abstract:While fifth-generation (5G) communications are being rolled out worldwide, sixth-generation (6G) communications have attracted much attention from both the industry and the academia. Compared with 5G, 6G will have a wider frequency band, higher transmission rate, spectrum efficiency, greater connection capacity, shorter delay, wider coverage, and stronger anti-interference capability to satisfy various network requirements. In this paper, we present a survey of potential essential technologies in 6G. In particular, we will give an insightful understanding of the paradigms and applications of the future 6G wireless communications by introducing index modulation (IM), artificial intelligence (AI), intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRS), simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT), space-air-ground-sea integrated network (SAGSIN), terahertz (THz), visible light communications (VLC), blockchain-enabled wireless network, holographic radio, full-duplex technology (FD), Cell-Free Massive MIMO (CFmMM), and security and privacy problems behind technologies mentioned above.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge