Wenchang Shi
Fight Fire with Fire: Combating Adversarial Patch Attacks using Pattern-randomized Defensive Patches
Nov 10, 2023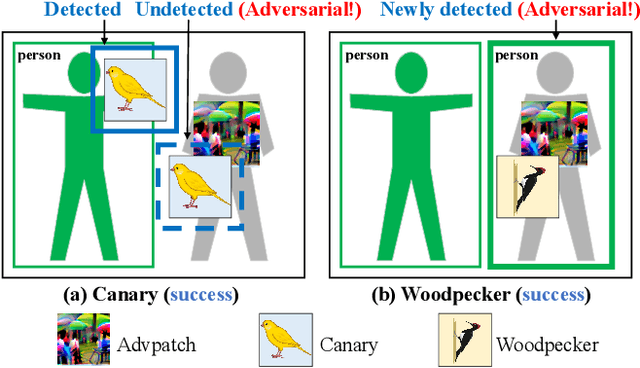
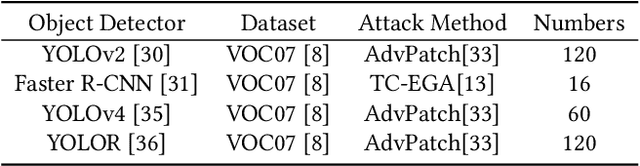
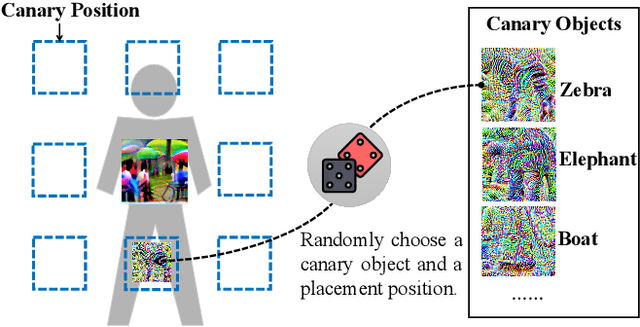
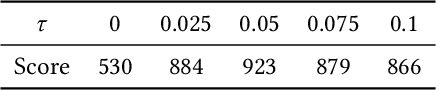
Abstract:Object detection has found extensive applications in various tasks, but it is also susceptible to adversarial patch attacks. Existing defense methods often necessitate modifications to the target model or result in unacceptable time overhead. In this paper, we adopt a counterattack approach, following the principle of "fight fire with fire," and propose a novel and general methodology for defending adversarial attacks. We utilize an active defense strategy by injecting two types of defensive patches, canary and woodpecker, into the input to proactively probe or weaken potential adversarial patches without altering the target model. Moreover, inspired by randomization techniques employed in software security, we employ randomized canary and woodpecker injection patterns to defend against defense-aware attacks. The effectiveness and practicality of the proposed method are demonstrated through comprehensive experiments. The results illustrate that canary and woodpecker achieve high performance, even when confronted with unknown attack methods, while incurring limited time overhead. Furthermore, our method also exhibits sufficient robustness against defense-aware attacks, as evidenced by adaptive attack experiments.
Detecting Adversarial Image Examples in Deep Networks with Adaptive Noise Reduction
Jun 03, 2018
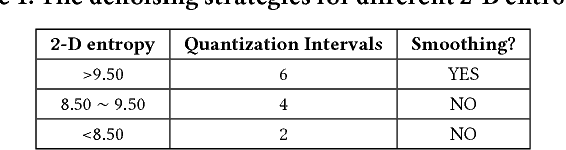
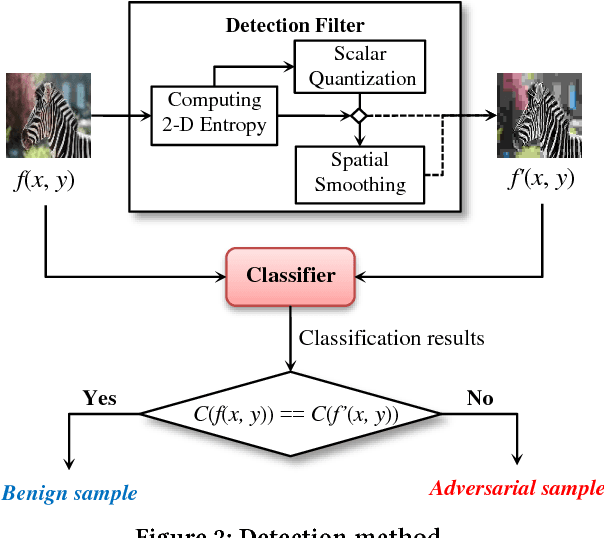
Abstract:Recently, many studies have demonstrated deep neural network (DNN) classifiers can be fooled by the adversarial example, which is crafted via introducing some perturbations into an original sample. Accordingly, some powerful defense techniques were proposed. However, existing defense techniques often require modifying the target model or depend on the prior knowledge of attacks. In this paper, we propose a straightforward method for detecting adversarial image examples, which can be directly deployed into unmodified off-the-shelf DNN models. We consider the perturbation to images as a kind of noise and introduce two classic image processing techniques, scalar quantization and smoothing spatial filter, to reduce its effect. The image entropy is employed as a metric to implement an adaptive noise reduction for different kinds of images. Consequently, the adversarial example can be effectively detected by comparing the classification results of a given sample and its denoised version, without referring to any prior knowledge of attacks. More than 20,000 adversarial examples against some state-of-the-art DNN models are used to evaluate the proposed method, which are crafted with different attack techniques. The experiments show that our detection method can achieve a high overall F1 score of 96.39% and certainly raises the bar for defense-aware attacks.
Deep Text Classification Can be Fooled
Apr 26, 2017
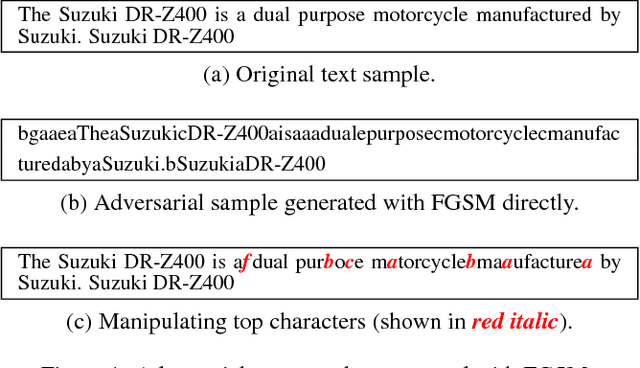
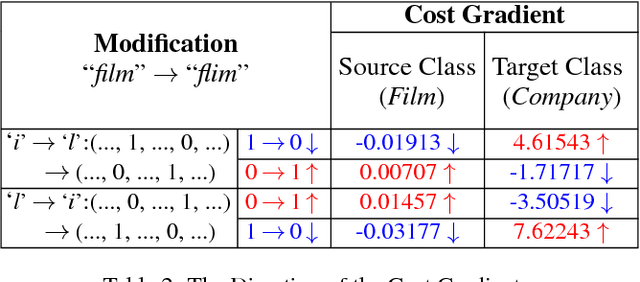

Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) play a key role in many applications. Current studies focus on crafting adversarial samples against DNN-based image classifiers by introducing some imperceptible perturbations to the input. However, DNNs for natural language processing have not got the attention they deserve. In fact, the existing perturbation algorithms for images cannot be directly applied to text. This paper presents a simple but effective method to attack DNN-based text classifiers. Three perturbation strategies, namely insertion, modification, and removal, are designed to generate an adversarial sample for a given text. By computing the cost gradients, what should be inserted, modified or removed, where to insert and how to modify are determined effectively. The experimental results show that the adversarial samples generated by our method can successfully fool a state-of-the-art model to misclassify them as any desirable classes without compromising their utilities. At the same time, the introduced perturbations are difficult to be perceived. Our study demonstrates that DNN-based text classifiers are also prone to the adversarial sample attack.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge