Weiyuan Peng
TSceneJAL: Joint Active Learning of Traffic Scenes for 3D Object Detection
Dec 25, 2024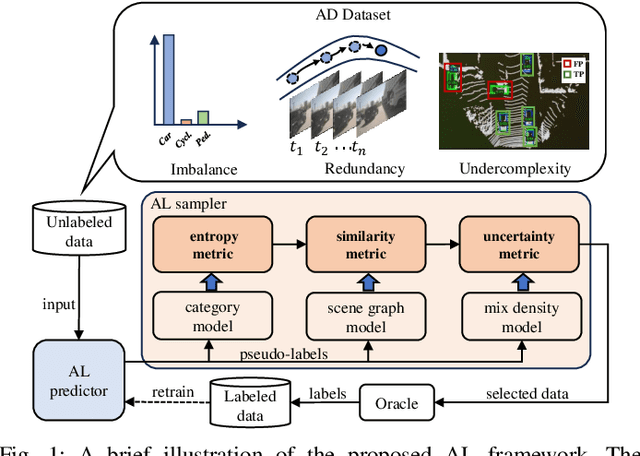
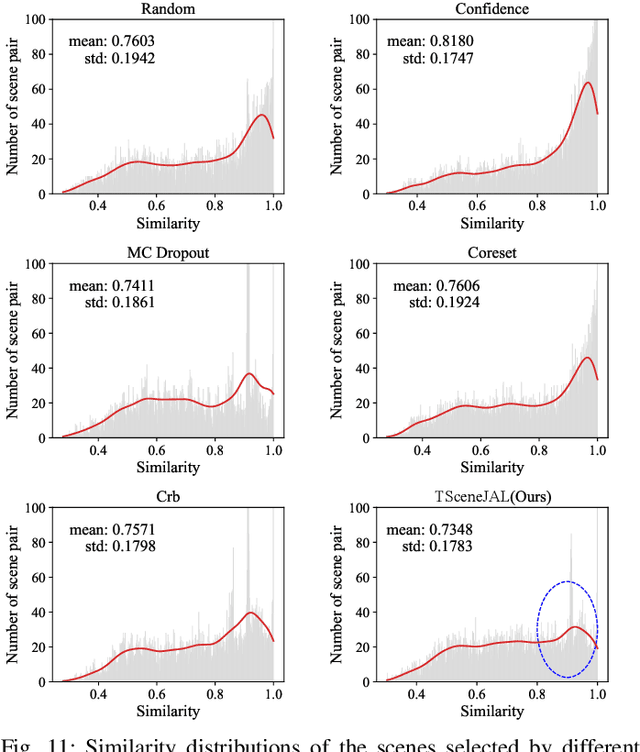
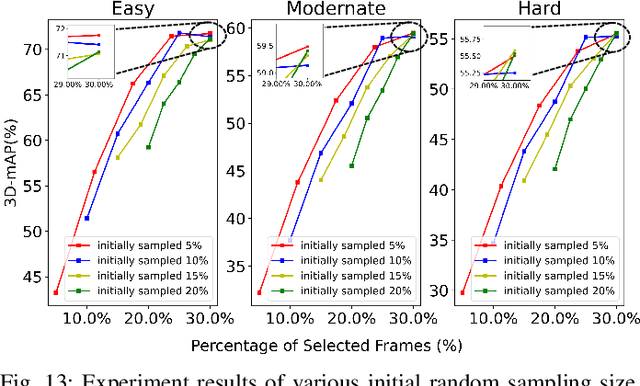
Abstract:Most autonomous driving (AD) datasets incur substantial costs for collection and labeling, inevitably yielding a plethora of low-quality and redundant data instances, thereby compromising performance and efficiency. Many applications in AD systems necessitate high-quality training datasets using both existing datasets and newly collected data. In this paper, we propose a traffic scene joint active learning (TSceneJAL) framework that can efficiently sample the balanced, diverse, and complex traffic scenes from both labeled and unlabeled data. The novelty of this framework is threefold: 1) a scene sampling scheme based on a category entropy, to identify scenes containing multiple object classes, thus mitigating class imbalance for the active learner; 2) a similarity sampling scheme, estimated through the directed graph representation and a marginalize kernel algorithm, to pick sparse and diverse scenes; 3) an uncertainty sampling scheme, predicted by a mixture density network, to select instances with the most unclear or complex regression outcomes for the learner. Finally, the integration of these three schemes in a joint selection strategy yields an optimal and valuable subdataset. Experiments on the KITTI, Lyft, nuScenes and SUScape datasets demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods on 3D object detection tasks with up to 12% improvements.
CTS: Sim-to-Real Unsupervised Domain Adaptation on 3D Detection
Jun 26, 2024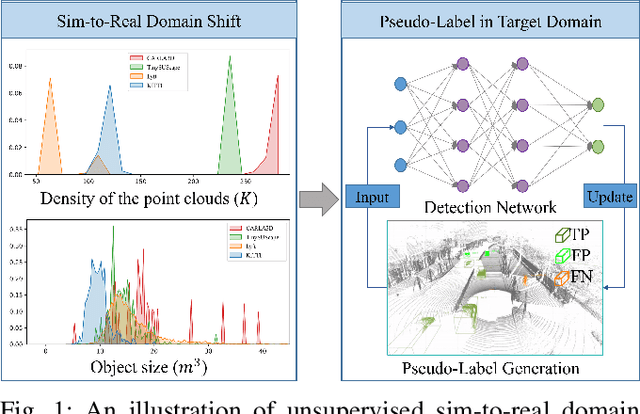
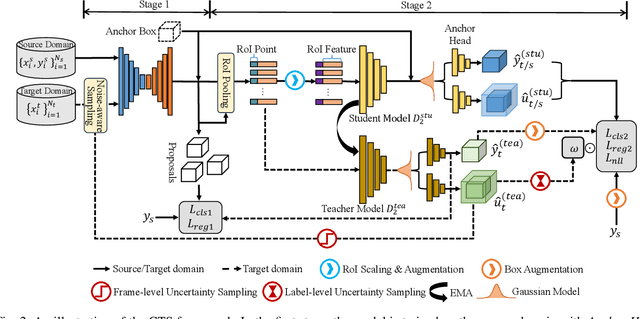
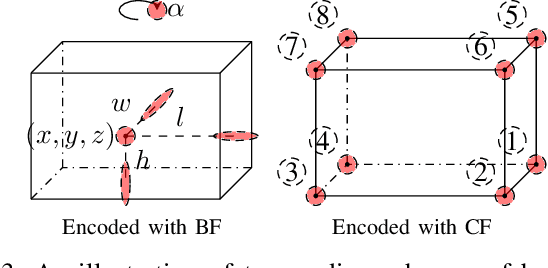
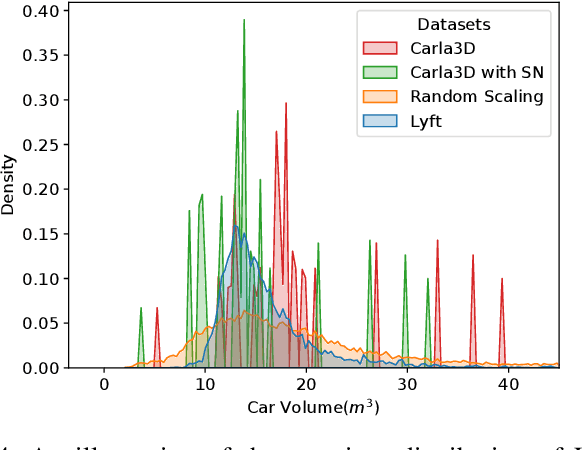
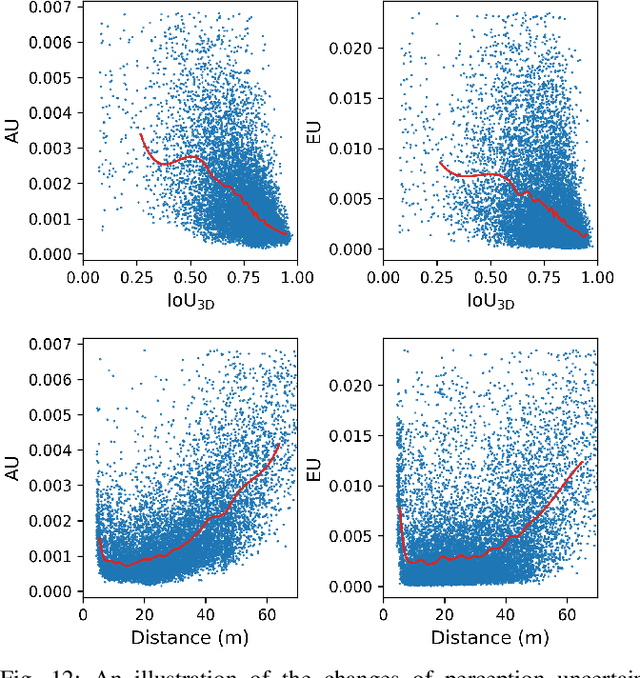
Abstract:Simulation data can be accurately labeled and have been expected to improve the performance of data-driven algorithms, including object detection. However, due to the various domain inconsistencies from simulation to reality (sim-to-real), cross-domain object detection algorithms usually suffer from dramatic performance drops. While numerous unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) methods have been developed to address cross-domain tasks between real-world datasets, progress in sim-to-real remains limited. This paper presents a novel Complex-to-Simple (CTS) framework to transfer models from labeled simulation (source) to unlabeled reality (target) domains. Based on a two-stage detector, the novelty of this work is threefold: 1) developing fixed-size anchor heads and RoI augmentation to address size bias and feature diversity between two domains, thereby improving the quality of pseudo-label; 2) developing a novel corner-format representation of aleatoric uncertainty (AU) for the bounding box, to uniformly quantify pseudo-label quality; 3) developing a noise-aware mean teacher domain adaptation method based on AU, as well as object-level and frame-level sampling strategies, to migrate the impact of noisy labels. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed approach significantly enhances the sim-to-real domain adaptation capability of 3D object detection models, outperforming state-of-the-art cross-domain algorithms, which are usually developed for real-to-real UDA tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge