Weixin Jin
OMG-HD: A High-Resolution AI Weather Model for End-to-End Forecasts from Observations
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, Artificial Intelligence Weather Prediction (AIWP) models have achieved performance comparable to, or even surpassing, traditional Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models by leveraging reanalysis data. However, a less-explored approach involves training AIWP models directly on observational data, enhancing computational efficiency and improving forecast accuracy by reducing the uncertainties introduced through data assimilation processes. In this study, we propose OMG-HD, a novel AI-based regional high-resolution weather forecasting model designed to make predictions directly from observational data sources, including surface stations, radar, and satellite, thereby removing the need for operational data assimilation. Our evaluation shows that OMG-HD outperforms both the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF)'s high-resolution operational forecasting system, IFS-HRES, and the High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) model at lead times of up to 12 hours across the contiguous United States (CONUS) region. We achieve up to a 13% improvement on RMSE for 2-meter temperature, 17% on 10-meter wind speed, 48% on 2-meter specific humidity, and 32% on surface pressure compared to HRRR. Our method shows that it is possible to use AI-driven approaches for rapid weather predictions without relying on NWP-derived weather fields as model input. This is a promising step towards using observational data directly to make operational forecasts with AIWP models.
ADAF: An Artificial Intelligence Data Assimilation Framework for Weather Forecasting
Nov 25, 2024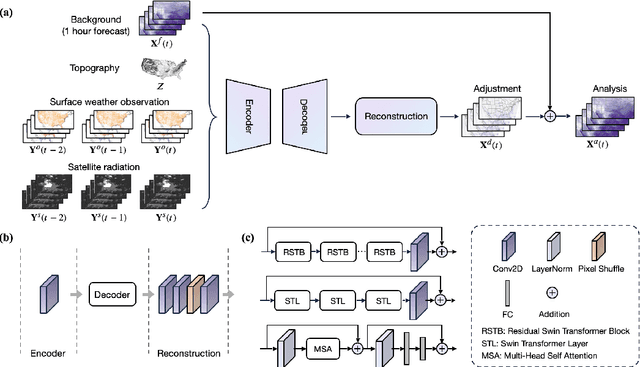



Abstract:The forecasting skill of numerical weather prediction (NWP) models critically depends on the accurate initial conditions, also known as analysis, provided by data assimilation (DA). Traditional DA methods often face a trade-off between computational cost and accuracy due to complex linear algebra computations and the high dimensionality of the model, especially in nonlinear systems. Moreover, processing massive data in real-time requires substantial computational resources. To address this, we introduce an artificial intelligence-based data assimilation framework (ADAF) to generate high-quality kilometer-scale analysis. This study is the pioneering work using real-world observations from varied locations and multiple sources to verify the AI method's efficacy in DA, including sparse surface weather observations and satellite imagery. We implemented ADAF for four near-surface variables in the Contiguous United States (CONUS). The results indicate that ADAF surpasses the High Resolution Rapid Refresh Data Assimilation System (HRRRDAS) in accuracy by 16% to 33% for near-surface atmospheric conditions, aligning more closely with actual observations, and can effectively reconstruct extreme events, such as tropical cyclone wind fields. Sensitivity experiments reveal that ADAF can generate high-quality analysis even with low-accuracy backgrounds and extremely sparse surface observations. ADAF can assimilate massive observations within a three-hour window at low computational cost, taking about two seconds on an AMD MI200 graphics processing unit (GPU). ADAF has been shown to be efficient and effective in real-world DA, underscoring its potential role in operational weather forecasting.
WeatherReal: A Benchmark Based on In-Situ Observations for Evaluating Weather Models
Sep 14, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, AI-based weather forecasting models have matched or even outperformed numerical weather prediction systems. However, most of these models have been trained and evaluated on reanalysis datasets like ERA5. These datasets, being products of numerical models, often diverge substantially from actual observations in some crucial variables like near-surface temperature, wind, precipitation and clouds - parameters that hold significant public interest. To address this divergence, we introduce WeatherReal, a novel benchmark dataset for weather forecasting, derived from global near-surface in-situ observations. WeatherReal also features a publicly accessible quality control and evaluation framework. This paper details the sources and processing methodologies underlying the dataset, and further illustrates the advantage of in-situ observations in capturing hyper-local and extreme weather through comparative analyses and case studies. Using WeatherReal, we evaluated several data-driven models and compared them with leading numerical models. Our work aims to advance the AI-based weather forecasting research towards a more application-focused and operation-ready approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge