Weiquan Wang
Uncertainty-Aware 4D Gaussian Splatting for Monocular Occluded Human Rendering
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:High-fidelity rendering of dynamic humans from monocular videos typically degrades catastrophically under occlusions. Existing solutions incorporate external priors-either hallucinating missing content via generative models, which induces severe temporal flickering, or imposing rigid geometric heuristics that fail to capture diverse appearances. To this end, we reformulate the task as a Maximum A Posteriori estimation problem under heteroscedastic observation noise. In this paper, we propose U-4DGS, a framework integrating a Probabilistic Deformation Network and a Double Rasterization pipeline. This architecture renders pixel-aligned uncertainty maps that act as an adaptive gradient modulator, automatically attenuating artifacts from unreliable observations. Furthermore, to prevent geometric drift in regions lacking reliable visual cues, we enforce Confidence-Aware Regularizations, which leverage the learned uncertainty to selectively propagate spatial-temporal validity. Extensive experiments on ZJU-MoCap and OcMotion demonstrate that U-4DGS achieves SOTA rendering fidelity and robustness.
$\text{Di}^2\text{Pose}$: Discrete Diffusion Model for Occluded 3D Human Pose Estimation
May 27, 2024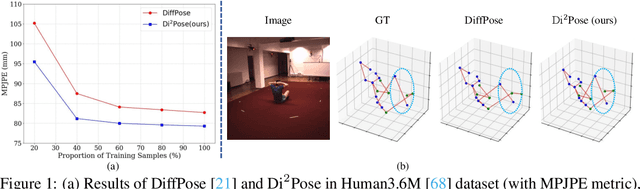
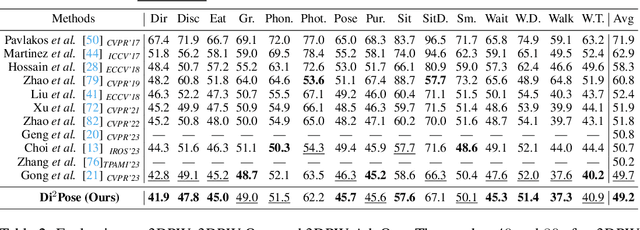
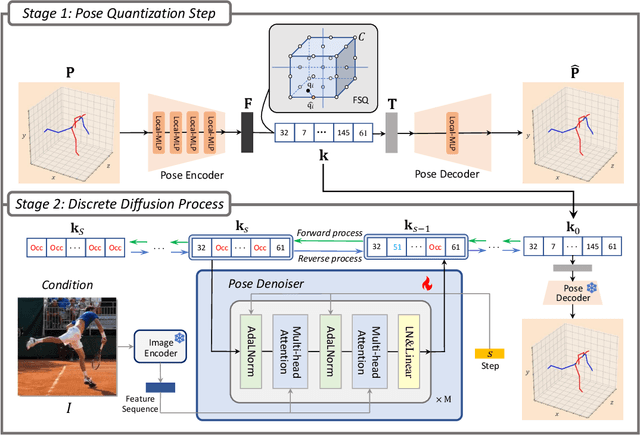
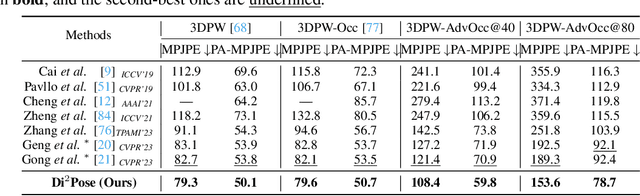
Abstract:Continuous diffusion models have demonstrated their effectiveness in addressing the inherent uncertainty and indeterminacy in monocular 3D human pose estimation (HPE). Despite their strengths, the need for large search spaces and the corresponding demand for substantial training data make these models prone to generating biomechanically unrealistic poses. This challenge is particularly noticeable in occlusion scenarios, where the complexity of inferring 3D structures from 2D images intensifies. In response to these limitations, we introduce the Discrete Diffusion Pose ($\text{Di}^2\text{Pose}$), a novel framework designed for occluded 3D HPE that capitalizes on the benefits of a discrete diffusion model. Specifically, $\text{Di}^2\text{Pose}$ employs a two-stage process: it first converts 3D poses into a discrete representation through a \emph{pose quantization step}, which is subsequently modeled in latent space through a \emph{discrete diffusion process}. This methodological innovation restrictively confines the search space towards physically viable configurations and enhances the model's capability to comprehend how occlusions affect human pose within the latent space. Extensive evaluations conducted on various benchmarks (e.g., Human3.6M, 3DPW, and 3DPW-Occ) have demonstrated its effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge