Weibing Sun
Interactive Spatial-Frequency Fusion Mamba for Multi-Modal Image Fusion
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Multi-Modal Image Fusion (MMIF) aims to combine images from different modalities to produce fused images, retaining texture details and preserving significant information. Recently, some MMIF methods incorporate frequency domain information to enhance spatial features. However, these methods typically rely on simple serial or parallel spatial-frequency fusion without interaction. In this paper, we propose a novel Interactive Spatial-Frequency Fusion Mamba (ISFM) framework for MMIF. Specifically, we begin with a Modality-Specific Extractor (MSE) to extract features from different modalities. It models long-range dependencies across the image with linear computational complexity. To effectively leverage frequency information, we then propose a Multi-scale Frequency Fusion (MFF). It adaptively integrates low-frequency and high-frequency components across multiple scales, enabling robust representations of frequency features. More importantly, we further propose an Interactive Spatial-Frequency Fusion (ISF). It incorporates frequency features to guide spatial features across modalities, enhancing complementary representations. Extensive experiments are conducted on six MMIF datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that our ISFM can achieve better performances than other state-of-the-art methods. The source code is available at https://github.com/Namn23/ISFM.
Spatial-Frequency Enhanced Mamba for Multi-Modal Image Fusion
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Multi-Modal Image Fusion (MMIF) aims to integrate complementary image information from different modalities to produce informative images. Previous deep learning-based MMIF methods generally adopt Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) or Transformers for feature extraction. However, these methods deliver unsatisfactory performances due to the limited receptive field of CNNs and the high computational cost of Transformers. Recently, Mamba has demonstrated a powerful potential for modeling long-range dependencies with linear complexity, providing a promising solution to MMIF. Unfortunately, Mamba lacks full spatial and frequency perceptions, which are very important for MMIF. Moreover, employing Image Reconstruction (IR) as an auxiliary task has been proven beneficial for MMIF. However, a primary challenge is how to leverage IR efficiently and effectively. To address the above issues, we propose a novel framework named Spatial-Frequency Enhanced Mamba Fusion (SFMFusion) for MMIF. More specifically, we first propose a three-branch structure to couple MMIF and IR, which can retain complete contents from source images. Then, we propose the Spatial-Frequency Enhanced Mamba Block (SFMB), which can enhance Mamba in both spatial and frequency domains for comprehensive feature extraction. Finally, we propose the Dynamic Fusion Mamba Block (DFMB), which can be deployed across different branches for dynamic feature fusion. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves better results than most state-of-the-art methods on six MMIF datasets. The source code is available at https://github.com/SunHui1216/SFMFusion.
P3Net: Progressive and Periodic Perturbation for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
May 21, 2025Abstract:Perturbation with diverse unlabeled data has proven beneficial for semi-supervised medical image segmentation (SSMIS). While many works have successfully used various perturbation techniques, a deeper understanding of learning perturbations is needed. Excessive or inappropriate perturbation can have negative effects, so we aim to address two challenges: how to use perturbation mechanisms to guide the learning of unlabeled data through labeled data, and how to ensure accurate predictions in boundary regions. Inspired by human progressive and periodic learning, we propose a progressive and periodic perturbation mechanism (P3M) and a boundary-focused loss. P3M enables dynamic adjustment of perturbations, allowing the model to gradually learn them. Our boundary-focused loss encourages the model to concentrate on boundary regions, enhancing sensitivity to intricate details and ensuring accurate predictions. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on two 2D and 3D datasets. Moreover, P3M is extendable to other methods, and the proposed loss serves as a universal tool for improving existing methods, highlighting the scalability and applicability of our approach.
CNN-Transformer Rectified Collaborative Learning for Medical Image Segmentation
Aug 27, 2024



Abstract:Automatic and precise medical image segmentation (MIS) is of vital importance for clinical diagnosis and analysis. Current MIS methods mainly rely on the convolutional neural network (CNN) or self-attention mechanism (Transformer) for feature modeling. However, CNN-based methods suffer from the inaccurate localization owing to the limited global dependency while Transformer-based methods always present the coarse boundary for the lack of local emphasis. Although some CNN-Transformer hybrid methods are designed to synthesize the complementary local and global information for better performance, the combination of CNN and Transformer introduces numerous parameters and increases the computation cost. To this end, this paper proposes a CNN-Transformer rectified collaborative learning (CTRCL) framework to learn stronger CNN-based and Transformer-based models for MIS tasks via the bi-directional knowledge transfer between them. Specifically, we propose a rectified logit-wise collaborative learning (RLCL) strategy which introduces the ground truth to adaptively select and rectify the wrong regions in student soft labels for accurate knowledge transfer in the logit space. We also propose a class-aware feature-wise collaborative learning (CFCL) strategy to achieve effective knowledge transfer between CNN-based and Transformer-based models in the feature space by granting their intermediate features the similar capability of category perception. Extensive experiments on three popular MIS benchmarks demonstrate that our CTRCL outperforms most state-of-the-art collaborative learning methods under different evaluation metrics.
M$^{2}$SNet: Multi-scale in Multi-scale Subtraction Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 20, 2023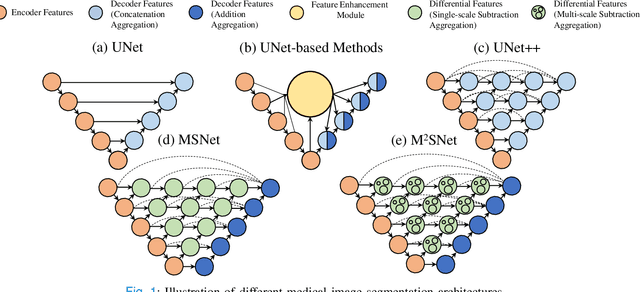
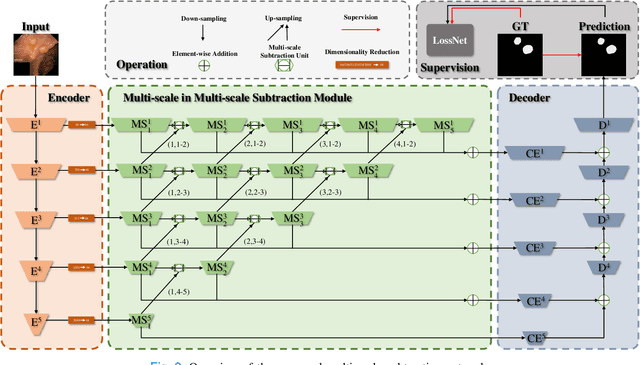
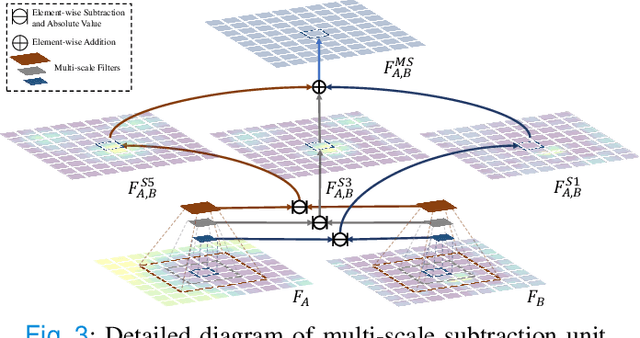
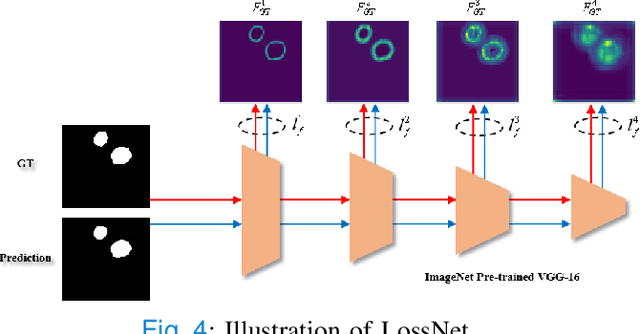
Abstract:Accurate medical image segmentation is critical for early medical diagnosis. Most existing methods are based on U-shape structure and use element-wise addition or concatenation to fuse different level features progressively in decoder. However, both the two operations easily generate plenty of redundant information, which will weaken the complementarity between different level features, resulting in inaccurate localization and blurred edges of lesions. To address this challenge, we propose a general multi-scale in multi-scale subtraction network (M$^{2}$SNet) to finish diverse segmentation from medical image. Specifically, we first design a basic subtraction unit (SU) to produce the difference features between adjacent levels in encoder. Next, we expand the single-scale SU to the intra-layer multi-scale SU, which can provide the decoder with both pixel-level and structure-level difference information. Then, we pyramidally equip the multi-scale SUs at different levels with varying receptive fields, thereby achieving the inter-layer multi-scale feature aggregation and obtaining rich multi-scale difference information. In addition, we build a training-free network ``LossNet'' to comprehensively supervise the task-aware features from bottom layer to top layer, which drives our multi-scale subtraction network to capture the detailed and structural cues simultaneously. Without bells and whistles, our method performs favorably against most state-of-the-art methods under different evaluation metrics on eleven datasets of four different medical image segmentation tasks of diverse image modalities, including color colonoscopy imaging, ultrasound imaging, computed tomography (CT), and optical coherence tomography (OCT). The source code can be available at \url{https://github.com/Xiaoqi-Zhao-DLUT/MSNet}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge