Wei-Chien Wang
A Review of Predictive and Contrastive Self-supervised Learning for Medical Images
Feb 10, 2023Abstract:Over the last decade, supervised deep learning on manually annotated big data has been progressing significantly on computer vision tasks. But the application of deep learning in medical image analysis was limited by the scarcity of high-quality annotated medical imaging data. An emerging solution is self-supervised learning (SSL), among which contrastive SSL is the most successful approach to rivalling or outperforming supervised learning. This review investigates several state-of-the-art contrastive SSL algorithms originally on natural images as well as their adaptations for medical images, and concludes by discussing recent advances, current limitations, and future directions in applying contrastive SSL in the medical domain.
A Novel Temporal Attentive-Pooling based Convolutional Recurrent Architecture for Acoustic Signal Enhancement
Jan 24, 2022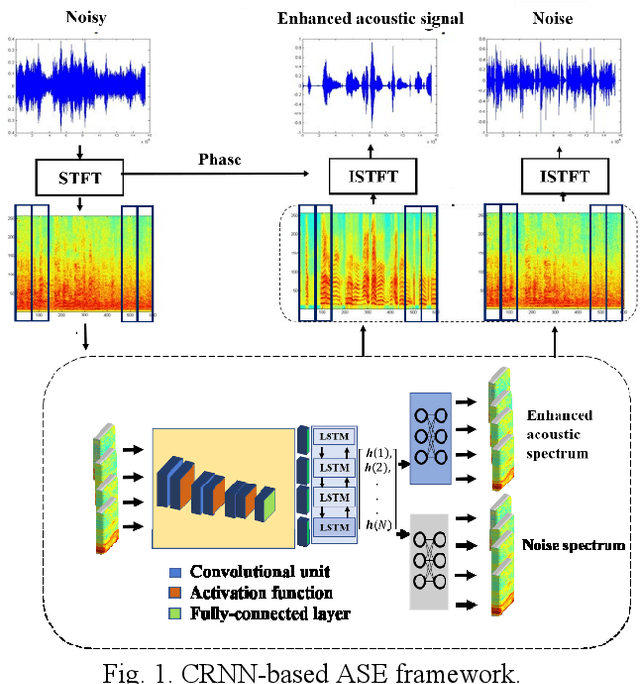
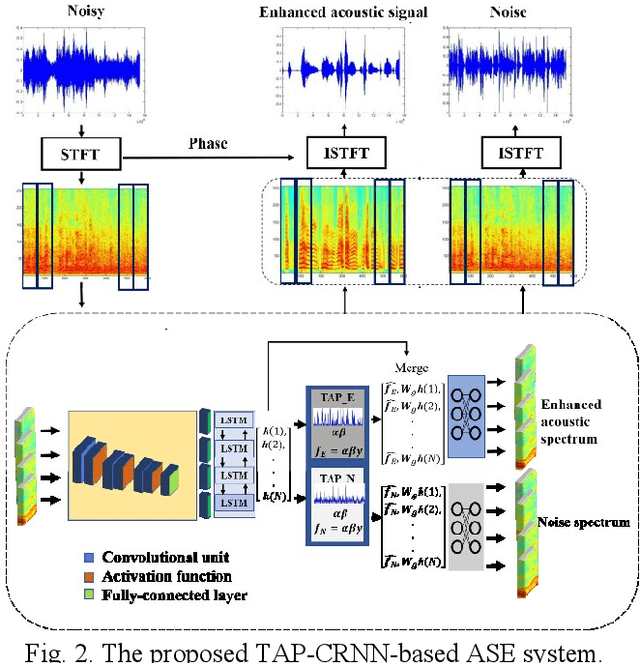
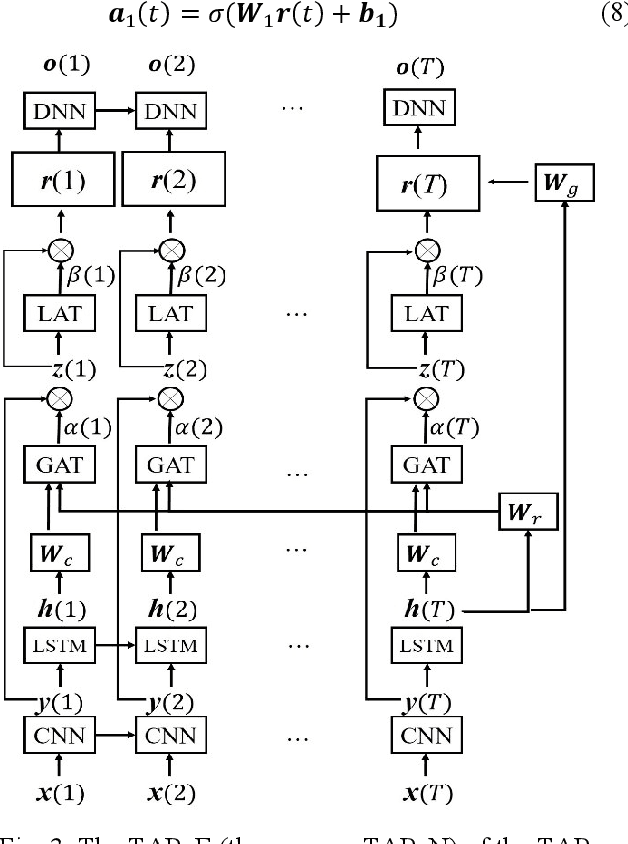
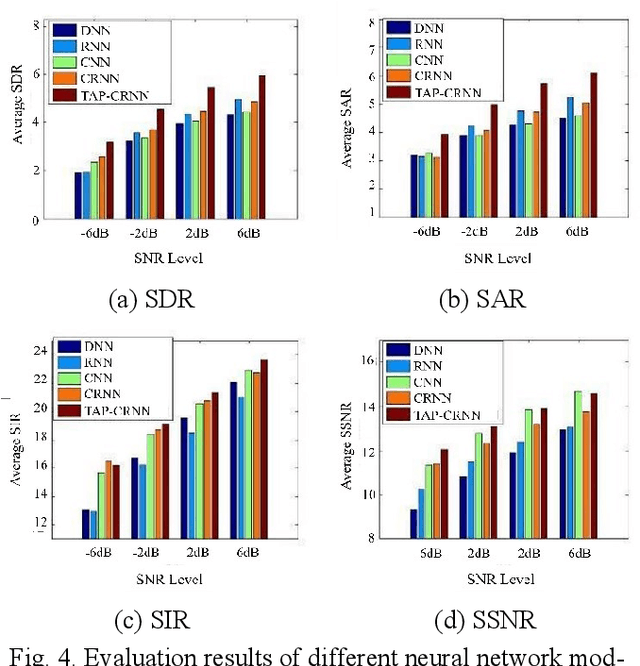
Abstract:In acoustic signal processing, the target signals usually carry semantic information, which is encoded in a hierarchal structure of short and long-term contexts. However, the background noise distorts these structures in a nonuniform way. The existing deep acoustic signal enhancement (ASE) architectures ignore this kind of local and global effect. To address this problem, we propose to integrate a novel temporal attentive-pooling (TAP) mechanism into a conventional convolutional recurrent neural network, termed as TAP-CRNN. The proposed approach considers both global and local attention for ASE tasks. Specifically, we first utilize a convolutional layer to extract local information of the acoustic signals and then a recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture is used to characterize temporal contextual information. Second, we exploit a novelattention mechanism to contextually process salient regions of the noisy signals. The proposed ASE system is evaluated using a benchmark infant cry dataset and compared with several well-known methods. It is shown that the TAPCRNN can more effectively reduce noise components from infant cry signals in unseen background noises at challenging signal-to-noise levels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge