Wanyi Chen
ECHO-2: A Large-Scale Distributed Rollout Framework for Cost-Efficient Reinforcement Learning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) is a critical stage in post-training large language models (LLMs), involving repeated interaction between rollout generation, reward evaluation, and centralized learning. Distributing rollout execution offers opportunities to leverage more cost-efficient inference resources, but introduces challenges in wide-area coordination and policy dissemination. We present ECHO-2, a distributed RL framework for post-training with remote inference workers and non-negligible dissemination latency. ECHO-2 combines centralized learning with distributed rollouts and treats bounded policy staleness as a user-controlled parameter, enabling rollout generation, dissemination, and training to overlap. We introduce an overlap-based capacity model that relates training time, dissemination latency, and rollout throughput, yielding a practical provisioning rule for sustaining learner utilization. To mitigate dissemination bottlenecks and lower cost, ECHO-2 employs peer-assisted pipelined broadcast and cost-aware activation of heterogeneous workers. Experiments on GRPO post-training of 4B and 8B models under real wide-area bandwidth regimes show that ECHO-2 significantly improves cost efficiency while preserving RL reward comparable to strong baselines.
EVM-QuestBench: An Execution-Grounded Benchmark for Natural-Language Transaction Code Generation
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Large language models are increasingly applied to various development scenarios. However, in on-chain transaction scenarios, even a minor error can cause irreversible loss for users. Existing evaluations often overlook execution accuracy and safety. We introduce EVM-QuestBench, an execution-grounded benchmark for natural-language transaction-script generation on EVM-compatible chains. The benchmark employs dynamic evaluation: instructions are sampled from template pools, numeric parameters are drawn from predefined intervals, and validators verify outcomes against these instantiated values. EVM-QuestBench contains 107 tasks (62 atomic, 45 composite). Its modular architecture enables rapid task development. The runner executes scripts on a forked EVM chain with snapshot isolation; composite tasks apply step-efficiency decay. We evaluate 20 models and find large performance gaps, with split scores revealing persistent asymmetry between single-action precision and multi-step workflow completion. Code: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/bsc_quest_bench-A9CF/.
Speculative Decoding in Decentralized LLM Inference: Turning Communication Latency into Computation Throughput
Nov 13, 2025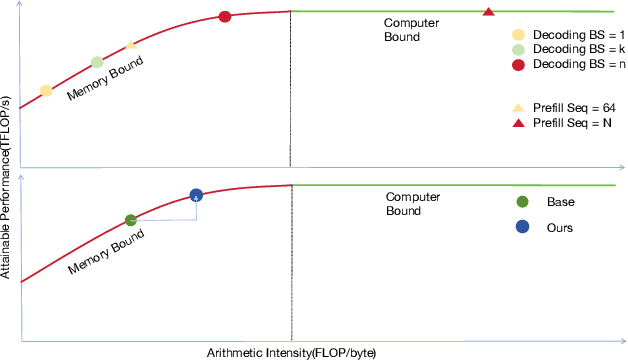
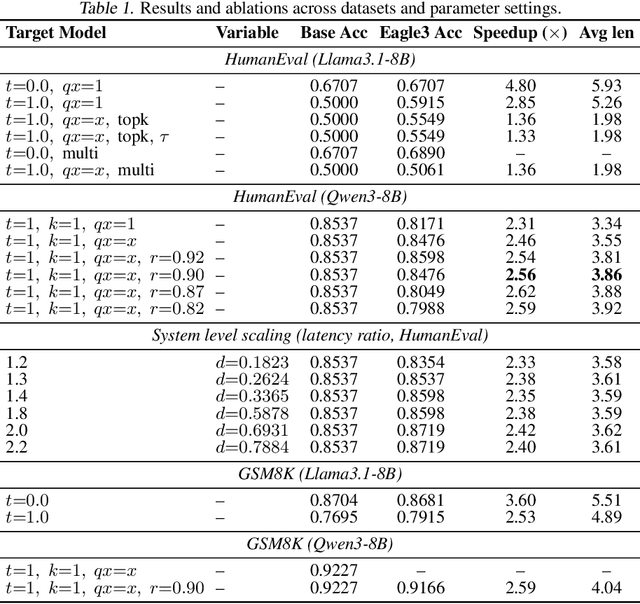
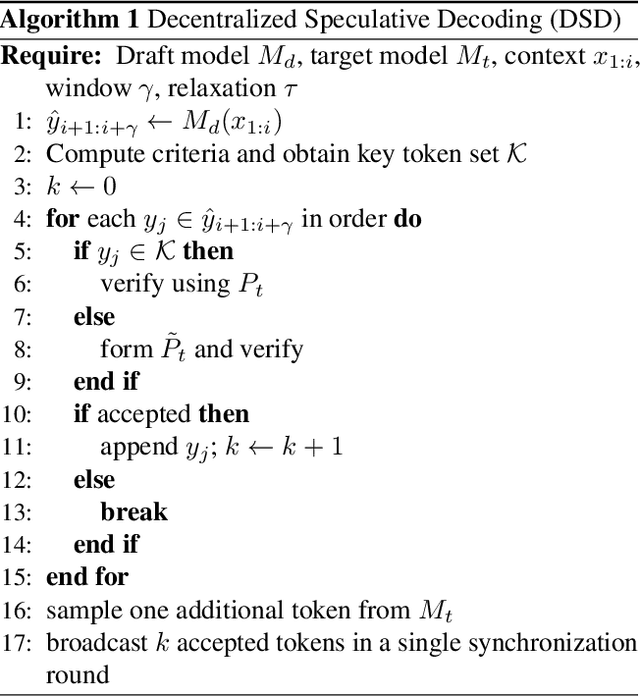
Abstract:Speculative decoding accelerates large language model (LLM) inference by using a lightweight draft model to propose tokens that are later verified by a stronger target model. While effective in centralized systems, its behavior in decentralized settings, where network latency often dominates compute, remains under-characterized. We present Decentralized Speculative Decoding (DSD), a plug-and-play framework for decentralized inference that turns communication delay into useful computation by verifying multiple candidate tokens in parallel across distributed nodes. We further introduce an adaptive speculative verification strategy that adjusts acceptance thresholds by token-level semantic importance, delivering an additional 15% to 20% end-to-end speedup without retraining. In theory, DSD reduces cross-node communication cost by approximately (N-1)t1(k-1)/k, where t1 is per-link latency and k is the average number of tokens accepted per round. In practice, DSD achieves up to 2.56x speedup on HumanEval and 2.59x on GSM8K, surpassing the Eagle3 baseline while preserving accuracy. These results show that adapting speculative decoding for decentralized execution provides a system-level optimization that converts network stalls into throughput, enabling faster distributed LLM inference with no model retraining or architectural changes.
Assessing LLM code generation quality through path planning tasks
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:As LLM-generated code grows in popularity, more evaluation is needed to assess the risks of using such tools, especially for safety-critical applications such as path planning. Existing coding benchmarks are insufficient as they do not reflect the context and complexity of safety-critical applications. To this end, we assessed six LLMs' abilities to generate the code for three different path-planning algorithms and tested them on three maps of various difficulties. Our results suggest that LLM-generated code presents serious hazards for path planning applications and should not be applied in safety-critical contexts without rigorous testing.
To impute or not to impute: How machine learning modelers treat missing data
Mar 20, 2025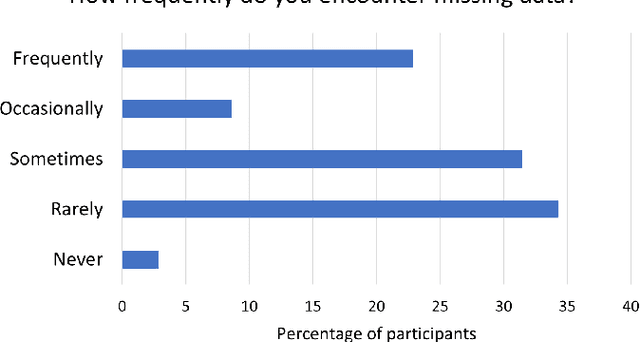
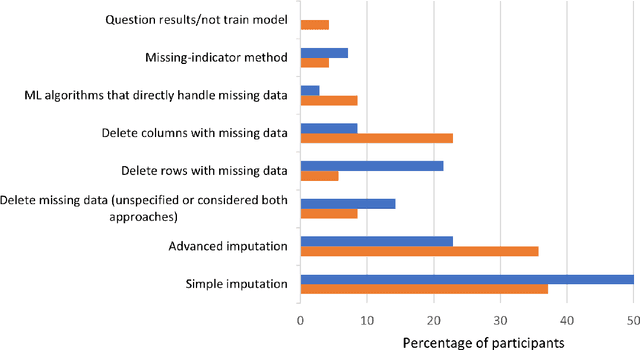
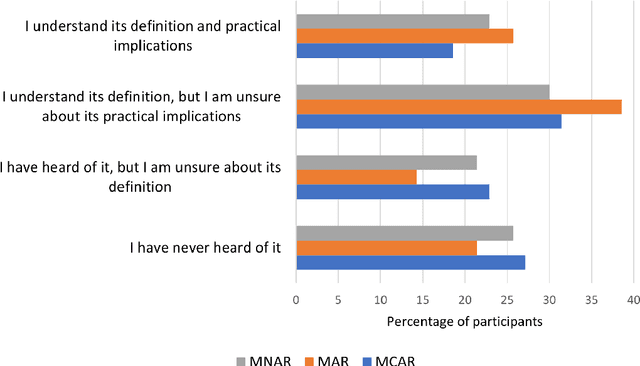
Abstract:Missing data is prevalent in tabular machine learning (ML) models, and different missing data treatment methods can significantly affect ML model training results. However, little is known about how ML researchers and engineers choose missing data treatment methods and what factors affect their choices. To this end, we conducted a survey of 70 ML researchers and engineers. Our results revealed that most participants were not making informed decisions regarding missing data treatment, which could significantly affect the validity of the ML models trained by these researchers. We advocate for better education on missing data, more standardized missing data reporting, and better missing data analysis tools.
Can LLMs plan paths in the real world?
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) increasingly integrate into vehicle navigation systems, understanding their path-planning capability is crucial. We tested three LLMs through six real-world path-planning scenarios in various settings and with various difficulties. Our experiments showed that all LLMs made numerous errors in all scenarios, revealing that they are unreliable path planners. We suggest that future work focus on implementing mechanisms for reality checks, enhancing model transparency, and developing smaller models.
A Safe Screening Rule with Bi-level Optimization of $ν$ Support Vector Machine
Mar 04, 2024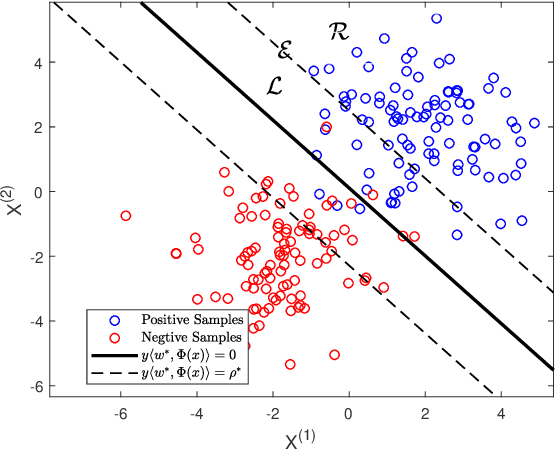
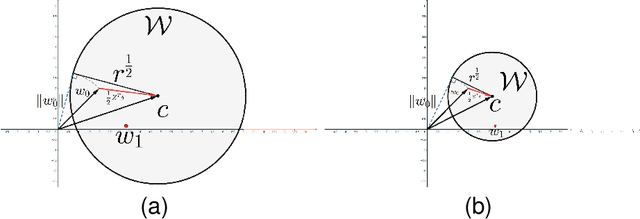
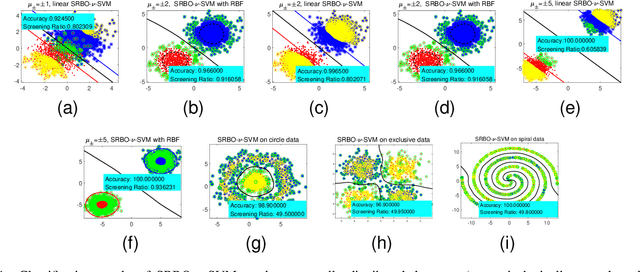
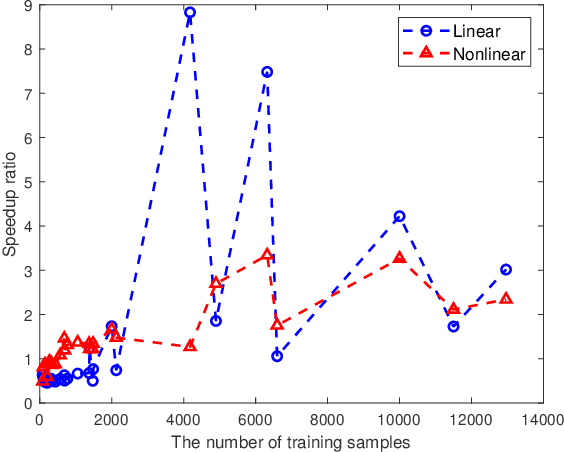
Abstract:Support vector machine (SVM) has achieved many successes in machine learning, especially for a small sample problem. As a famous extension of the traditional SVM, the $\nu$ support vector machine ($\nu$-SVM) has shown outstanding performance due to its great model interpretability. However, it still faces challenges in training overhead for large-scale problems. To address this issue, we propose a safe screening rule with bi-level optimization for $\nu$-SVM (SRBO-$\nu$-SVM) which can screen out inactive samples before training and reduce the computational cost without sacrificing the prediction accuracy. Our SRBO-$\nu$-SVM is strictly deduced by integrating the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) conditions, the variational inequalities of convex problems and the $\nu$-property. Furthermore, we develop an efficient dual coordinate descent method (DCDM) to further improve computational speed. Finally, a unified framework for SRBO is proposed to accelerate many SVM-type models, and it is successfully applied to one-class SVM. Experimental results on 6 artificial data sets and 30 benchmark data sets have verified the effectiveness and safety of our proposed methods in supervised and unsupervised tasks.
Subjectivity in Unsupervised Machine Learning Model Selection
Sep 01, 2023Abstract:Model selection is a necessary step in unsupervised machine learning. Despite numerous criteria and metrics, model selection remains subjective. A high degree of subjectivity may lead to questions about repeatability and reproducibility of various machine learning studies and doubts about the robustness of models deployed in the real world. Yet, the impact of modelers' preferences on model selection outcomes remains largely unexplored. This study uses the Hidden Markov Model as an example to investigate the subjectivity involved in model selection. We asked 33 participants and three Large Language Models (LLMs) to make model selections in three scenarios. Results revealed variability and inconsistencies in both the participants' and the LLMs' choices, especially when different criteria and metrics disagree. Sources of subjectivity include varying opinions on the importance of different criteria and metrics, differing views on how parsimonious a model should be, and how the size of a dataset should influence model selection. The results underscore the importance of developing a more standardized way to document subjective choices made in model selection processes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge