Wangyu Wu
Beyond Shadows: A Large-Scale Benchmark and Multi-Stage Framework for High-Fidelity Facial Shadow Removal
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Facial shadows often degrade image quality and the performance of vision algorithms. Existing methods struggle to remove shadows while preserving texture, especially under complex lighting conditions, and they lack real-world paired datasets for training. We present the Augmented Shadow Face in the Wild (ASFW) dataset, the first large-scale real-world dataset for facial shadow removal, containing 1,081 paired shadow and shadow-free images created via a professional Photoshop workflow. ASFW offers photorealistic shadow variations and accurate ground truths, bridging the gap between synthetic and real domains. Deep models trained on ASFW demonstrate improved shadow removal in real-world conditions. We also introduce the Face Shadow Eraser (FSE) method to showcase the effectiveness of the dataset. Experiments demonstrate that ASFW enhances the performance of facial shadow removal models, setting new standards for this task.
ProMist-5K: A Comprehensive Dataset for Digital Emulation of Cinematic Pro-Mist Filter Effects
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Pro-Mist filters are widely used in cinematography for their ability to create soft halation, lower contrast, and produce a distinctive, atmospheric style. These effects are difficult to reproduce digitally due to the complex behavior of light diffusion. We present ProMist-5K, a dataset designed to support cinematic style emulation. It is built using a physically inspired pipeline in a scene-referred linear space and includes 20,000 high-resolution image pairs across four configurations, covering two filter densities (1/2 and 1/8) and two focal lengths (20mm and 50mm). Unlike general style datasets, ProMist-5K focuses on realistic glow and highlight diffusion effects. Multiple blur layers and carefully tuned weighting are used to model the varying intensity and spread of optical diffusion. The dataset provides a consistent and controllable target domain that supports various image translation models and learning paradigms. Experiments show that the dataset works well across different training settings and helps capture both subtle and strong cinematic appearances. ProMist-5K offers a practical and physically grounded resource for film-inspired image transformation, bridging the gap between digital flexibility and traditional lens aesthetics. The dataset is available at https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/yingtielei/promist5k.
Context Patch Fusion With Class Token Enhancement for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS), which relies only on image-level labels, has attracted significant attention for its cost-effectiveness and scalability. Existing methods mainly enhance inter-class distinctions and employ data augmentation to mitigate semantic ambiguity and reduce spurious activations. However, they often neglect the complex contextual dependencies among image patches, resulting in incomplete local representations and limited segmentation accuracy. To address these issues, we propose the Context Patch Fusion with Class Token Enhancement (CPF-CTE) framework, which exploits contextual relations among patches to enrich feature representations and improve segmentation. At its core, the Contextual-Fusion Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (CF-BiLSTM) module captures spatial dependencies between patches and enables bidirectional information flow, yielding a more comprehensive understanding of spatial correlations. This strengthens feature learning and segmentation robustness. Moreover, we introduce learnable class tokens that dynamically encode and refine class-specific semantics, enhancing discriminative capability. By effectively integrating spatial and semantic cues, CPF-CTE produces richer and more accurate representations of image content. Extensive experiments on PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 validate that CPF-CTE consistently surpasses prior WSSS methods.
SynthSeg-Agents: Multi-Agent Synthetic Data Generation for Zero-Shot Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Dec 17, 2025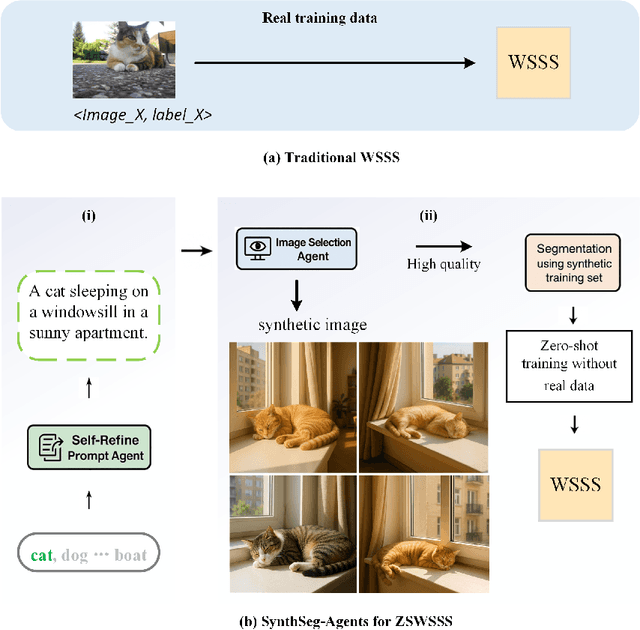
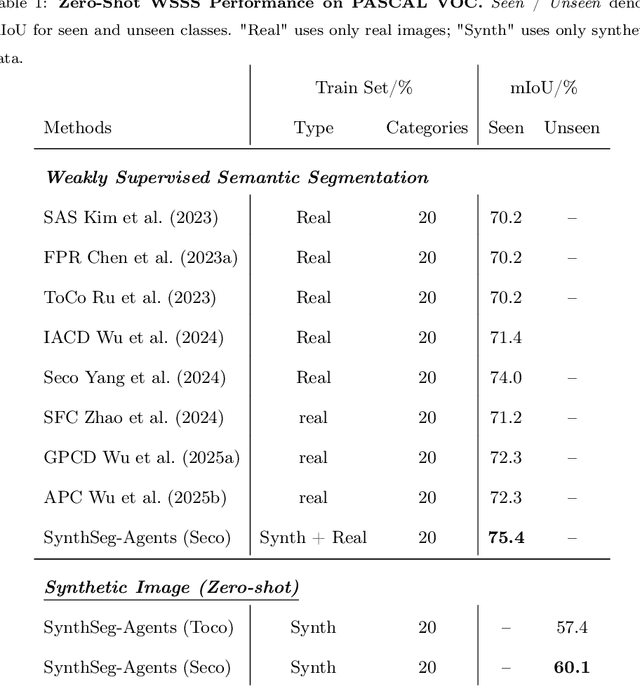
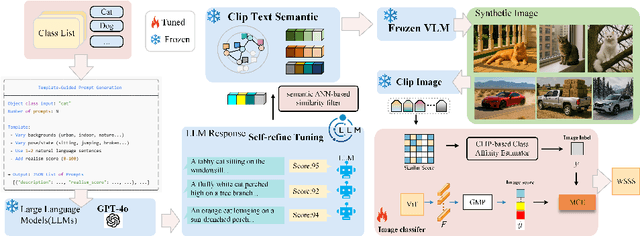
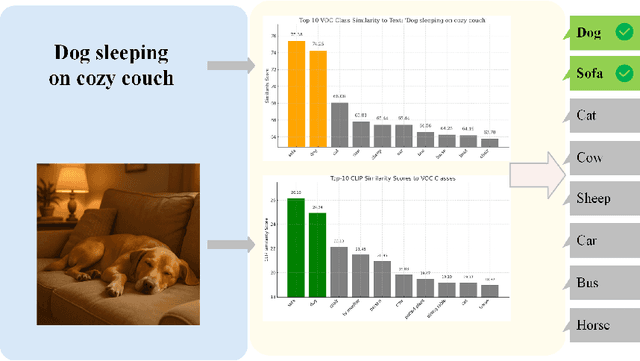
Abstract:Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) with image level labels aims to produce pixel level predictions without requiring dense annotations. While recent approaches have leveraged generative models to augment existing data, they remain dependent on real world training samples. In this paper, we introduce a novel direction, Zero Shot Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (ZSWSSS), and propose SynthSeg Agents, a multi agent framework driven by Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate synthetic training data entirely without real images. SynthSeg Agents comprises two key modules, a Self Refine Prompt Agent and an Image Generation Agent. The Self Refine Prompt Agent autonomously crafts diverse and semantically rich image prompts via iterative refinement, memory mechanisms, and prompt space exploration, guided by CLIP based similarity and nearest neighbor diversity filtering. These prompts are then passed to the Image Generation Agent, which leverages Vision Language Models (VLMs) to synthesize candidate images. A frozen CLIP scoring model is employed to select high quality samples, and a ViT based classifier is further trained to relabel the entire synthetic dataset with improved semantic precision. Our framework produces high quality training data without any real image supervision. Experiments on PASCAL VOC 2012 and COCO 2014 show that SynthSeg Agents achieves competitive performance without using real training images. This highlights the potential of LLM driven agents in enabling cost efficient and scalable semantic segmentation.
Contrastive Prompt Clustering for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Aug 23, 2025



Abstract:Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) with image-level labels has gained attention for its cost-effectiveness. Most existing methods emphasize inter-class separation, often neglecting the shared semantics among related categories and lacking fine-grained discrimination. To address this, we propose Contrastive Prompt Clustering (CPC), a novel WSSS framework. CPC exploits Large Language Models (LLMs) to derive category clusters that encode intrinsic inter-class relationships, and further introduces a class-aware patch-level contrastive loss to enforce intra-class consistency and inter-class separation. This hierarchical design leverages clusters as coarse-grained semantic priors while preserving fine-grained boundaries, thereby reducing confusion among visually similar categories. Experiments on PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 demonstrate that CPC surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods in WSSS.
MAC-Lookup: Multi-Axis Conditional Lookup Model for Underwater Image Enhancement
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Enhancing underwater images is crucial for exploration. These images face visibility and color issues due to light changes, water turbidity, and bubbles. Traditional prior-based methods and pixel-based methods often fail, while deep learning lacks sufficient high-quality datasets. We introduce the Multi-Axis Conditional Lookup (MAC-Lookup) model, which enhances visual quality by improving color accuracy, sharpness, and contrast. It includes Conditional 3D Lookup Table Color Correction (CLTCC) for preliminary color and quality correction and Multi-Axis Adaptive Enhancement (MAAE) for detail refinement. This model prevents over-enhancement and saturation while handling underwater challenges. Extensive experiments show that MAC-Lookup excels in enhancing underwater images by restoring details and colors better than existing methods. The code is https://github.com/onlycatdoraemon/MAC-Lookup.
Hierarchical Attention Fusion of Visual and Textual Representations for Cross-Domain Sequential Recommendation
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Cross-Domain Sequential Recommendation (CDSR) predicts user behavior by leveraging historical interactions across multiple domains, focusing on modeling cross-domain preferences through intra- and inter-sequence item relationships. Inspired by human cognitive processes, we propose Hierarchical Attention Fusion of Visual and Textual Representations (HAF-VT), a novel approach integrating visual and textual data to enhance cognitive modeling. Using the frozen CLIP model, we generate image and text embeddings, enriching item representations with multimodal data. A hierarchical attention mechanism jointly learns single-domain and cross-domain preferences, mimicking human information integration. Evaluated on four e-commerce datasets, HAF-VT outperforms existing methods in capturing cross-domain user interests, bridging cognitive principles with computational models and highlighting the role of multimodal data in sequential decision-making.
CubeRobot: Grounding Language in Rubik's Cube Manipulation via Vision-Language Model
Mar 25, 2025



Abstract:Proving Rubik's Cube theorems at the high level represents a notable milestone in human-level spatial imagination and logic thinking and reasoning. Traditional Rubik's Cube robots, relying on complex vision systems and fixed algorithms, often struggle to adapt to complex and dynamic scenarios. To overcome this limitation, we introduce CubeRobot, a novel vision-language model (VLM) tailored for solving 3x3 Rubik's Cubes, empowering embodied agents with multimodal understanding and execution capabilities. We used the CubeCoT image dataset, which contains multiple-level tasks (43 subtasks in total) that humans are unable to handle, encompassing various cube states. We incorporate a dual-loop VisionCoT architecture and Memory Stream, a paradigm for extracting task-related features from VLM-generated planning queries, thus enabling CubeRobot to independent planning, decision-making, reflection and separate management of high- and low-level Rubik's Cube tasks. Furthermore, in low-level Rubik's Cube restoration tasks, CubeRobot achieved a high accuracy rate of 100%, similar to 100% in medium-level tasks, and achieved an accuracy rate of 80% in high-level tasks.
Image Augmentation Agent for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Dec 29, 2024Abstract:Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) has achieved remarkable progress using only image-level labels. However, most existing WSSS methods focus on designing new network structures and loss functions to generate more accurate dense labels, overlooking the limitations imposed by fixed datasets, which can constrain performance improvements. We argue that more diverse trainable images provides WSSS richer information and help model understand more comprehensive semantic pattern. Therefore in this paper, we introduce a novel approach called Image Augmentation Agent (IAA) which shows that it is possible to enhance WSSS from data generation perspective. IAA mainly design an augmentation agent that leverages large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models to automatically generate additional images for WSSS. In practice, to address the instability in prompt generation by LLMs, we develop a prompt self-refinement mechanism. It allow LLMs to re-evaluate the rationality of generated prompts to produce more coherent prompts. Additionally, we insert an online filter into diffusion generation process to dynamically ensure the quality and balance of generated images. Experimental results show that our method significantly surpasses state-of-the-art WSSS approaches on the PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 datasets.
Prompt Categories Cluster for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS), which leverages image-level labels, has garnered significant attention due to its cost-effectiveness. The previous methods mainly strengthen the inter-class differences to avoid class semantic ambiguity which may lead to erroneous activation. However, they overlook the positive function of some shared information between similar classes. Categories within the same cluster share some similar features. Allowing the model to recognize these features can further relieve the semantic ambiguity between these classes. To effectively identify and utilize this shared information, in this paper, we introduce a novel WSSS framework called Prompt Categories Clustering (PCC). Specifically, we explore the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to derive category clusters through prompts. These clusters effectively represent the intrinsic relationships between categories. By integrating this relational information into the training network, our model is able to better learn the hidden connections between categories. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, showing its ability to enhance performance on the PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset and surpass existing state-of-the-art methods in WSSS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge