Walter Stewart
EVA: Generating Longitudinal Electronic Health Records Using Conditional Variational Autoencoders
Dec 18, 2020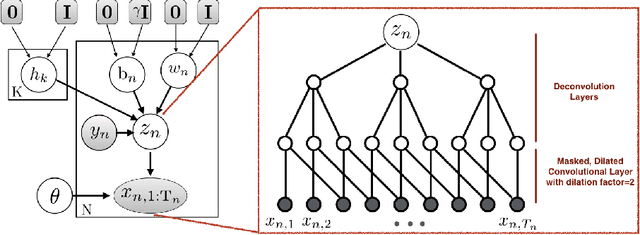
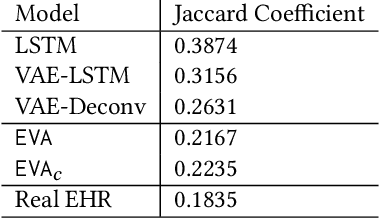
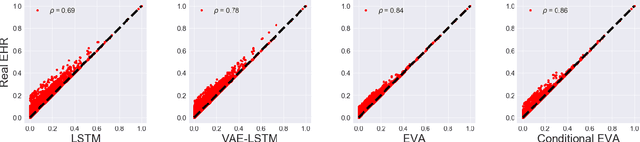
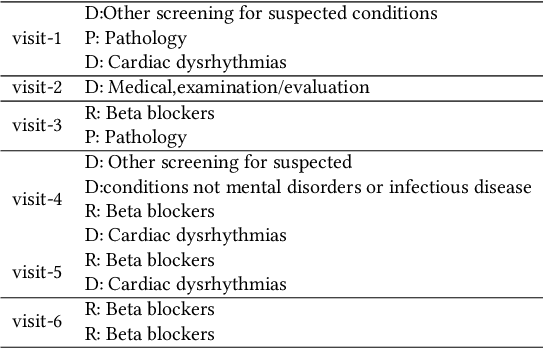
Abstract:Researchers require timely access to real-world longitudinal electronic health records (EHR) to develop, test, validate, and implement machine learning solutions that improve the quality and efficiency of healthcare. In contrast, health systems value deeply patient privacy and data security. De-identified EHRs do not adequately address the needs of health systems, as de-identified data are susceptible to re-identification and its volume is also limited. Synthetic EHRs offer a potential solution. In this paper, we propose EHR Variational Autoencoder (EVA) for synthesizing sequences of discrete EHR encounters (e.g., clinical visits) and encounter features (e.g., diagnoses, medications, procedures). We illustrate that EVA can produce realistic EHR sequences, account for individual differences among patients, and can be conditioned on specific disease conditions, thus enabling disease-specific studies. We design efficient, accurate inference algorithms by combining stochastic gradient Markov Chain Monte Carlo with amortized variational inference. We assess the utility of the methods on large real-world EHR repositories containing over 250, 000 patients. Our experiments, which include user studies with knowledgeable clinicians, indicate the generated EHR sequences are realistic. We confirmed the performance of predictive models trained on the synthetic data are similar with those trained on real EHRs. Additionally, our findings indicate that augmenting real data with synthetic EHRs results in the best predictive performance - improving the best baseline by as much as 8% in top-20 recall.
TASTE: Temporal and Static Tensor Factorization for Phenotyping Electronic Health Records
Nov 13, 2019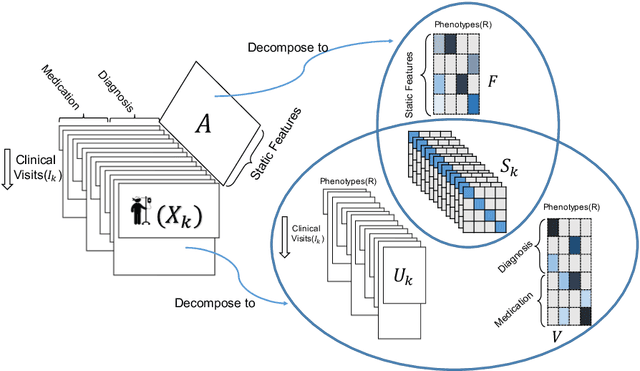
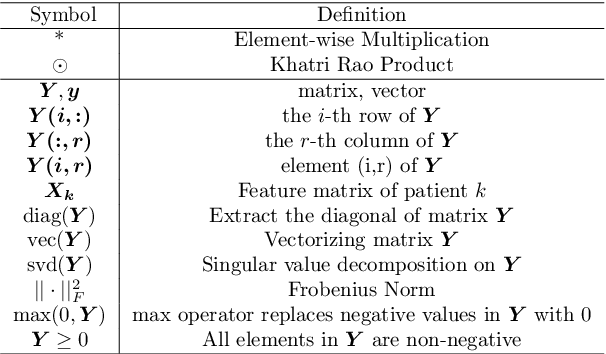
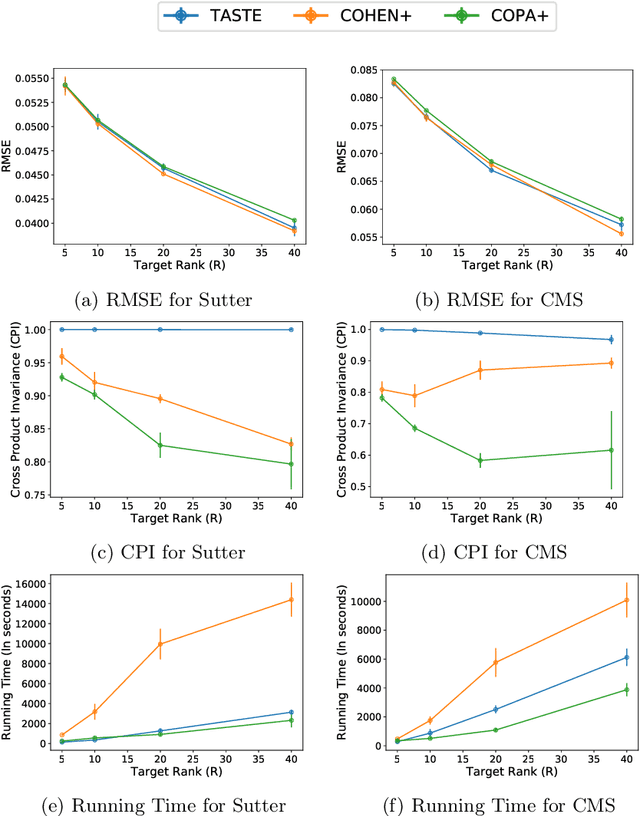
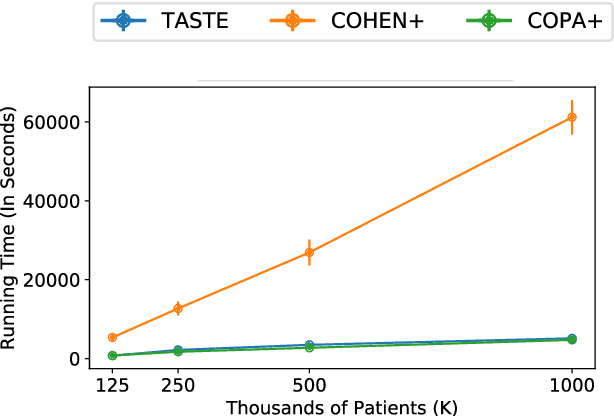
Abstract:Phenotyping electronic health records (EHR) focuses on defining meaningful patient groups (e.g., heart failure group and diabetes group) and identifying the temporal evolution of patients in those groups. Tensor factorization has been an effective tool for phenotyping. Most of the existing works assume either a static patient representation with aggregate data or only model temporal data. However, real EHR data contain both temporal (e.g., longitudinal clinical visits) and static information (e.g., patient demographics), which are difficult to model simultaneously. In this paper, we propose Temporal And Static TEnsor factorization (TASTE) that jointly models both static and temporal information to extract phenotypes. TASTE combines the PARAFAC2 model with non-negative matrix factorization to model a temporal and a static tensor. To fit the proposed model, we transform the original problem into simpler ones which are optimally solved in an alternating fashion. For each of the sub-problems, our proposed mathematical reformulations lead to efficient sub-problem solvers. Comprehensive experiments on large EHR data from a heart failure (HF) study confirmed that TASTE is up to 14x faster than several baselines and the resulting phenotypes were confirmed to be clinically meaningful by a cardiologist. Using 80 phenotypes extracted by TASTE, a simple logistic regression can achieve the same level of area under the curve (AUC) for HF prediction compared to a deep learning model using recurrent neural networks (RNN) with 345 features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge