Vukan Ninkovic
Learning Binary Autoencoder-Based Codes with Progressive Training
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Error correcting codes play a central role in digital communication, ensuring that transmitted information can be accurately reconstructed despite channel impairments. Recently, autoencoder (AE) based approaches have gained attention for the end-to-end design of communication systems, offering a data driven alternative to conventional coding schemes. However, enforcing binary codewords within differentiable AE architectures remains difficult, as discretization breaks gradient flow and often leads to unstable convergence. To overcome this limitation, a simplified two stage training procedure is proposed, consisting of a continuous pretraining phase followed by direct binarization and fine tuning without gradient approximation techniques. For the (7,4) block configuration over a binary symmetric channel (BSC), the learned encoder-decoder pair learns a rotated version (coset code) of the optimal Hamming code, naturally recovering its linear and distance properties and thereby achieving the same block error rate (BLER) with maximum likelihood (ML) decoding. These results indicate that compact AE architectures can effectively learn structured, algebraically optimal binary codes through stable and straightforward training.
Structured Superposition of Autoencoders for UEP Codes at Intermediate Blocklengths
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Unequal error protection (UEP) coding that enables differentiated reliability levels within a transmitted message is essential for modern communication systems. Autoencoder (AE)-based code designs have shown promise in the context of learned equal error protection (EEP) coding schemes. However, their application to UEP remains largely unexplored, particularly at intermediate blocklengths, due to the increasing complexity of AE-based models. Inspired by the proven effectiveness of superposition coding and successive interference cancellation (SIC) decoding in conventional UEP schemes, we propose a structured AE-based architecture that extends AE-based UEP codes to substantially larger blocklengths while maintaining efficient training. By structuring encoding and decoding into smaller AE subblocks, our method provides a flexible framework for fine-tuning UEP reliability levels while adapting to diverse system parameters. Numerical results show that the proposed approach improves over established achievability bounds of randomized superposition coding-based UEP schemes with SIC decoding, making the proposed structured AE-based UEP codes a scalable and efficient solution for next-generation networks.
Efficient Split Learning LSTM Models for FPGA-based Edge IoT Devices
Feb 12, 2025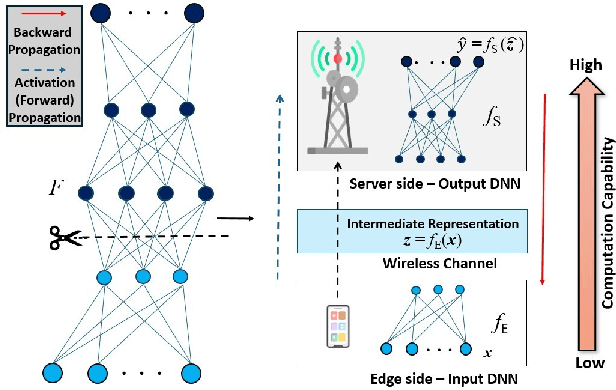
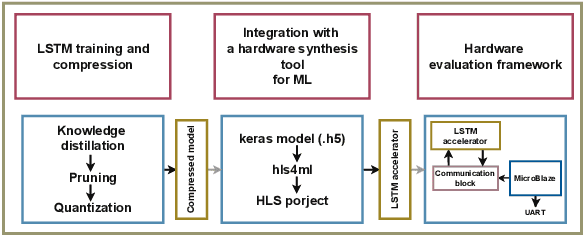
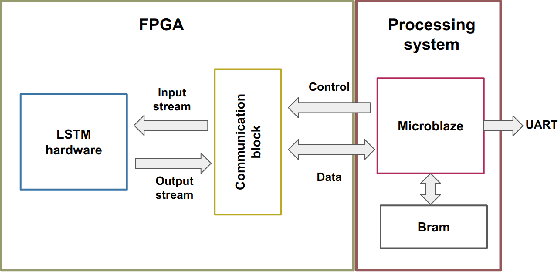
Abstract:Split Learning (SL) recently emerged as an efficient paradigm for distributed Machine Learning (ML) suitable for the Internet Of Things (IoT)-Cloud systems. However, deploying SL on resource-constrained edge IoT platforms poses a significant challenge in terms of balancing the model performance against the processing, memory, and energy resources. In this work, we present a practical study of deploying SL framework on a real-world Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA)-based edge IoT platform. We address the SL framework applied to a time-series processing model based on Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs). Set in the context of river water quality monitoring and using real-world data, we train, optimize, and deploy a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model on a given edge IoT FPGA platform in different SL configurations. Our results demonstrate the importance of aligning design choices with specific application requirements, whether it is maximizing speed, minimizing power, or optimizing for resource constraints.
COMSPLIT: A Communication-Aware Split Learning Design for Heterogeneous IoT Platforms
Oct 25, 2024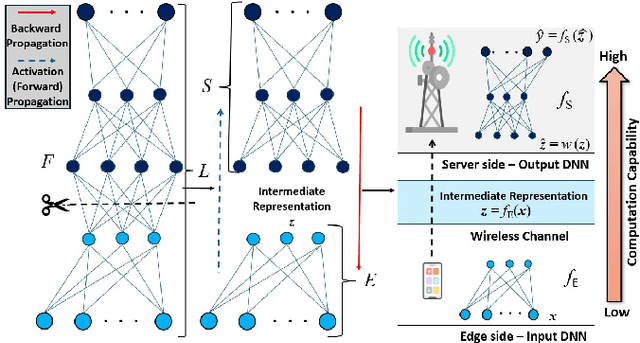
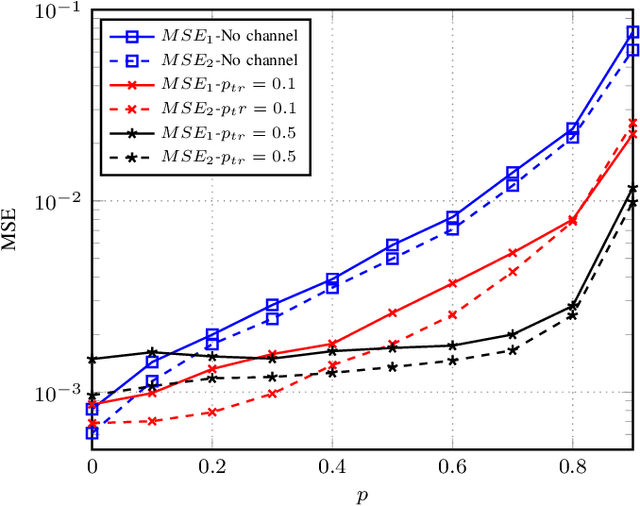
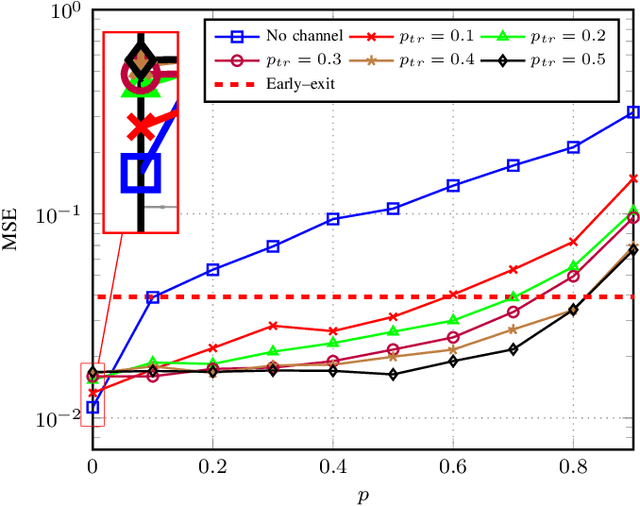
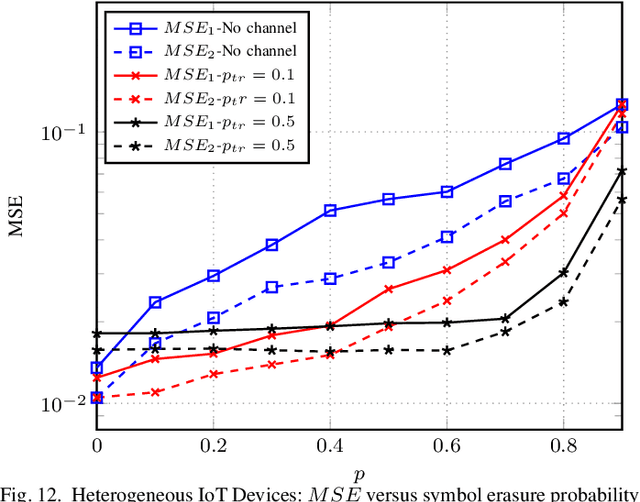
Abstract:The significance of distributed learning and inference algorithms in Internet of Things (IoT) network is growing since they flexibly distribute computation load between IoT devices and the infrastructure, enhance data privacy, and minimize latency. However, a notable challenge stems from the influence of communication channel conditions on their performance. In this work, we introduce COMSPLIT: a novel communication-aware design for split learning (SL) and inference paradigm tailored to processing time series data in IoT networks. COMSPLIT provides a versatile framework for deploying adaptable SL in IoT networks affected by diverse channel conditions. In conjunction with the integration of an early-exit strategy, and addressing IoT scenarios containing devices with heterogeneous computational capabilities, COMSPLIT represents a comprehensive design solution for communication-aware SL in IoT networks. Numerical results show superior performance of COMSPLIT compared to vanilla SL approaches (that assume ideal communication channel), demonstrating its ability to offer both design simplicity and adaptability to different channel conditions.
Autonomous Self-Trained Channel State Prediction Method for mmWave Vehicular Communications
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:Establishing and maintaining 5G mmWave vehicular connectivity poses a significant challenge due to high user mobility that necessitates frequent triggering of beam switching procedures. Departing from reactive beam switching based on the user device channel state feedback, proactive beam switching prepares in advance for upcoming beam switching decisions by exploiting accurate channel state information (CSI) prediction. In this paper, we develop a framework for autonomous self-trained CSI prediction for mmWave vehicular users where a base station (gNB) collects and labels a dataset that it uses for training recurrent neural network (RNN)-based CSI prediction model. The proposed framework exploits the CSI feedback from vehicular users combined with overhearing the C-V2X cooperative awareness messages (CAMs) they broadcast. We implement and evaluate the proposed framework using deepMIMO dataset generation environment and demonstrate its capability to provide accurate CSI prediction for 5G mmWave vehicular users. CSI prediction model is trained and its capability to provide accurate CSI predictions from various input features are investigated.
Decoding Quantum LDPC Codes Using Graph Neural Networks
Aug 09, 2024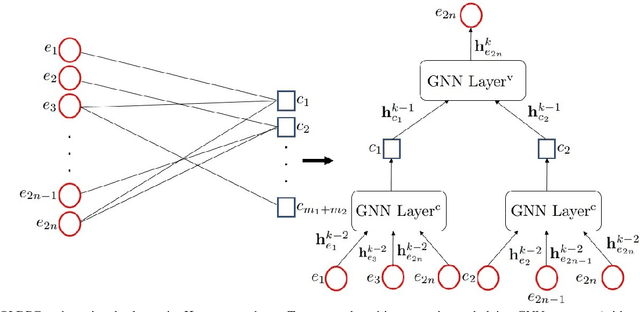
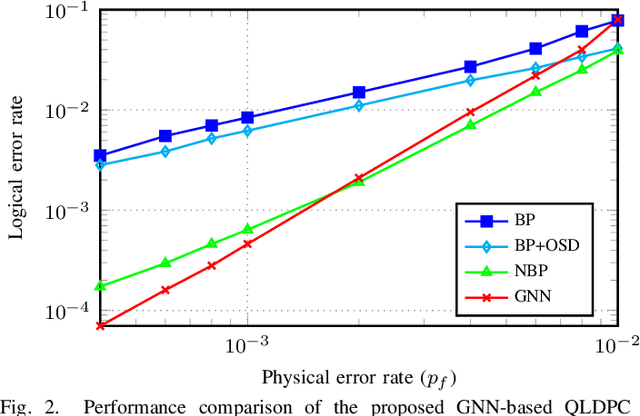
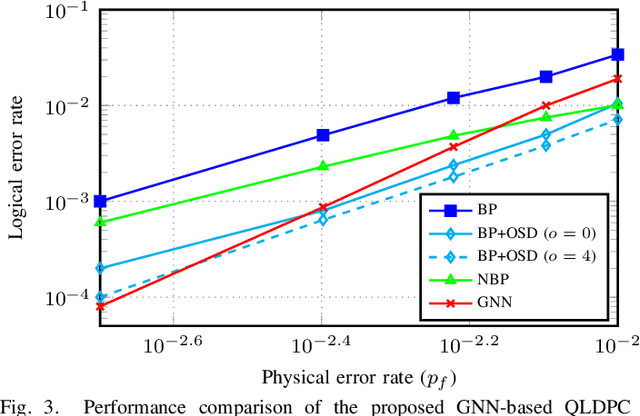
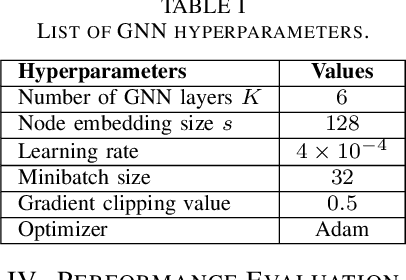
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel decoding method for Quantum Low-Density Parity-Check (QLDPC) codes based on Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). Similar to the Belief Propagation (BP)-based QLDPC decoders, the proposed GNN-based QLDPC decoder exploits the sparse graph structure of QLDPC codes and can be implemented as a message-passing decoding algorithm. We compare the proposed GNN-based decoding algorithm against selected classes of both conventional and neural-enhanced QLDPC decoding algorithms across several QLDPC code designs. The simulation results demonstrate excellent performance of GNN-based decoders along with their low complexity compared to competing methods.
UAV-assisted Distributed Learning for Environmental Monitoring in Rural Environments
Jul 02, 2024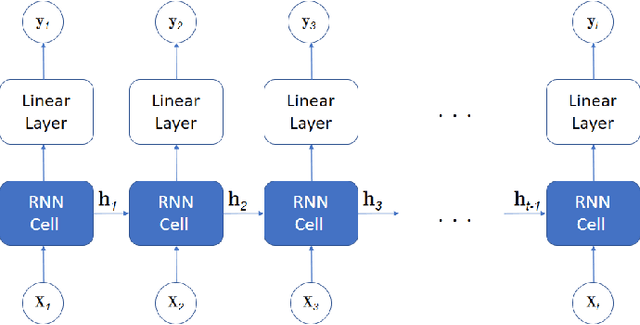
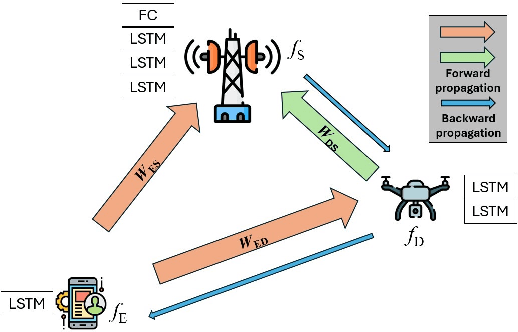
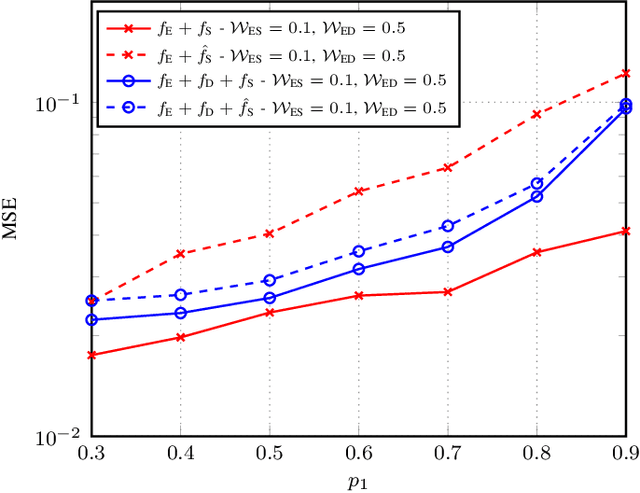

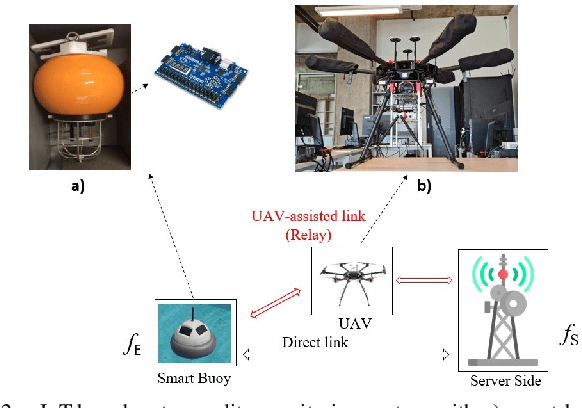
Abstract:Distributed learning and inference algorithms have become indispensable for IoT systems, offering benefits such as workload alleviation, data privacy preservation, and reduced latency. This paper introduces an innovative approach that utilizes unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) as a coverage extension relay for IoT environmental monitoring in rural areas. Our method integrates a split learning (SL) strategy between edge devices, a UAV and a server to enhance adaptability and performance of inference mechanisms. By employing UAVs as a relay and by incorporating SL, we address connectivity and resource constraints for applications of learning in IoT in remote settings. Our system model accounts for diverse channel conditions to determine the most suitable transmission strategy for optimal system behaviour. Through simulation analysis, the proposed approach demonstrates its robustness and adaptability, even excelling under adverse channel conditions. Integrating UAV relaying and the SL paradigm offers significant flexibility to the server, enabling adaptive strategies that consider various trade-offs beyond simply minimizing overall inference quality.
A Weighted Autoencoder-Based Approach to Downlink NOMA Constellation Design
Jun 23, 2023Abstract:End-to-end design of communication systems using deep autoencoders (AEs) is gaining attention due to its flexibility and excellent performance. Besides single-user transmission, AE-based design is recently explored in multi-user setup, e.g., for designing constellations for non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA). In this paper, we further advance the design of AE-based downlink NOMA by introducing weighted loss function in the AE training. By changing the weight coefficients, one can flexibly tune the constellation design to balance error probability of different users, without relying on explicit information about their channel quality. Combined with the SICNet decoder, we demonstrate a significant improvement in achievable levels and flexible control of error probability of different users using the proposed weighted AE-based framework.
Rateless Autoencoder Codes: Trading off Decoding Delay and Reliability
Jan 31, 2023



Abstract:Most of today's communication systems are designed to target reliable message recovery after receiving the entire encoded message (codeword). However, in many practical scenarios, the transmission process may be interrupted before receiving the complete codeword. This paper proposes a novel rateless autoencoder (AE)-based code design suitable for decoding the transmitted message before the noisy codeword is fully received. Using particular dropout strategies applied during the training process, rateless AE codes allow to trade off between decoding delay and reliability, providing a graceful improvement of the latter with each additionally received codeword symbol. The proposed rateless AEs significantly outperform the conventional AE designs for scenarios where it is desirable to trade off reliability for lower decoding delay.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge